Xinfa Zhu
Qwen3-TTS Technical Report
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:In this report, we present the Qwen3-TTS series, a family of advanced multilingual, controllable, robust, and streaming text-to-speech models. Qwen3-TTS supports state-of-the-art 3-second voice cloning and description-based control, allowing both the creation of entirely novel voices and fine-grained manipulation over the output speech. Trained on over 5 million hours of speech data spanning 10 languages, Qwen3-TTS adopts a dual-track LM architecture for real-time synthesis, coupled with two speech tokenizers: 1) Qwen-TTS-Tokenizer-25Hz is a single-codebook codec emphasizing semantic content, which offers seamlessly integration with Qwen-Audio and enables streaming waveform reconstruction via a block-wise DiT. 2) Qwen-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz achieves extreme bitrate reduction and ultra-low-latency streaming, enabling immediate first-packet emission ($97\,\mathrm{ms}$) through its 12.5 Hz, 16-layer multi-codebook design and a lightweight causal ConvNet. Extensive experiments indicate state-of-the-art performance across diverse objective and subjective benchmark (e.g., TTS multilingual test set, InstructTTSEval, and our long speech test set). To facilitate community research and development, we release both tokenizers and models under the Apache 2.0 license.
PodEval: A Multimodal Evaluation Framework for Podcast Audio Generation
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Recently, an increasing number of multimodal (text and audio) benchmarks have emerged, primarily focusing on evaluating models' understanding capability. However, exploration into assessing generative capabilities remains limited, especially for open-ended long-form content generation. Significant challenges lie in no reference standard answer, no unified evaluation metrics and uncontrollable human judgments. In this work, we take podcast-like audio generation as a starting point and propose PodEval, a comprehensive and well-designed open-source evaluation framework. In this framework: 1) We construct a real-world podcast dataset spanning diverse topics, serving as a reference for human-level creative quality. 2) We introduce a multimodal evaluation strategy and decompose the complex task into three dimensions: text, speech and audio, with different evaluation emphasis on "Content" and "Format". 3) For each modality, we design corresponding evaluation methods, involving both objective metrics and subjective listening test. We leverage representative podcast generation systems (including open-source, close-source, and human-made) in our experiments. The results offer in-depth analysis and insights into podcast generation, demonstrating the effectiveness of PodEval in evaluating open-ended long-form audio. This project is open-source to facilitate public use: https://github.com/yujxx/PodEval.
XEmoRAG: Cross-Lingual Emotion Transfer with Controllable Intensity Using Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Aug 12, 2025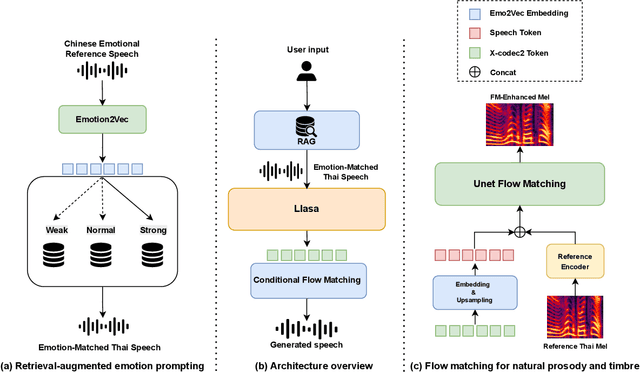
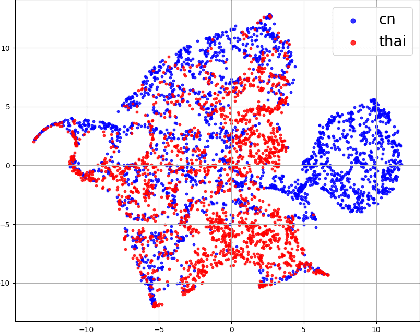
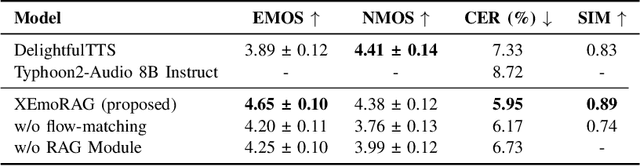
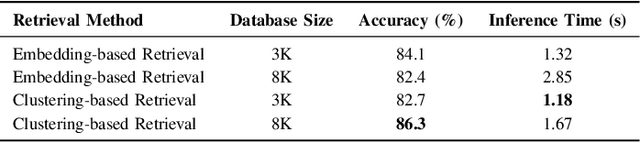
Abstract:Zero-shot emotion transfer in cross-lingual speech synthesis refers to generating speech in a target language, where the emotion is expressed based on reference speech from a different source language. However, this task remains challenging due to the scarcity of parallel multilingual emotional corpora, the presence of foreign accent artifacts, and the difficulty of separating emotion from language-specific prosodic features. In this paper, we propose XEmoRAG, a novel framework to enable zero-shot emotion transfer from Chinese to Thai using a large language model (LLM)-based model, without relying on parallel emotional data. XEmoRAG extracts language-agnostic emotional embeddings from Chinese speech and retrieves emotionally matched Thai utterances from a curated emotional database, enabling controllable emotion transfer without explicit emotion labels. Additionally, a flow-matching alignment module minimizes pitch and duration mismatches, ensuring natural prosody. It also blends Chinese timbre into the Thai synthesis, enhancing rhythmic accuracy and emotional expression, while preserving speaker characteristics and emotional consistency. Experimental results show that XEmoRAG synthesizes expressive and natural Thai speech using only Chinese reference audio, without requiring explicit emotion labels. These results highlight XEmoRAG's capability to achieve flexible and low-resource emotional transfer across languages. Our demo is available at https://tlzuo-lesley.github.io/Demo-page/ .
Llasa+: Free Lunch for Accelerated and Streaming Llama-Based Speech Synthesis
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in text-to-speech (TTS) has achieved impressive naturalness and flexibility, especially with the development of large language model (LLM)-based approaches. However, existing autoregressive (AR) structures and large-scale models, such as Llasa, still face significant challenges in inference latency and streaming synthesis. To deal with the limitations, we introduce Llasa+, an accelerated and streaming TTS model built on Llasa. Specifically, to accelerate the generation process, we introduce two plug-and-play Multi-Token Prediction (MTP) modules following the frozen backbone. These modules allow the model to predict multiple tokens in one AR step. Additionally, to mitigate potential error propagation caused by inaccurate MTP, we design a novel verification algorithm that leverages the frozen backbone to validate the generated tokens, thus allowing Llasa+ to achieve speedup without sacrificing generation quality. Furthermore, we design a causal decoder that enables streaming speech reconstruction from tokens. Extensive experiments show that Llasa+ achieves a 1.48X speedup without sacrificing generation quality, despite being trained only on LibriTTS. Moreover, the MTP-and-verification framework can be applied to accelerate any LLM-based model. All codes and models are publicly available at https://github.com/ASLP-lab/LLaSA_Plus.
Weakly Supervised Data Refinement and Flexible Sequence Compression for Efficient Thai LLM-based ASR
May 28, 2025Abstract:Despite remarkable achievements, automatic speech recognition (ASR) in low-resource scenarios still faces two challenges: high-quality data scarcity and high computational demands. This paper proposes EThai-ASR, the first to apply large language models (LLMs) to Thai ASR and create an efficient LLM-based ASR system. EThai-ASR comprises a speech encoder, a connection module and a Thai LLM decoder. To address the data scarcity and obtain a powerful speech encoder, EThai-ASR introduces a self-evolving data refinement strategy to refine weak labels, yielding an enhanced speech encoder. Moreover, we propose a pluggable sequence compression module used in the connection module with three modes designed to reduce the sequence length, thus decreasing computational demands while maintaining decent performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EThai-ASR has achieved state-of-the-art accuracy in multiple datasets. We release our refined text transcripts to promote further research.
FlowSE: Efficient and High-Quality Speech Enhancement via Flow Matching
May 26, 2025Abstract:Generative models have excelled in audio tasks using approaches such as language models, diffusion, and flow matching. However, existing generative approaches for speech enhancement (SE) face notable challenges: language model-based methods suffer from quantization loss, leading to compromised speaker similarity and intelligibility, while diffusion models require complex training and high inference latency. To address these challenges, we propose FlowSE, a flow-matching-based model for SE. Flow matching learns a continuous transformation between noisy and clean speech distributions in a single pass, significantly reducing inference latency while maintaining high-quality reconstruction. Specifically, FlowSE trains on noisy mel spectrograms and optional character sequences, optimizing a conditional flow matching loss with ground-truth mel spectrograms as supervision. It implicitly learns speech's temporal-spectral structure and text-speech alignment. During inference, FlowSE can operate with or without textual information, achieving impressive results in both scenarios, with further improvements when transcripts are available. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FlowSE significantly outperforms state-of-the-art generative methods, establishing a new paradigm for generative-based SE and demonstrating the potential of flow matching to advance the field. Our code, pre-trained checkpoints, and audio samples are available.
U-SAM: An audio language Model for Unified Speech, Audio, and Music Understanding
May 20, 2025Abstract:The text generation paradigm for audio tasks has opened new possibilities for unified audio understanding. However, existing models face significant challenges in achieving a comprehensive understanding across diverse audio types, such as speech, general audio events, and music. Furthermore, their exclusive reliance on cross-entropy loss for alignment often falls short, as it treats all tokens equally and fails to account for redundant audio features, leading to weaker cross-modal alignment. To deal with the above challenges, this paper introduces U-SAM, an advanced audio language model that integrates specialized encoders for speech, audio, and music with a pre-trained large language model (LLM). U-SAM employs a Mixture of Experts (MoE) projector for task-aware feature fusion, dynamically routing and integrating the domain-specific encoder outputs. Additionally, U-SAM incorporates a Semantic-Aware Contrastive Loss Module, which explicitly identifies redundant audio features under language supervision and rectifies their semantic and spectral representations to enhance cross-modal alignment. Extensive experiments demonstrate that U-SAM consistently outperforms both specialized models and existing audio language models across multiple benchmarks. Moreover, it exhibits emergent capabilities on unseen tasks, showcasing its generalization potential. Code is available (https://github.com/Honee-W/U-SAM/).
Spark-TTS: An Efficient LLM-Based Text-to-Speech Model with Single-Stream Decoupled Speech Tokens
Mar 03, 2025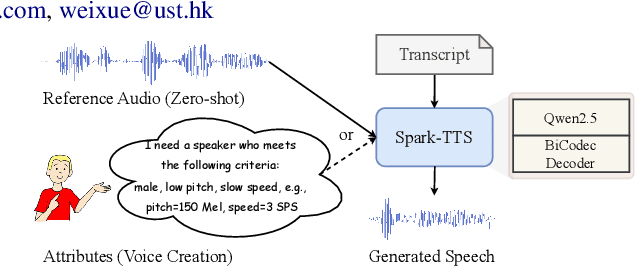
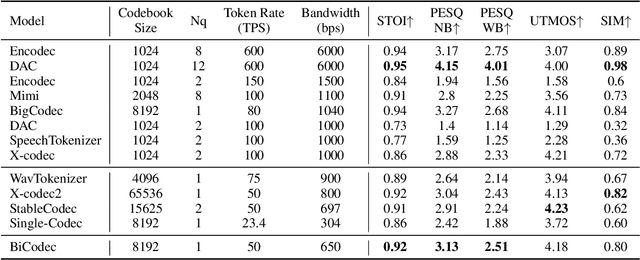
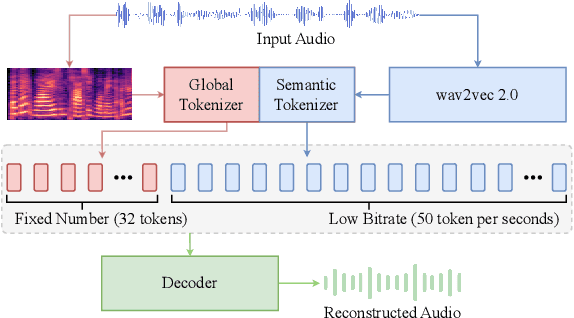
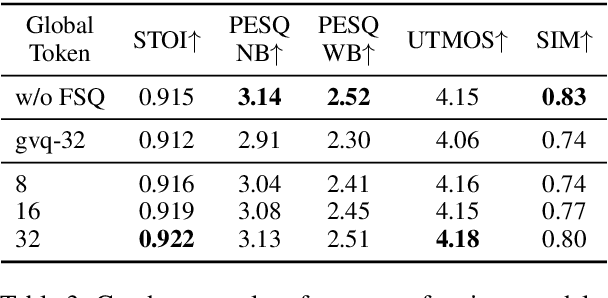
Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have driven significant progress in zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis. However, existing foundation models rely on multi-stage processing or complex architectures for predicting multiple codebooks, limiting efficiency and integration flexibility. To overcome these challenges, we introduce Spark-TTS, a novel system powered by BiCodec, a single-stream speech codec that decomposes speech into two complementary token types: low-bitrate semantic tokens for linguistic content and fixed-length global tokens for speaker attributes. This disentangled representation, combined with the Qwen2.5 LLM and a chain-of-thought (CoT) generation approach, enables both coarse-grained control (e.g., gender, speaking style) and fine-grained adjustments (e.g., precise pitch values, speaking rate). To facilitate research in controllable TTS, we introduce VoxBox, a meticulously curated 100,000-hour dataset with comprehensive attribute annotations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Spark-TTS not only achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot voice cloning but also generates highly customizable voices that surpass the limitations of reference-based synthesis. Source code, pre-trained models, and audio samples are available at https://github.com/SparkAudio/Spark-TTS.
Steering Language Model to Stable Speech Emotion Recognition via Contextual Perception and Chain of Thought
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Large-scale audio language models (ALMs), such as Qwen2-Audio, are capable of comprehending diverse audio signal, performing audio analysis and generating textual responses. However, in speech emotion recognition (SER), ALMs often suffer from hallucinations, resulting in misclassifications or irrelevant outputs. To address these challenges, we propose C$^2$SER, a novel ALM designed to enhance the stability and accuracy of SER through Contextual perception and Chain of Thought (CoT). C$^2$SER integrates the Whisper encoder for semantic perception and Emotion2Vec-S for acoustic perception, where Emotion2Vec-S extends Emotion2Vec with semi-supervised learning to enhance emotional discrimination. Additionally, C$^2$SER employs a CoT approach, processing SER in a step-by-step manner while leveraging speech content and speaking styles to improve recognition. To further enhance stability, C$^2$SER introduces self-distillation from explicit CoT to implicit CoT, mitigating error accumulation and boosting recognition accuracy. Extensive experiments show that C$^2$SER outperforms existing popular ALMs, such as Qwen2-Audio and SECap, delivering more stable and precise emotion recognition. We release the training code, checkpoints, and test sets to facilitate further research.
Llasa: Scaling Train-Time and Inference-Time Compute for Llama-based Speech Synthesis
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in text-based large language models (LLMs), particularly in the GPT series and the o1 model, have demonstrated the effectiveness of scaling both training-time and inference-time compute. However, current state-of-the-art TTS systems leveraging LLMs are often multi-stage, requiring separate models (e.g., diffusion models after LLM), complicating the decision of whether to scale a particular model during training or testing. This work makes the following contributions: First, we explore the scaling of train-time and inference-time compute for speech synthesis. Second, we propose a simple framework Llasa for speech synthesis that employs a single-layer vector quantizer (VQ) codec and a single Transformer architecture to fully align with standard LLMs such as Llama. Our experiments reveal that scaling train-time compute for Llasa consistently improves the naturalness of synthesized speech and enables the generation of more complex and accurate prosody patterns. Furthermore, from the perspective of scaling inference-time compute, we employ speech understanding models as verifiers during the search, finding that scaling inference-time compute shifts the sampling modes toward the preferences of specific verifiers, thereby improving emotional expressiveness, timbre consistency, and content accuracy. In addition, we released the checkpoint and training code for our TTS model (1B, 3B, 8B) and codec model publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge