Randomized Structural Sparsity via Constrained Block Subsampling for Improved Sensitivity of Discriminative Voxel Identification
Paper and Code
Jun 07, 2015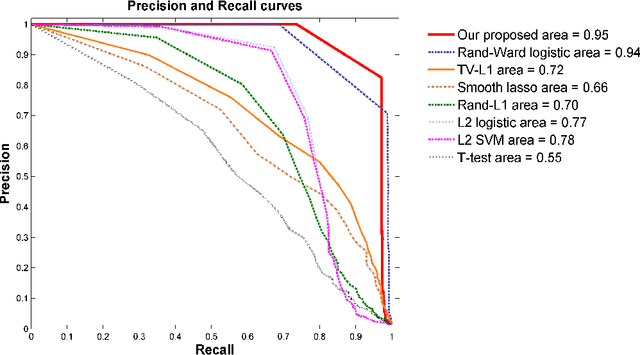



In this paper, we consider voxel selection for functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) brain data with the aim of finding a more complete set of probably correlated discriminative voxels, thus improving interpretation of the discovered potential biomarkers. The main difficulty in doing this is an extremely high dimensional voxel space and few training samples, resulting in unreliable feature selection. In order to deal with the difficulty, stability selection has received a great deal of attention lately, especially due to its finite sample control of false discoveries and transparent principle for choosing a proper amount of regularization. However, it fails to make explicit use of the correlation property or structural information of these discriminative features and leads to large false negative rates. In other words, many relevant but probably correlated discriminative voxels are missed. Thus, we propose a new variant on stability selection "randomized structural sparsity", which incorporates the idea of structural sparsity. Numerical experiments demonstrate that our method can be superior in controlling for false negatives while also keeping the control of false positives inherited from stability selection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge