Junhui Liu
XEmoRAG: Cross-Lingual Emotion Transfer with Controllable Intensity Using Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Aug 12, 2025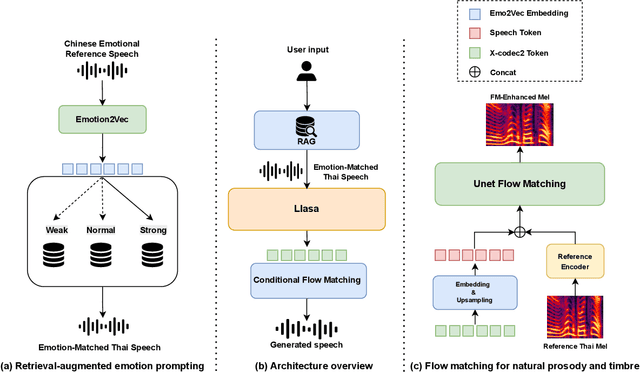
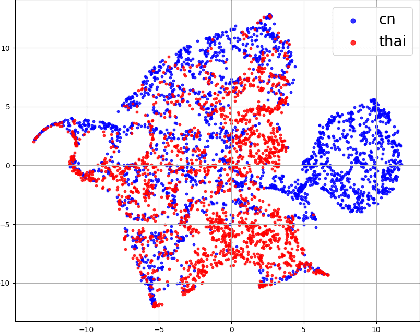
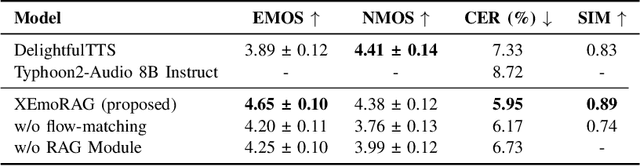
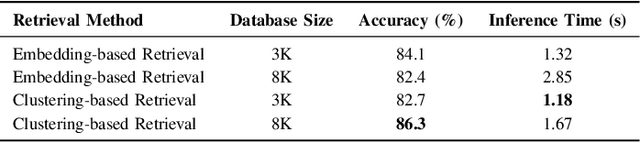
Abstract:Zero-shot emotion transfer in cross-lingual speech synthesis refers to generating speech in a target language, where the emotion is expressed based on reference speech from a different source language. However, this task remains challenging due to the scarcity of parallel multilingual emotional corpora, the presence of foreign accent artifacts, and the difficulty of separating emotion from language-specific prosodic features. In this paper, we propose XEmoRAG, a novel framework to enable zero-shot emotion transfer from Chinese to Thai using a large language model (LLM)-based model, without relying on parallel emotional data. XEmoRAG extracts language-agnostic emotional embeddings from Chinese speech and retrieves emotionally matched Thai utterances from a curated emotional database, enabling controllable emotion transfer without explicit emotion labels. Additionally, a flow-matching alignment module minimizes pitch and duration mismatches, ensuring natural prosody. It also blends Chinese timbre into the Thai synthesis, enhancing rhythmic accuracy and emotional expression, while preserving speaker characteristics and emotional consistency. Experimental results show that XEmoRAG synthesizes expressive and natural Thai speech using only Chinese reference audio, without requiring explicit emotion labels. These results highlight XEmoRAG's capability to achieve flexible and low-resource emotional transfer across languages. Our demo is available at https://tlzuo-lesley.github.io/Demo-page/ .
Weakly Supervised Data Refinement and Flexible Sequence Compression for Efficient Thai LLM-based ASR
May 28, 2025Abstract:Despite remarkable achievements, automatic speech recognition (ASR) in low-resource scenarios still faces two challenges: high-quality data scarcity and high computational demands. This paper proposes EThai-ASR, the first to apply large language models (LLMs) to Thai ASR and create an efficient LLM-based ASR system. EThai-ASR comprises a speech encoder, a connection module and a Thai LLM decoder. To address the data scarcity and obtain a powerful speech encoder, EThai-ASR introduces a self-evolving data refinement strategy to refine weak labels, yielding an enhanced speech encoder. Moreover, we propose a pluggable sequence compression module used in the connection module with three modes designed to reduce the sequence length, thus decreasing computational demands while maintaining decent performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EThai-ASR has achieved state-of-the-art accuracy in multiple datasets. We release our refined text transcripts to promote further research.
Applications of Large Models in Medicine
Feb 24, 2025



Abstract:This paper explores the advancements and applications of large-scale models in the medical field, with a particular focus on Medical Large Models (MedLMs). These models, encompassing Large Language Models (LLMs), Vision Models, 3D Large Models, and Multimodal Models, are revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing disease prediction, diagnostic assistance, personalized treatment planning, and drug discovery. The integration of graph neural networks in medical knowledge graphs and drug discovery highlights the potential of Large Graph Models (LGMs) in understanding complex biomedical relationships. The study also emphasizes the transformative role of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and 3D Large Models in medical image analysis, anatomical modeling, and prosthetic design. Despite the challenges, these technologies are setting new benchmarks in medical innovation, improving diagnostic accuracy, and paving the way for personalized healthcare solutions. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state and future directions of large models in medicine, underscoring their significance in advancing global health.
FreeV: Free Lunch For Vocoders Through Pseudo Inversed Mel Filter
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Vocoders reconstruct speech waveforms from acoustic features and play a pivotal role in modern TTS systems. Frequent-domain GAN vocoders like Vocos and APNet2 have recently seen rapid advancements, outperforming time-domain models in inference speed while achieving comparable audio quality. However, these frequency-domain vocoders suffer from large parameter sizes, thus introducing extra memory burden. Inspired by PriorGrad and SpecGrad, we employ pseudo-inverse to estimate the amplitude spectrum as the initialization roughly. This simple initialization significantly mitigates the parameter demand for vocoder. Based on APNet2 and our streamlined Amplitude prediction branch, we propose our FreeV, compared with its counterpart APNet2, our FreeV achieves 1.8 times inference speed improvement with nearly half parameters. Meanwhile, our FreeV outperforms APNet2 in resynthesis quality, marking a step forward in pursuing real-time, high-fidelity speech synthesis. Code and checkpoints is available at: https://github.com/BakerBunker/FreeV
Zero-Shot Emotion Transfer For Cross-Lingual Speech Synthesis
Oct 06, 2023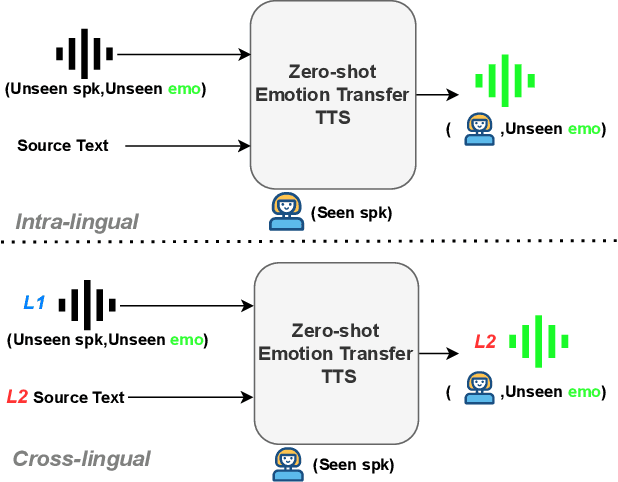
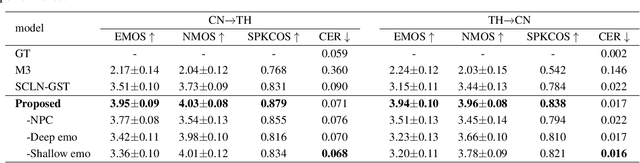
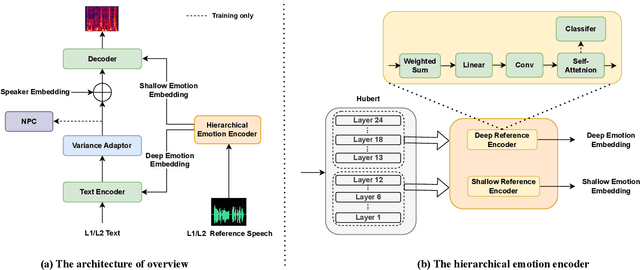
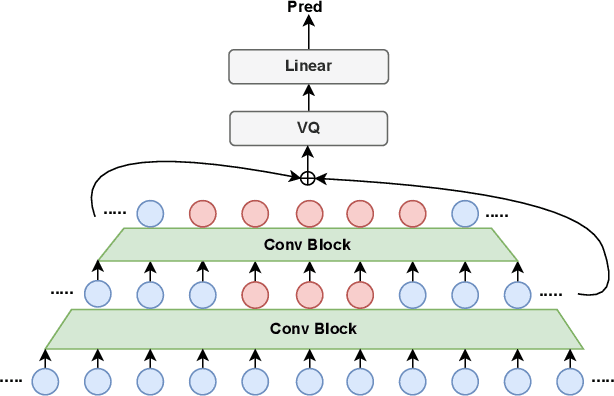
Abstract:Zero-shot emotion transfer in cross-lingual speech synthesis aims to transfer emotion from an arbitrary speech reference in the source language to the synthetic speech in the target language. Building such a system faces challenges of unnatural foreign accents and difficulty in modeling the shared emotional expressions of different languages. Building on the DelightfulTTS neural architecture, this paper addresses these challenges by introducing specifically-designed modules to model the language-specific prosody features and language-shared emotional expressions separately. Specifically, the language-specific speech prosody is learned by a non-autoregressive predictive coding (NPC) module to improve the naturalness of the synthetic cross-lingual speech. The shared emotional expression between different languages is extracted from a pre-trained self-supervised model HuBERT with strong generalization capabilities. We further use hierarchical emotion modeling to capture more comprehensive emotions across different languages. Experimental results demonstrate the proposed framework's effectiveness in synthesizing bi-lingual emotional speech for the monolingual target speaker without emotional training data.
TKwinFormer: Top k Window Attention in Vision Transformers for Feature Matching
Aug 29, 2023



Abstract:Local feature matching remains a challenging task, primarily due to difficulties in matching sparse keypoints and low-texture regions. The key to solving this problem lies in effectively and accurately integrating global and local information. To achieve this goal, we introduce an innovative local feature matching method called TKwinFormer. Our approach employs a multi-stage matching strategy to optimize the efficiency of information interaction. Furthermore, we propose a novel attention mechanism called Top K Window Attention, which facilitates global information interaction through window tokens prior to patch-level matching, resulting in improved matching accuracy. Additionally, we design an attention block to enhance attention between channels. Experimental results demonstrate that TKwinFormer outperforms state-of-the-art methods on various benchmarks. Code is available at: https://github.com/LiaoYun0x0/TKwinFormer.
A Review and Comparative Study of Close-Range Geometric Camera Calibration Tools
Jun 15, 2023
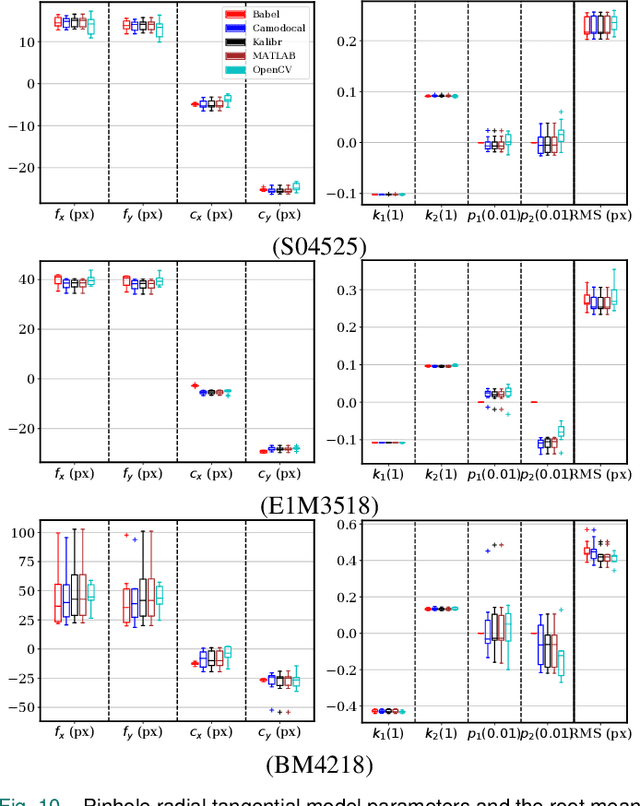
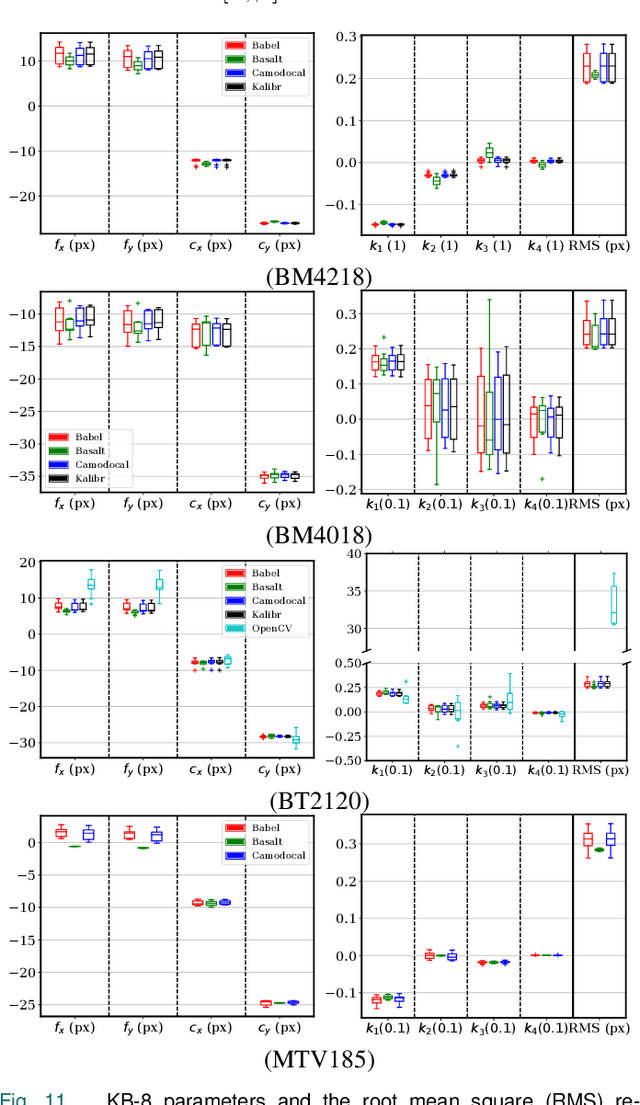
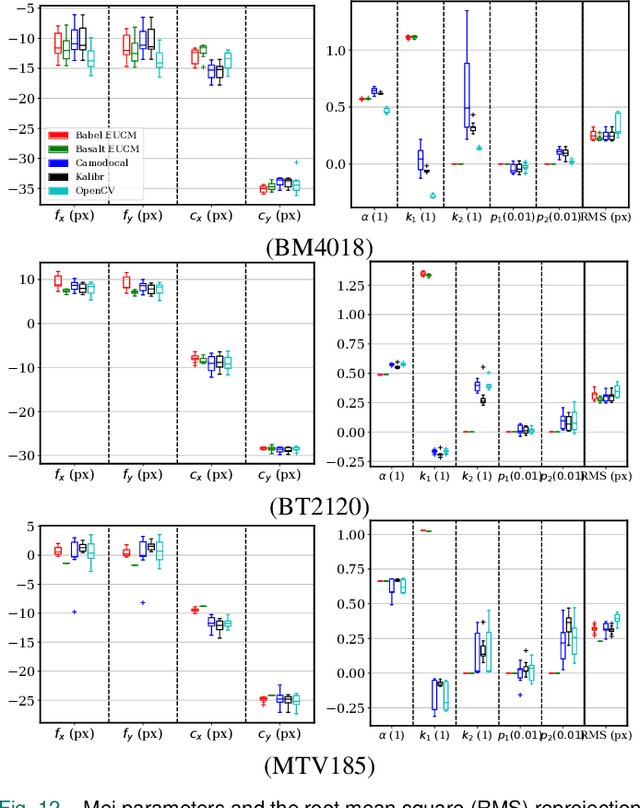
Abstract:In many camera-based applications, it is necessary to find the geometric relationship between incoming rays and image pixels, i.e., the projection model, through the geometric camera calibration (GCC). Aiming to provide practical calibration guidelines, this work surveys and evaluates the existing GCC tools. The survey covers camera models, calibration targets, and algorithms used in these tools, highlighting their properties and the trends in GCC development. The evaluation compares six target-based GCC tools, namely, BabelCalib, Basalt, Camodocal, Kalibr, the MATLAB calibrator, and the OpenCV-based ROS calibrator, with simulated and real data for cameras of wide-angle and fisheye lenses described by three traditional projection models. These tests reveal the strengths and weaknesses of these camera models, as well as the repeatability of these GCC tools. In view of the survey and evaluation, future research directions of GCC are also discussed.
Preserving background sound in noise-robust voice conversion via multi-task learning
Nov 06, 2022Abstract:Background sound is an informative form of art that is helpful in providing a more immersive experience in real-application voice conversion (VC) scenarios. However, prior research about VC, mainly focusing on clean voices, pay rare attention to VC with background sound. The critical problem for preserving background sound in VC is inevitable speech distortion by the neural separation model and the cascade mismatch between the source separation model and the VC model. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end framework via multi-task learning which sequentially cascades a source separation (SS) module, a bottleneck feature extraction module and a VC module. Specifically, the source separation task explicitly considers critical phase information and confines the distortion caused by the imperfect separation process. The source separation task, the typical VC task and the unified task shares a uniform reconstruction loss constrained by joint training to reduce the mismatch between the SS and VC modules. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed framework significantly outperforms the baseline systems while achieving comparable quality and speaker similarity to the VC models trained with clean data.
ClothFormer:Taming Video Virtual Try-on in All Module
Apr 26, 2022
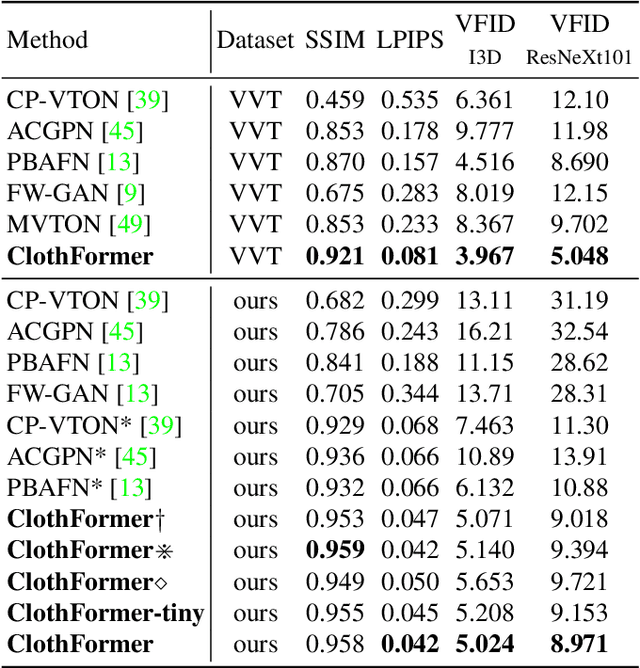
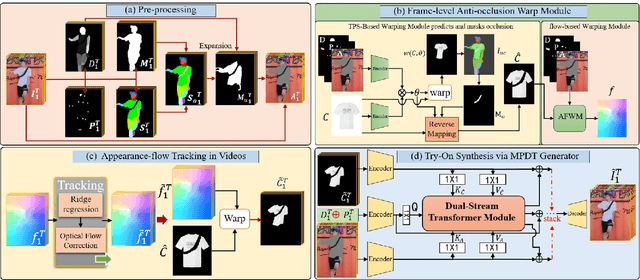
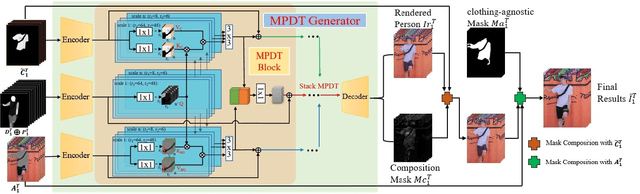
Abstract:The task of video virtual try-on aims to fit the target clothes to a person in the video with spatio-temporal consistency. Despite tremendous progress of image virtual try-on, they lead to inconsistency between frames when applied to videos. Limited work also explored the task of video-based virtual try-on but failed to produce visually pleasing and temporally coherent results. Moreover, there are two other key challenges: 1) how to generate accurate warping when occlusions appear in the clothing region; 2) how to generate clothes and non-target body parts (e.g. arms, neck) in harmony with the complicated background; To address them, we propose a novel video virtual try-on framework, ClothFormer, which successfully synthesizes realistic, harmonious, and spatio-temporal consistent results in complicated environment. In particular, ClothFormer involves three major modules. First, a two-stage anti-occlusion warping module that predicts an accurate dense flow mapping between the body regions and the clothing regions. Second, an appearance-flow tracking module utilizes ridge regression and optical flow correction to smooth the dense flow sequence and generate a temporally smooth warped clothing sequence. Third, a dual-stream transformer extracts and fuses clothing textures, person features, and environment information to generate realistic try-on videos. Through rigorous experiments, we demonstrate that our method highly surpasses the baselines in terms of synthesized video quality both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Migrating Face Swap to Mobile Devices: A lightweight Framework and A Supervised Training Solution
Apr 13, 2022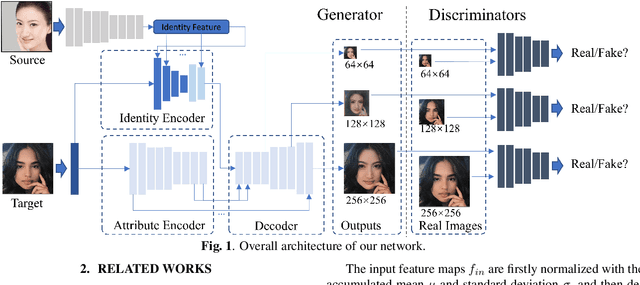
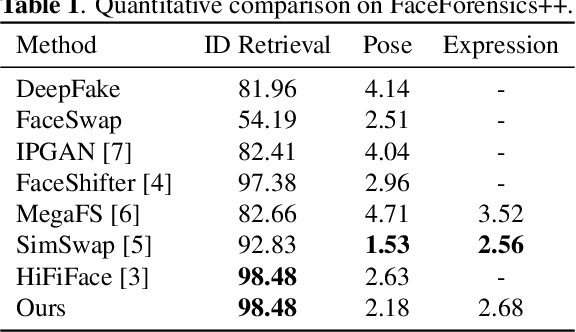
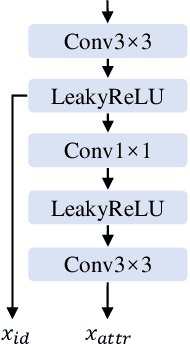
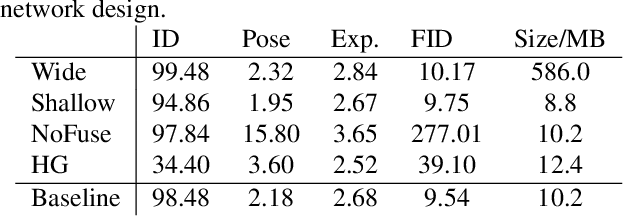
Abstract:Existing face swap methods rely heavily on large-scale networks for adequate capacity to generate visually plausible results, which inhibits its applications on resource-constraint platforms. In this work, we propose MobileFSGAN, a novel lightweight GAN for face swap that can run on mobile devices with much fewer parameters while achieving competitive performance. A lightweight encoder-decoder structure is designed especially for image synthesis tasks, which is only 10.2MB and can run on mobile devices at a real-time speed. To tackle the unstability of training such a small network, we construct the FSTriplets dataset utilizing facial attribute editing techniques. FSTriplets provides source-target-result training triplets, yielding pixel-level labels thus for the first time making the training process supervised. We also designed multi-scale gradient losses for efficient back-propagation, resulting in faster and better convergence. Experimental results show that our model reaches comparable performance towards state-of-the-art methods, while significantly reducing the number of network parameters. Codes and the dataset have been released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge