Qing Wang
MTFM: A Scalable and Alignment-free Foundation Model for Industrial Recommendation in Meituan
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Industrial recommendation systems typically involve multiple scenarios, yet existing cross-domain (CDR) and multi-scenario (MSR) methods often require prohibitive resources and strict input alignment, limiting their extensibility. We propose MTFM (Meituan Foundation Model for Recommendation), a transformer-based framework that addresses these challenges. Instead of pre-aligning inputs, MTFM transforms cross-domain data into heterogeneous tokens, capturing multi-scenario knowledge in an alignment-free manner. To enhance efficiency, we first introduce a multi-scenario user-level sample aggregation that significantly enhances training throughput by reducing the total number of instances. We further integrate Grouped-Query Attention and a customized Hybrid Target Attention to minimize memory usage and computational complexity. Furthermore, we implement various system-level optimizations, such as kernel fusion and the elimination of CPU-GPU blocking, to further enhance both training and inference throughput. Offline and online experiments validate the effectiveness of MTFM, demonstrating that significant performance gains are achieved by scaling both model capacity and multi-scenario training data.
GPO: Growing Policy Optimization for Legged Robot Locomotion and Whole-Body Control
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Training reinforcement learning (RL) policies for legged robots remains challenging due to high-dimensional continuous actions, hardware constraints, and limited exploration. Existing methods for locomotion and whole-body control work well for position-based control with environment-specific heuristics (e.g., reward shaping, curriculum design, and manual initialization), but are less effective for torque-based control, where sufficiently exploring the action space and obtaining informative gradient signals for training is significantly more difficult. We introduce Growing Policy Optimization (GPO), a training framework that applies a time-varying action transformation to restrict the effective action space in the early stage, thereby encouraging more effective data collection and policy learning, and then progressively expands it to enhance exploration and achieve higher expected return. We prove that this transformation preserves the PPO update rule and introduces only bounded, vanishing gradient distortion, thereby ensuring stable training. We evaluate GPO on both quadruped and hexapod robots, including zero-shot deployment of simulation-trained policies on hardware. Policies trained with GPO consistently achieve better performance. These results suggest that GPO provides a general, environment-agnostic optimization framework for learning legged locomotion.
Frame-Guided Synthetic Claim Generation for Automatic Fact-Checking Using High-Volume Tabular Data
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Automated fact-checking benchmarks have largely ignored the challenge of verifying claims against real-world, high-volume structured data, instead focusing on small, curated tables. We introduce a new large-scale, multilingual dataset to address this critical gap. It contains 78,503 synthetic claims grounded in 434 complex OECD tables, which average over 500K rows each. We propose a novel, frame-guided methodology where algorithms programmatically select significant data points based on six semantic frames to generate realistic claims in English, Chinese, Spanish, and Hindi. Crucially, we demonstrate through knowledge-probing experiments that LLMs have not memorized these facts, forcing systems to perform genuine retrieval and reasoning rather than relying on parameterized knowledge. We provide a baseline SQL-generation system and show that our benchmark is highly challenging. Our analysis identifies evidence retrieval as the primary bottleneck, with models struggling to find the correct data in massive tables. This dataset provides a critical new resource for advancing research on this unsolved, real-world problem.
All Changes May Have Invariant Principles: Improving Ever-Shifting Harmful Meme Detection via Design Concept Reproduction
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Harmful memes are ever-shifting in the Internet communities, which are difficult to analyze due to their type-shifting and temporal-evolving nature. Although these memes are shifting, we find that different memes may share invariant principles, i.e., the underlying design concept of malicious users, which can help us analyze why these memes are harmful. In this paper, we propose RepMD, an ever-shifting harmful meme detection method based on the design concept reproduction. We first refer to the attack tree to define the Design Concept Graph (DCG), which describes steps that people may take to design a harmful meme. Then, we derive the DCG from historical memes with design step reproduction and graph pruning. Finally, we use DCG to guide the Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) to detect harmful memes. The evaluation results show that RepMD achieves the highest accuracy with 81.1% and has slight accuracy decreases when generalized to type-shifting and temporal-evolving memes. Human evaluation shows that RepMD can improve the efficiency of human discovery on harmful memes, with 15$\sim$30 seconds per meme.
Know Thy Enemy: Securing LLMs Against Prompt Injection via Diverse Data Synthesis and Instruction-Level Chain-of-Thought Learning
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-integrated applications have become increasingly prevalent, yet face critical security vulnerabilities from prompt injection (PI) attacks. Defending against PI attacks faces two major issues: malicious instructions can be injected through diverse vectors, and injected instructions often lack clear semantic boundaries from the surrounding context, making them difficult to identify. To address these issues, we propose InstruCoT, a model enhancement method for PI defense that synthesizes diverse training data and employs instruction-level chain-of-thought fine-tuning, enabling LLMs to effectively identify and reject malicious instructions regardless of their source or position in the context. We evaluate InstruCoT across three critical dimensions: Behavior Deviation, Privacy Leakage, and Harmful Output. Experimental results across four LLMs demonstrate that InstruCoT significantly outperforms baselines in all dimensions while maintaining utility performance without degradation
A Unified Spoken Language Model with Injected Emotional-Attribution Thinking for Human-like Interaction
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:This paper presents a unified spoken language model for emotional intelligence, enhanced by a novel data construction strategy termed Injected Emotional-Attribution Thinking (IEAT). IEAT incorporates user emotional states and their underlying causes into the model's internal reasoning process, enabling emotion-aware reasoning to be internalized rather than treated as explicit supervision. The model is trained with a two-stage progressive strategy. The first stage performs speech-text alignment and emotional attribute modeling via self-distillation, while the second stage conducts end-to-end cross-modal joint optimization to ensure consistency between textual and spoken emotional expressions. Experiments on the Human-like Spoken Dialogue Systems Challenge (HumDial) Emotional Intelligence benchmark demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves top-ranked performance across emotional trajectory modeling, emotional reasoning, and empathetic response generation under both LLM-based and human evaluations.
DINO-BOLDNet: A DINOv3-Guided Multi-Slice Attention Network for T1-to-BOLD Generation
Dec 09, 2025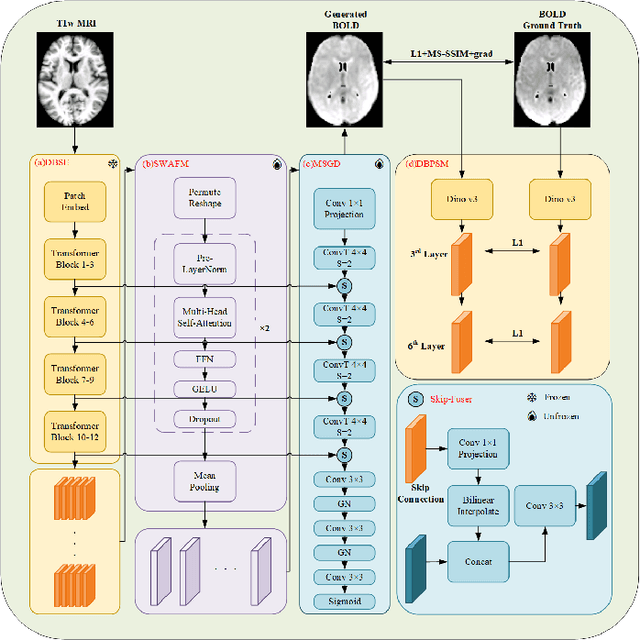
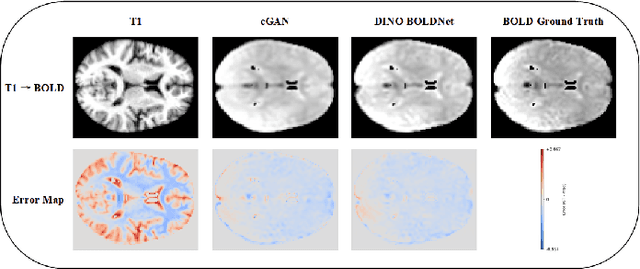
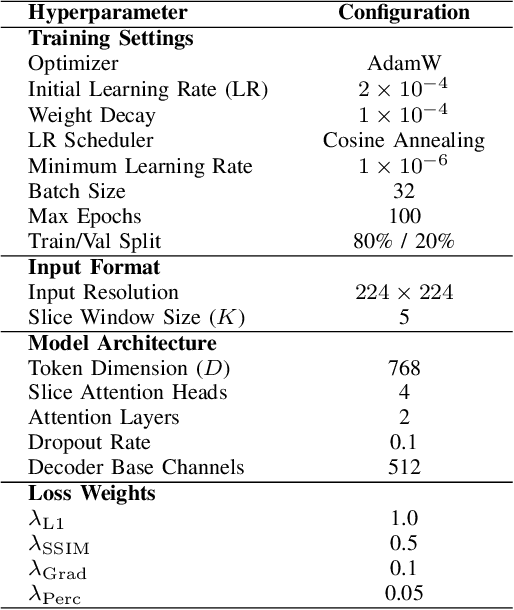
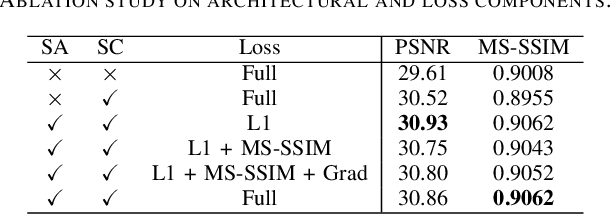
Abstract:Generating BOLD images from T1w images offers a promising solution for recovering missing BOLD information and enabling downstream tasks when BOLD images are corrupted or unavailable. Motivated by this, we propose DINO-BOLDNet, a DINOv3-guided multi-slice attention framework that integrates a frozen self-supervised DINOv3 encoder with a lightweight trainable decoder. The model uses DINOv3 to extract within-slice structural representations, and a separate slice-attention module to fuse contextual information across neighboring slices. A multi-scale generation decoder then restores fine-grained functional contrast, while a DINO-based perceptual loss encourages structural and textural consistency between predictions and ground-truth BOLD in the transformer feature space. Experiments on a clinical dataset of 248 subjects show that DINO-BOLDNet surpasses a conditional GAN baseline in both PSNR and MS-SSIM. To our knowledge, this is the first framework capable of generating mean BOLD images directly from T1w images, highlighting the potential of self-supervised transformer guidance for structural-to-functional mapping.
Towards Unbiased Cross-Modal Representation Learning for Food Image-to-Recipe Retrieval
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the challenges of learning representations for recipes and food images in the cross-modal retrieval problem. As the relationship between a recipe and its cooked dish is cause-and-effect, treating a recipe as a text source describing the visual appearance of a dish for learning representation, as the existing approaches, will create bias misleading image-and-recipe similarity judgment. Specifically, a food image may not equally capture every detail in a recipe, due to factors such as the cooking process, dish presentation, and image-capturing conditions. The current representation learning tends to capture dominant visual-text alignment while overlooking subtle variations that determine retrieval relevance. In this paper, we model such bias in cross-modal representation learning using causal theory. The causal view of this problem suggests ingredients as one of the confounder sources and a simple backdoor adjustment can alleviate the bias. By causal intervention, we reformulate the conventional model for food-to-recipe retrieval with an additional term to remove the potential bias in similarity judgment. Based on this theory-informed formulation, we empirically prove the oracle performance of retrieval on the Recipe1M dataset to be MedR=1 across the testing data sizes of 1K, 10K, and even 50K. We also propose a plug-and-play neural module, which is essentially a multi-label ingredient classifier for debiasing. New state-of-the-art search performances are reported on the Recipe1M dataset.
SMoFi: Step-wise Momentum Fusion for Split Federated Learning on Heterogeneous Data
Nov 16, 2025



Abstract:Split Federated Learning is a system-efficient federated learning paradigm that leverages the rich computing resources at a central server to train model partitions. Data heterogeneity across silos, however, presents a major challenge undermining the convergence speed and accuracy of the global model. This paper introduces Step-wise Momentum Fusion (SMoFi), an effective and lightweight framework that counteracts gradient divergence arising from data heterogeneity by synchronizing the momentum buffers across server-side optimizers. To control gradient divergence over the training process, we design a staleness-aware alignment mechanism that imposes constraints on gradient updates of the server-side submodel at each optimization step. Extensive validations on multiple real-world datasets show that SMoFi consistently improves global model accuracy (up to 7.1%) and convergence speed (up to 10.25$\times$). Furthermore, SMoFi has a greater impact with more clients involved and deeper learning models, making it particularly suitable for model training in resource-constrained contexts.
Enhancing DPSGD via Per-Sample Momentum and Low-Pass Filtering
Nov 11, 2025



Abstract:Differentially Private Stochastic Gradient Descent (DPSGD) is widely used to train deep neural networks with formal privacy guarantees. However, the addition of differential privacy (DP) often degrades model accuracy by introducing both noise and bias. Existing techniques typically address only one of these issues, as reducing DP noise can exacerbate clipping bias and vice-versa. In this paper, we propose a novel method, \emph{DP-PMLF}, which integrates per-sample momentum with a low-pass filtering strategy to simultaneously mitigate DP noise and clipping bias. Our approach uses per-sample momentum to smooth gradient estimates prior to clipping, thereby reducing sampling variance. It further employs a post-processing low-pass filter to attenuate high-frequency DP noise without consuming additional privacy budget. We provide a theoretical analysis demonstrating an improved convergence rate under rigorous DP guarantees, and our empirical evaluations reveal that DP-PMLF significantly enhances the privacy-utility trade-off compared to several state-of-the-art DPSGD variants.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge