Junjie Zheng
R2-SVC: Towards Real-World Robust and Expressive Zero-shot Singing Voice Conversion
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:In real-world singing voice conversion (SVC) applications, environmental noise and the demand for expressive output pose significant challenges. Conventional methods, however, are typically designed without accounting for real deployment scenarios, as both training and inference usually rely on clean data. This mismatch hinders practical use, given the inevitable presence of diverse noise sources and artifacts from music separation. To tackle these issues, we propose R2-SVC, a robust and expressive SVC framework. First, we introduce simulation-based robustness enhancement through random fundamental frequency ($F_0$) perturbations and music separation artifact simulations (e.g., reverberation, echo), substantially improving performance under noisy conditions. Second, we enrich speaker representation using domain-specific singing data: alongside clean vocals, we incorporate DNSMOS-filtered separated vocals and public singing corpora, enabling the model to preserve speaker timbre while capturing singing style nuances. Third, we integrate the Neural Source-Filter (NSF) model to explicitly represent harmonic and noise components, enhancing the naturalness and controllability of converted singing. R2-SVC achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple SVC benchmarks under both clean and noisy conditions.
MM-MovieDubber: Towards Multi-Modal Learning for Multi-Modal Movie Dubbing
May 22, 2025Abstract:Current movie dubbing technology can produce the desired speech using a reference voice and input video, maintaining perfect synchronization with the visuals while effectively conveying the intended emotions. However, crucial aspects of movie dubbing, including adaptation to various dubbing styles, effective handling of dialogue, narration, and monologues, as well as consideration of subtle details such as speaker age and gender, remain insufficiently explored. To tackle these challenges, we introduce a multi-modal generative framework. First, it utilizes a multi-modal large vision-language model (VLM) to analyze visual inputs, enabling the recognition of dubbing types and fine-grained attributes. Second, it produces high-quality dubbing using large speech generation models, guided by multi-modal inputs. Additionally, a movie dubbing dataset with annotations for dubbing types and subtle details is constructed to enhance movie understanding and improve dubbing quality for the proposed multi-modal framework. Experimental results across multiple benchmark datasets show superior performance compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. In details, the LSE-D, SPK-SIM, EMO-SIM, and MCD exhibit improvements of up to 1.09%, 8.80%, 19.08%, and 18.74%, respectively.
Towards Film-Making Production Dialogue, Narration, Monologue Adaptive Moving Dubbing Benchmarks
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Movie dubbing has advanced significantly, yet assessing the real-world effectiveness of these models remains challenging. A comprehensive evaluation benchmark is crucial for two key reasons: 1) Existing metrics fail to fully capture the complexities of dialogue, narration, monologue, and actor adaptability in movie dubbing. 2) A practical evaluation system should offer valuable insights to improve movie dubbing quality and advancement in film production. To this end, we introduce Talking Adaptive Dubbing Benchmarks (TA-Dubbing), designed to improve film production by adapting to dialogue, narration, monologue, and actors in movie dubbing. TA-Dubbing offers several key advantages: 1) Comprehensive Dimensions: TA-Dubbing covers a variety of dimensions of movie dubbing, incorporating metric evaluations for both movie understanding and speech generation. 2) Versatile Benchmarking: TA-Dubbing is designed to evaluate state-of-the-art movie dubbing models and advanced multi-modal large language models. 3) Full Open-Sourcing: We fully open-source TA-Dubbing at https://github.com/woka- 0a/DeepDubber- V1 including all video suits, evaluation methods, annotations. We also continuously integrate new movie dubbing models into the TA-Dubbing leaderboard at https://github.com/woka- 0a/DeepDubber-V1 to drive forward the field of movie dubbing.
DeepDubber-V1: Towards High Quality and Dialogue, Narration, Monologue Adaptive Movie Dubbing Via Multi-Modal Chain-of-Thoughts Reasoning Guidance
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Current movie dubbing technology can generate the desired voice from a given speech prompt, ensuring good synchronization between speech and visuals while accurately conveying the intended emotions. However, in movie dubbing, key aspects such as adapting to different dubbing styles, handling dialogue, narration, and monologue effectively, and understanding subtle details like the age and gender of speakers, have not been well studied. To address this challenge, we propose a framework of multi-modal large language model. First, it utilizes multimodal Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning methods on visual inputs to understand dubbing styles and fine-grained attributes. Second, it generates high-quality dubbing through large speech generation models, guided by multimodal conditions. Additionally, we have developed a movie dubbing dataset with CoT annotations. The evaluation results demonstrate a performance improvement over state-of-the-art methods across multiple datasets. In particular, for the evaluation metrics, the SPK-SIM and EMO-SIM increases from 82.48% to 89.74%, 66.24% to 78.88% for dubbing setting 2.0 on V2C Animation dataset, LSE-D and MCD-SL decreases from 14.79 to 14.63, 5.24 to 4.74 for dubbing setting 2.0 on Grid dataset, SPK-SIM increases from 64.03 to 83.42 and WER decreases from 52.69% to 23.20% for initial reasoning setting on proposed CoT-Movie-Dubbing dataset in the comparison with the state-of-the art models.
DeepAudio-V1:Towards Multi-Modal Multi-Stage End-to-End Video to Speech and Audio Generation
Mar 28, 2025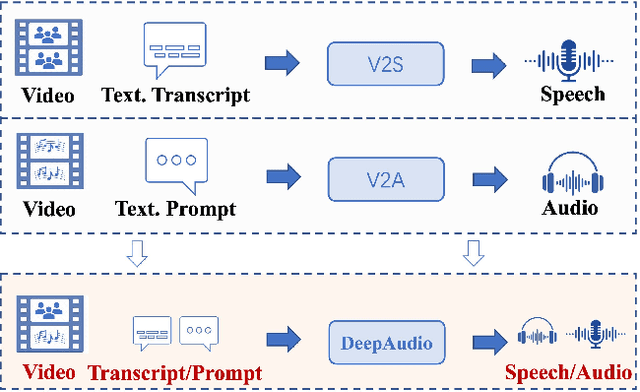
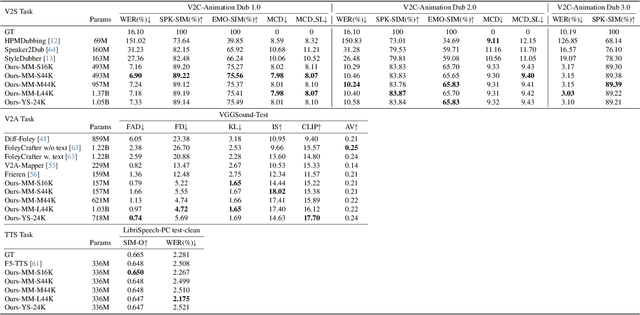
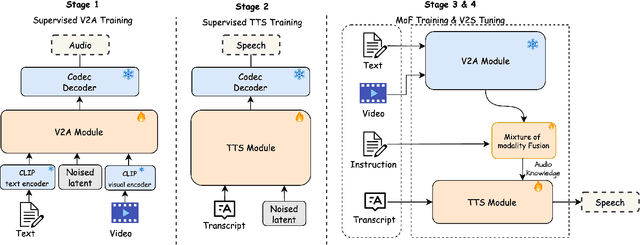

Abstract:Currently, high-quality, synchronized audio is synthesized using various multi-modal joint learning frameworks, leveraging video and optional text inputs. In the video-to-audio benchmarks, video-to-audio quality, semantic alignment, and audio-visual synchronization are effectively achieved. However, in real-world scenarios, speech and audio often coexist in videos simultaneously, and the end-to-end generation of synchronous speech and audio given video and text conditions are not well studied. Therefore, we propose an end-to-end multi-modal generation framework that simultaneously produces speech and audio based on video and text conditions. Furthermore, the advantages of video-to-audio (V2A) models for generating speech from videos remain unclear. The proposed framework, DeepAudio, consists of a video-to-audio (V2A) module, a text-to-speech (TTS) module, and a dynamic mixture of modality fusion (MoF) module. In the evaluation, the proposed end-to-end framework achieves state-of-the-art performance on the video-audio benchmark, video-speech benchmark, and text-speech benchmark. In detail, our framework achieves comparable results in the comparison with state-of-the-art models for the video-audio and text-speech benchmarks, and surpassing state-of-the-art models in the video-speech benchmark, with WER 16.57% to 3.15% (+80.99%), SPK-SIM 78.30% to 89.38% (+14.15%), EMO-SIM 66.24% to 75.56% (+14.07%), MCD 8.59 to 7.98 (+7.10%), MCD SL 11.05 to 9.40 (+14.93%) across a variety of dubbing settings.
YingSound: Video-Guided Sound Effects Generation with Multi-modal Chain-of-Thought Controls
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:Generating sound effects for product-level videos, where only a small amount of labeled data is available for diverse scenes, requires the production of high-quality sounds in few-shot settings. To tackle the challenge of limited labeled data in real-world scenes, we introduce YingSound, a foundation model designed for video-guided sound generation that supports high-quality audio generation in few-shot settings. Specifically, YingSound consists of two major modules. The first module uses a conditional flow matching transformer to achieve effective semantic alignment in sound generation across audio and visual modalities. This module aims to build a learnable audio-visual aggregator (AVA) that integrates high-resolution visual features with corresponding audio features at multiple stages. The second module is developed with a proposed multi-modal visual-audio chain-of-thought (CoT) approach to generate finer sound effects in few-shot settings. Finally, an industry-standard video-to-audio (V2A) dataset that encompasses various real-world scenarios is presented. We show that YingSound effectively generates high-quality synchronized sounds across diverse conditional inputs through automated evaluations and human studies. Project Page: \url{https://giantailab.github.io/yingsound/}
Bailing-TTS: Chinese Dialectal Speech Synthesis Towards Human-like Spontaneous Representation
Aug 01, 2024



Abstract:Large-scale text-to-speech (TTS) models have made significant progress recently.However, they still fall short in the generation of Chinese dialectal speech. Toaddress this, we propose Bailing-TTS, a family of large-scale TTS models capable of generating high-quality Chinese dialectal speech. Bailing-TTS serves as a foundation model for Chinese dialectal speech generation. First, continual semi-supervised learning is proposed to facilitate the alignment of text tokens and speech tokens. Second, the Chinese dialectal representation learning is developed using a specific transformer architecture and multi-stage training processes. With the proposed design of novel network architecture and corresponding strategy, Bailing-TTS is able to generate Chinese dialectal speech from text effectively and efficiently. Experiments demonstrate that Bailing-TTS generates Chinese dialectal speech towards human-like spontaneous representation. Readers are encouraged to listen to demos at \url{https://c9412600.github.io/bltts_tech_report/index.html}.
A Novel Approach for Stable Selection of Informative Redundant Features from High Dimensional fMRI Data
May 25, 2016
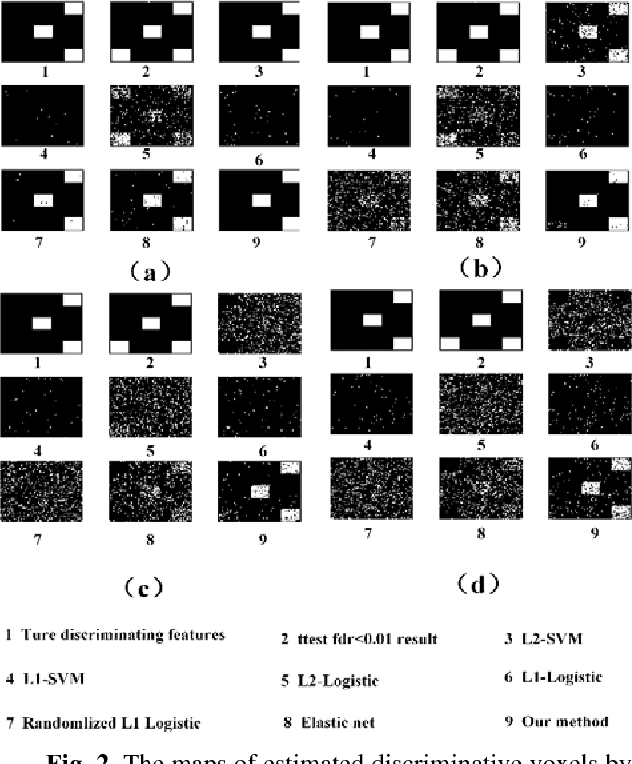
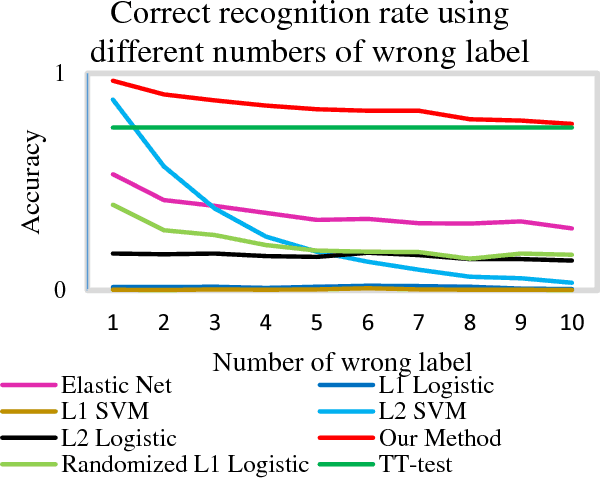
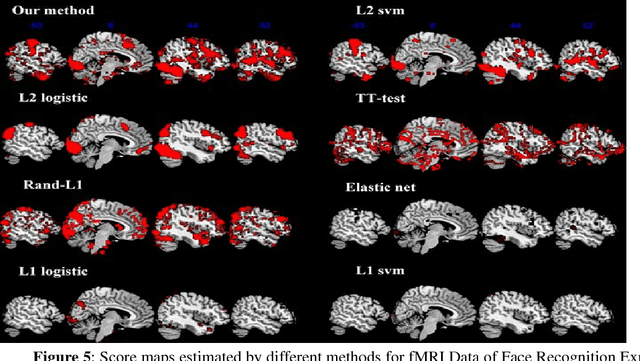
Abstract:Feature selection is among the most important components because it not only helps enhance the classification accuracy, but also or even more important provides potential biomarker discovery. However, traditional multivariate methods is likely to obtain unstable and unreliable results in case of an extremely high dimensional feature space and very limited training samples, where the features are often correlated or redundant. In order to improve the stability, generalization and interpretations of the discovered potential biomarker and enhance the robustness of the resultant classifier, the redundant but informative features need to be also selected. Therefore we introduced a novel feature selection method which combines a recent implementation of the stability selection approach and the elastic net approach. The advantage in terms of better control of false discoveries and missed discoveries of our approach, and the resulted better interpretability of the obtained potential biomarker is verified in both synthetic and real fMRI experiments. In addition, we are among the first to demonstrate the robustness of feature selection benefiting from the incorporation of stability selection and also among the first to demonstrate the possible unrobustness of the classical univariate two-sample t-test method. Specifically, we show the robustness of our feature selection results in existence of noisy (wrong) training labels, as well as the robustness of the resulted classifier based on our feature selection results in the existence of data variation, demonstrated by a multi-center attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) fMRI data.
Randomized Structural Sparsity based Support Identification with Applications to Locating Activated or Discriminative Brain Areas: A Multi-center Reproducibility Study
Jun 07, 2015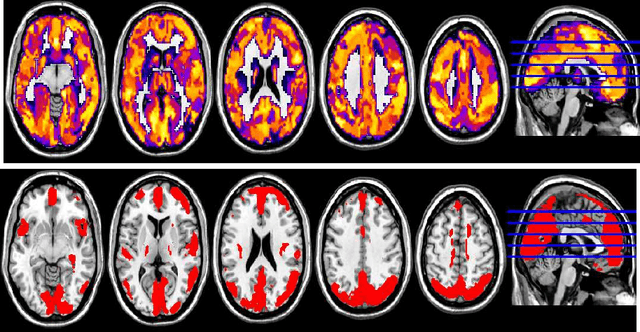
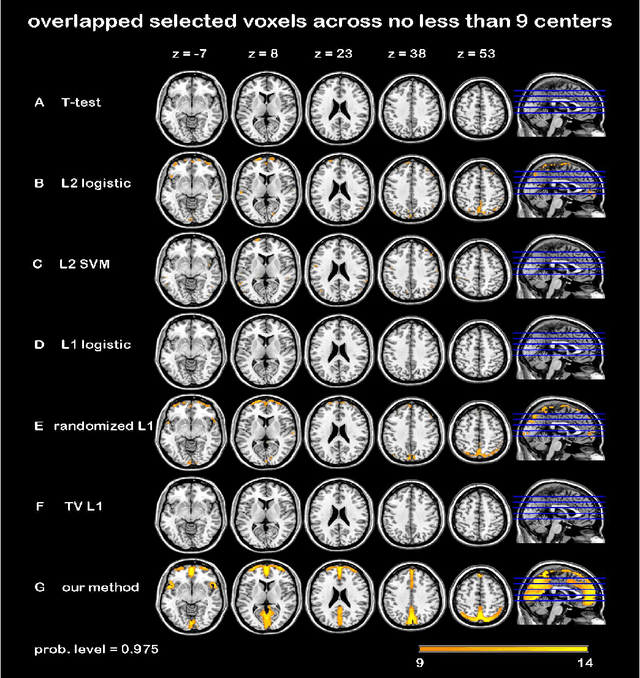
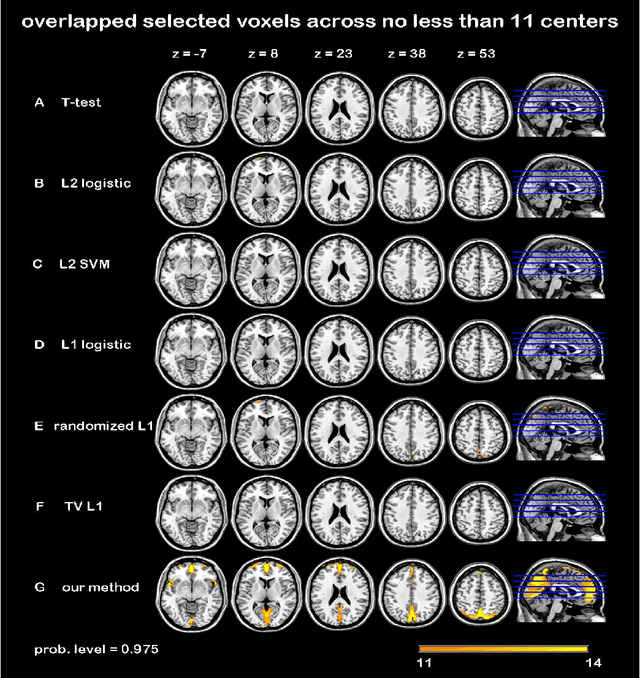

Abstract:In this paper, we focus on how to locate the relevant or discriminative brain regions related with external stimulus or certain mental decease, which is also called support identification, based on the neuroimaging data. The main difficulty lies in the extremely high dimensional voxel space and relatively few training samples, easily resulting in an unstable brain region discovery (or called feature selection in context of pattern recognition). When the training samples are from different centers and have betweencenter variations, it will be even harder to obtain a reliable and consistent result. Corresponding, we revisit our recently proposed algorithm based on stability selection and structural sparsity. It is applied to the multi-center MRI data analysis for the first time. A consistent and stable result is achieved across different centers despite the between-center data variation while many other state-of-the-art methods such as two sample t-test fail. Moreover, we have empirically showed that the performance of this algorithm is robust and insensitive to several of its key parameters. In addition, the support identification results on both functional MRI and structural MRI are interpretable and can be the potential biomarkers.
Randomized Structural Sparsity via Constrained Block Subsampling for Improved Sensitivity of Discriminative Voxel Identification
Jun 07, 2015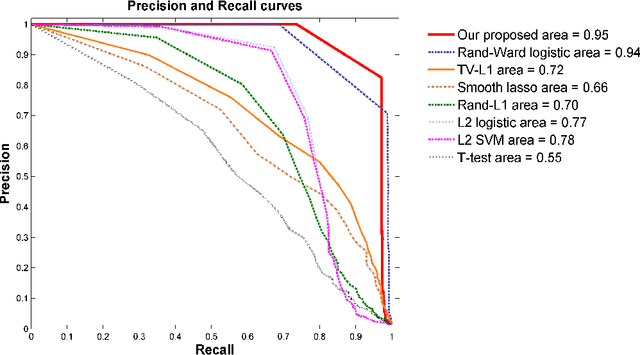



Abstract:In this paper, we consider voxel selection for functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) brain data with the aim of finding a more complete set of probably correlated discriminative voxels, thus improving interpretation of the discovered potential biomarkers. The main difficulty in doing this is an extremely high dimensional voxel space and few training samples, resulting in unreliable feature selection. In order to deal with the difficulty, stability selection has received a great deal of attention lately, especially due to its finite sample control of false discoveries and transparent principle for choosing a proper amount of regularization. However, it fails to make explicit use of the correlation property or structural information of these discriminative features and leads to large false negative rates. In other words, many relevant but probably correlated discriminative voxels are missed. Thus, we propose a new variant on stability selection "randomized structural sparsity", which incorporates the idea of structural sparsity. Numerical experiments demonstrate that our method can be superior in controlling for false negatives while also keeping the control of false positives inherited from stability selection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge