Huan Yang
Depatment of Gastroenterology, Second Affiliated Hospital, Army Medical University
SemanticALLI: Caching Reasoning, Not Just Responses, in Agentic Systems
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Agentic AI pipelines suffer from a hidden inefficiency: they frequently reconstruct identical intermediate logic, such as metric normalization or chart scaffolding, even when the user's natural language phrasing is entirely novel. Conventional boundary caching fails to capture this inefficiency because it treats inference as a monolithic black box. We introduce SemanticALLI, a pipeline-aware architecture within Alli (PMG's marketing intelligence platform), designed to operationalize redundant reasoning. By decomposing generation into Analytic Intent Resolution (AIR) and Visualization Synthesis (VS), SemanticALLI elevates structured intermediate representations (IRs) to first-class, cacheable artifacts. The impact of caching within the agentic loop is substantial. In our evaluation, baseline monolithic caching caps at a 38.7% hit rate due to linguistic variance. In contrast, our structured approach allows for an additional stage, the Visualization Synthesis stage, to achieve an 83.10% hit rate, bypassing 4,023 LLM calls with a median latency of just 2.66 ms. This internal reuse reduces total token consumption, offering a practical lesson for AI system design: even when users rarely repeat themselves, the pipeline often does, at stable, structured checkpoints where caching is most reliable.
Artificial Intelligence Driven Channel Coding and Resource Optimization for Wireless Networks
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:The ongoing evolution of 5G and its enhanced version, 5G+, has significantly transformed the telecommunications landscape, driving an unprecedented demand for ultra-high-speed data transmission, ultra-low latency, and resilient connectivity. These capabilities are essential for enabling mission-critical applications such as the Internet of Things, autonomous vehicles, and smart city infrastructures. This paper investigates the important role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in addressing the key challenges faced by 5G/5G+ networks, including interference mitigation, dynamic resource allocation, and maintaining seamless network operation. The study particularly focuses on AI-driven innovations in coding theory, which offer advanced solutions to the limitations of conventional error correction and modulation techniques. By employing deep learning, reinforcement learning, and neural network-based approaches, this research demonstrates significant advancements in error correction performance, decoding efficiency, and adaptive transmission strategies. Additionally, the integration of AI with emerging technologies, such as massive multiple-input and multiple-output, intelligent reflecting surfaces, and privacy-enhancing mechanisms, is discussed, highlighting their potential to propel the next generation of wireless networks. This paper also provides insights into the transformative impact of AI on modern wireless communication, establishing a foundation for scalable, adaptive, and more efficient network architectures.
ResTok: Learning Hierarchical Residuals in 1D Visual Tokenizers for Autoregressive Image Generation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Existing 1D visual tokenizers for autoregressive (AR) generation largely follow the design principles of language modeling, as they are built directly upon transformers whose priors originate in language, yielding single-hierarchy latent tokens and treating visual data as flat sequential token streams. However, this language-like formulation overlooks key properties of vision, particularly the hierarchical and residual network designs that have long been essential for convergence and efficiency in visual models. To bring "vision" back to vision, we propose the Residual Tokenizer (ResTok), a 1D visual tokenizer that builds hierarchical residuals for both image tokens and latent tokens. The hierarchical representations obtained through progressively merging enable cross-level feature fusion at each layer, substantially enhancing representational capacity. Meanwhile, the semantic residuals between hierarchies prevent information overlap, yielding more concentrated latent distributions that are easier for AR modeling. Cross-level bindings consequently emerge without any explicit constraints. To accelerate the generation process, we further introduce a hierarchical AR generator that substantially reduces sampling steps by predicting an entire level of latent tokens at once rather than generating them strictly token-by-token. Extensive experiments demonstrate that restoring hierarchical residual priors in visual tokenization significantly improves AR image generation, achieving a gFID of 2.34 on ImageNet-256 with only 9 sampling steps. Code is available at https://github.com/Kwai-Kolors/ResTok.
SVG-T2I: Scaling Up Text-to-Image Latent Diffusion Model Without Variational Autoencoder
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Visual generation grounded in Visual Foundation Model (VFM) representations offers a highly promising unified pathway for integrating visual understanding, perception, and generation. Despite this potential, training large-scale text-to-image diffusion models entirely within the VFM representation space remains largely unexplored. To bridge this gap, we scale the SVG (Self-supervised representations for Visual Generation) framework, proposing SVG-T2I to support high-quality text-to-image synthesis directly in the VFM feature domain. By leveraging a standard text-to-image diffusion pipeline, SVG-T2I achieves competitive performance, reaching 0.75 on GenEval and 85.78 on DPG-Bench. This performance validates the intrinsic representational power of VFMs for generative tasks. We fully open-source the project, including the autoencoder and generation model, together with their training, inference, evaluation pipelines, and pre-trained weights, to facilitate further research in representation-driven visual generation.
ContextDrag: Precise Drag-Based Image Editing via Context-Preserving Token Injection and Position-Consistent Attention
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Drag-based image editing aims to modify visual content followed by user-specified drag operations. Despite existing methods having made notable progress, they still fail to fully exploit the contextual information in the reference image, including fine-grained texture details, leading to edits with limited coherence and fidelity. To address this challenge, we introduce ContextDrag, a new paradigm for drag-based editing that leverages the strong contextual modeling capability of editing models, such as FLUX-Kontext. By incorporating VAE-encoded features from the reference image, ContextDrag can leverage rich contextual cues and preserve fine-grained details, without the need for finetuning or inversion. Specifically, ContextDrag introduced a novel Context-preserving Token Injection (CTI) that injects noise-free reference features into their correct destination locations via a Latent-space Reverse Mapping (LRM) algorithm. This strategy enables precise drag control while preserving consistency in both semantics and texture details. Second, ContextDrag adopts a novel Position-Consistent Attention (PCA), which positional re-encodes the reference tokens and applies overlap-aware masking to eliminate interference from irrelevant reference features. Extensive experiments on DragBench-SR and DragBench-DR demonstrate that our approach surpasses all existing SOTA methods. Code will be publicly available.
DialogGraph-LLM: Graph-Informed LLMs for End-to-End Audio Dialogue Intent Recognition
Nov 17, 2025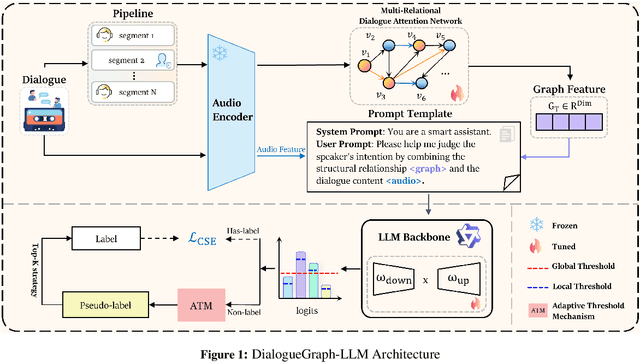



Abstract:Recognizing speaker intent in long audio dialogues among speakers has a wide range of applications, but is a non-trivial AI task due to complex inter-dependencies in speaker utterances and scarce annotated data. To address these challenges, an end-to-end framework, namely DialogGraph-LLM, is proposed in the current work. DialogGraph-LLM combines a novel Multi-Relational Dialogue Attention Network (MR-DAN) architecture with multimodal foundation models (e.g., Qwen2.5-Omni-7B) for direct acoustic-to-intent inference. An adaptive semi-supervised learning strategy is designed using LLM with a confidence-aware pseudo-label generation mechanism based on dual-threshold filtering using both global and class confidences, and an entropy-based sample selection process that prioritizes high-information unlabeled instances. Extensive evaluations on the proprietary MarketCalls corpus and the publicly available MIntRec 2.0 benchmark demonstrate DialogGraph-LLM's superiority over strong audio and text-driven baselines. The framework demonstrates strong performance and efficiency in intent recognition in real world scenario audio dialogues, proving its practical value for audio-rich domains with limited supervision. Our code is available at https://github.com/david188888/DialogGraph-LLM.
Align-then-Slide: A complete evaluation framework for Ultra-Long Document-Level Machine Translation
Sep 04, 2025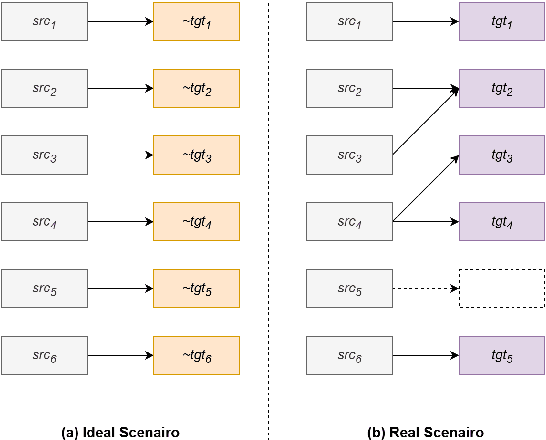
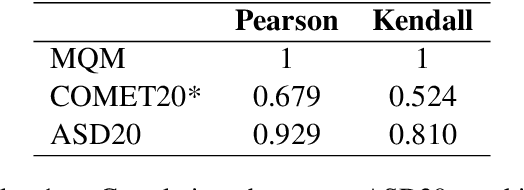
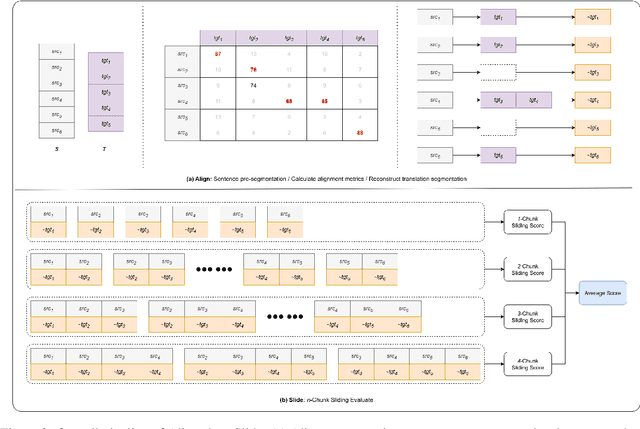
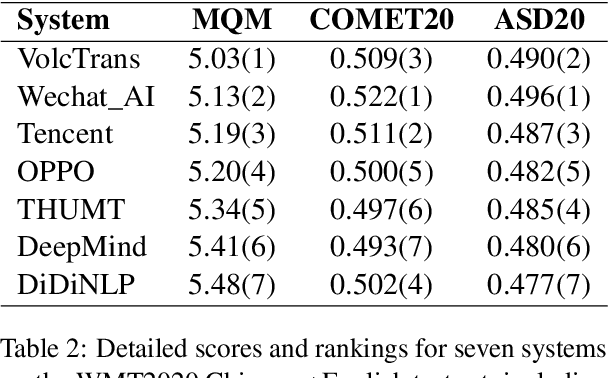
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have ushered in a new era for document-level machine translation (\textit{doc}-mt), yet their whole-document outputs challenge existing evaluation methods that assume sentence-by-sentence alignment. We introduce \textit{\textbf{Align-then-Slide}}, a complete evaluation framework for ultra-long doc-mt. In the Align stage, we automatically infer sentence-level source-target correspondences and rebuild the target to match the source sentence number, resolving omissions and many-to-one/one-to-many mappings. In the n-Chunk Sliding Evaluate stage, we calculate averaged metric scores under 1-, 2-, 3- and 4-chunk for multi-granularity assessment. Experiments on the WMT benchmark show a Pearson correlation of 0.929 between our method with expert MQM rankings. On a newly curated real-world test set, our method again aligns closely with human judgments. Furthermore, preference data produced by Align-then-Slide enables effective CPO training and its direct use as a reward model for GRPO, both yielding translations preferred over a vanilla SFT baseline. The results validate our framework as an accurate, robust, and actionable evaluation tool for doc-mt systems.
Mod-Adapter: Tuning-Free and Versatile Multi-concept Personalization via Modulation Adapter
May 24, 2025Abstract:Personalized text-to-image generation aims to synthesize images of user-provided concepts in diverse contexts. Despite recent progress in multi-concept personalization, most are limited to object concepts and struggle to customize abstract concepts (e.g., pose, lighting). Some methods have begun exploring multi-concept personalization supporting abstract concepts, but they require test-time fine-tuning for each new concept, which is time-consuming and prone to overfitting on limited training images. In this work, we propose a novel tuning-free method for multi-concept personalization that can effectively customize both object and abstract concepts without test-time fine-tuning. Our method builds upon the modulation mechanism in pretrained Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) model, leveraging the localized and semantically meaningful properties of the modulation space. Specifically, we propose a novel module, Mod-Adapter, to predict concept-specific modulation direction for the modulation process of concept-related text tokens. It incorporates vision-language cross-attention for extracting concept visual features, and Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) layers that adaptively map the concept features into the modulation space. Furthermore, to mitigate the training difficulty caused by the large gap between the concept image space and the modulation space, we introduce a VLM-guided pretraining strategy that leverages the strong image understanding capabilities of vision-language models to provide semantic supervision signals. For a comprehensive comparison, we extend a standard benchmark by incorporating abstract concepts. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in multi-concept personalization, supported by quantitative, qualitative, and human evaluations.
MM-MovieDubber: Towards Multi-Modal Learning for Multi-Modal Movie Dubbing
May 22, 2025Abstract:Current movie dubbing technology can produce the desired speech using a reference voice and input video, maintaining perfect synchronization with the visuals while effectively conveying the intended emotions. However, crucial aspects of movie dubbing, including adaptation to various dubbing styles, effective handling of dialogue, narration, and monologues, as well as consideration of subtle details such as speaker age and gender, remain insufficiently explored. To tackle these challenges, we introduce a multi-modal generative framework. First, it utilizes a multi-modal large vision-language model (VLM) to analyze visual inputs, enabling the recognition of dubbing types and fine-grained attributes. Second, it produces high-quality dubbing using large speech generation models, guided by multi-modal inputs. Additionally, a movie dubbing dataset with annotations for dubbing types and subtle details is constructed to enhance movie understanding and improve dubbing quality for the proposed multi-modal framework. Experimental results across multiple benchmark datasets show superior performance compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. In details, the LSE-D, SPK-SIM, EMO-SIM, and MCD exhibit improvements of up to 1.09%, 8.80%, 19.08%, and 18.74%, respectively.
KVShare: Semantic-Aware Key-Value Cache Sharing for Efficient Large Language Model Inference
Mar 17, 2025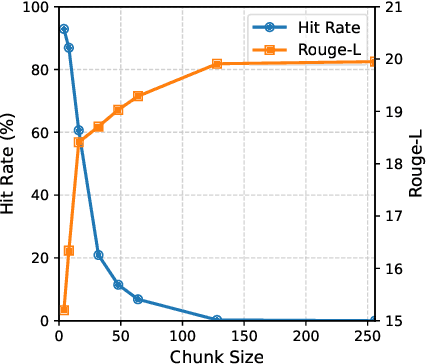


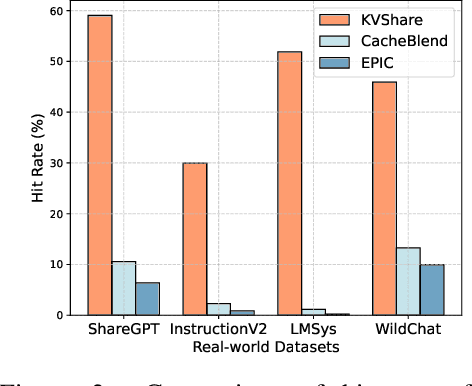
Abstract:This paper presents KVShare, a multi-user Key-Value (KV) Cache sharing technology based on semantic similarity, designed to enhance the inference efficiency of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Addressing the limitations of existing prefix caching (strict text prefix matching) and semantic caching (loss of response diversity), KVShare achieves fine-grained KV cache reuse through semantic alignment algorithms and differential editing operations. Experiments on real-world user conversation datasets demonstrate that KVShare improves KV cache hit rates by over 60%, while maintaining output quality comparable to full computation (no significant degradation in BLEU and Rouge-L metrics). This approach effectively reduces GPU resource consumption and is applicable to scenarios with repetitive queries, such as healthcare and education.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge