Qi Li
Residual Reinforcement Learning for Waste-Container Lifting Using Large-Scale Cranes with Underactuated Tools
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:This paper studies the container lifting phase of a waste-container recycling task in urban environments, performed by a hydraulic loader crane equipped with an underactuated discharge unit, and proposes a residual reinforcement learning (RRL) approach that combines a nominal Cartesian controller with a learned residual policy. All experiments are conducted in simulation, where the task is characterized by tight geometric tolerances between the discharge-unit hooks and the container rings relative to the overall crane scale, making precise trajectory tracking and swing suppression essential. The nominal controller uses admittance control for trajectory tracking and pendulum-aware swing damping, followed by damped least-squares inverse kinematics with a nullspace posture term to generate joint velocity commands. A PPO-trained residual policy in Isaac Lab compensates for unmodeled dynamics and parameter variations, improving precision and robustness without requiring end-to-end learning from scratch. We further employ randomized episode initialization and domain randomization over payload properties, actuator gains, and passive joint parameters to enhance generalization. Simulation results demonstrate improved tracking accuracy, reduced oscillations, and higher lifting success rates compared to the nominal controller alone.
Magic-MM-Embedding: Towards Visual-Token-Efficient Universal Multimodal Embedding with MLLMs
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown immense promise in universal multimodal retrieval, which aims to find relevant items of various modalities for a given query. But their practical application is often hindered by the substantial computational cost incurred from processing a large number of tokens from visual inputs. In this paper, we propose Magic-MM-Embedding, a series of novel models that achieve both high efficiency and state-of-the-art performance in universal multimodal embedding. Our approach is built on two synergistic pillars: (1) a highly efficient MLLM architecture incorporating visual token compression to drastically reduce inference latency and memory footprint, and (2) a multi-stage progressive training strategy designed to not only recover but significantly boost performance. This coarse-to-fine training paradigm begins with extensive continue pretraining to restore multimodal understanding and generation capabilities, progresses to large-scale contrastive pretraining and hard negative mining to enhance discriminative power, and culminates in a task-aware fine-tuning stage guided by an MLLM-as-a-Judge for precise data curation. Comprehensive experiments show that our model outperforms existing methods by a large margin while being more inference-efficient.
DMFlow: Disordered Materials Generation by Flow Matching
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:The design of materials with tailored properties is crucial for technological progress. However, most deep generative models focus exclusively on perfectly ordered crystals, neglecting the important class of disordered materials. To address this gap, we introduce DMFlow, a generative framework specifically designed for disordered crystals. Our approach introduces a unified representation for ordered, Substitutionally Disordered (SD), and Positionally Disordered (PD) crystals, and employs a flow matching model to jointly generate all structural components. A key innovation is a Riemannian flow matching framework with spherical reparameterization, which ensures physically valid disorder weights on the probability simplex. The vector field is learned by a novel Graph Neural Network (GNN) that incorporates physical symmetries and a specialized message-passing scheme. Finally, a two-stage discretization procedure converts the continuous weights into multi-hot atomic assignments. To support research in this area, we release a benchmark containing SD, PD, and mixed structures curated from the Crystallography Open Database. Experiments on Crystal Structure Prediction (CSP) and De Novo Generation (DNG) tasks demonstrate that DMFlow significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines adapted from ordered crystal generation. We hope our work provides a foundation for the AI-driven discovery of disordered materials.
The Forecast After the Forecast: A Post-Processing Shift in Time Series
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Time series forecasting has long been dominated by advances in model architecture, with recent progress driven by deep learning and hybrid statistical techniques. However, as forecasting models approach diminishing returns in accuracy, a critical yet underexplored opportunity emerges: the strategic use of post-processing. In this paper, we address the last-mile gap in time-series forecasting, which is to improve accuracy and uncertainty without retraining or modifying a deployed backbone. We propose $δ$-Adapter, a lightweight, architecture-agnostic way to boost deployed time series forecasters without retraining. $δ$-Adapter learns tiny, bounded modules at two interfaces: input nudging (soft edits to covariates) and output residual correction. We provide local descent guarantees, $O(δ)$ drift bounds, and compositional stability for combined adapters. Meanwhile, it can act as a feature selector by learning a sparse, horizon-aware mask over inputs to select important features, thereby improving interpretability. In addition, it can also be used as a distribution calibrator to measure uncertainty. Thus, we introduce a Quantile Calibrator and a Conformal Corrector that together deliver calibrated, personalized intervals with finite-sample coverage. Our experiments across diverse backbones and datasets show that $δ$-Adapter improves accuracy and calibration with negligible compute and no interface changes.
* 30 Pages
Sponge Tool Attack: Stealthy Denial-of-Efficiency against Tool-Augmented Agentic Reasoning
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Enabling large language models (LLMs) to solve complex reasoning tasks is a key step toward artificial general intelligence. Recent work augments LLMs with external tools to enable agentic reasoning, achieving high utility and efficiency in a plug-and-play manner. However, the inherent vulnerabilities of such methods to malicious manipulation of the tool-calling process remain largely unexplored. In this work, we identify a tool-specific attack surface and propose Sponge Tool Attack (STA), which disrupts agentic reasoning solely by rewriting the input prompt under a strict query-only access assumption. Without any modification on the underlying model or the external tools, STA converts originally concise and efficient reasoning trajectories into unnecessarily verbose and convoluted ones before arriving at the final answer. This results in substantial computational overhead while remaining stealthy by preserving the original task semantics and user intent. To achieve this, we design STA as an iterative, multi-agent collaborative framework with explicit rewritten policy control, and generates benign-looking prompt rewrites from the original one with high semantic fidelity. Extensive experiments across 6 models (including both open-source models and closed-source APIs), 12 tools, 4 agentic frameworks, and 13 datasets spanning 5 domains validate the effectiveness of STA.
Toward Efficient Agents: Memory, Tool learning, and Planning
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Recent years have witnessed increasing interest in extending large language models into agentic systems. While the effectiveness of agents has continued to improve, efficiency, which is crucial for real-world deployment, has often been overlooked. This paper therefore investigates efficiency from three core components of agents: memory, tool learning, and planning, considering costs such as latency, tokens, steps, etc. Aimed at conducting comprehensive research addressing the efficiency of the agentic system itself, we review a broad range of recent approaches that differ in implementation yet frequently converge on shared high-level principles including but not limited to bounding context via compression and management, designing reinforcement learning rewards to minimize tool invocation, and employing controlled search mechanisms to enhance efficiency, which we discuss in detail. Accordingly, we characterize efficiency in two complementary ways: comparing effectiveness under a fixed cost budget, and comparing cost at a comparable level of effectiveness. This trade-off can also be viewed through the Pareto frontier between effectiveness and cost. From this perspective, we also examine efficiency oriented benchmarks by summarizing evaluation protocols for these components and consolidating commonly reported efficiency metrics from both benchmark and methodological studies. Moreover, we discuss the key challenges and future directions, with the goal of providing promising insights.
Dual-Phase LLM Reasoning: Self-Evolved Mathematical Frameworks
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in complex reasoning tasks like mathematical problem-solving. However, existing research predominantly relies on reinforcement learning (RL) frameworks while overlooking supervised fine-tuning (SFT) methods. This paper proposes a new two-stage training framework that enhances models' self-correction capabilities through self-generated long chain-of-thought (CoT) data. During the first stage, a multi-turn dialogue strategy guides the model to generate CoT data incorporating verification, backtracking, subgoal decomposition, and backward reasoning, with predefined rules filtering high-quality samples for supervised fine-tuning. The second stage employs a difficulty-aware rejection sampling mechanism to dynamically optimize data distribution, strengthening the model's ability to handle complex problems. The approach generates reasoning chains extended over 4 times longer while maintaining strong scalability, proving that SFT effectively activates models' intrinsic reasoning capabilities and provides a resource-efficient pathway for complex task optimization. Experimental results demonstrate performance improvements on mathematical benchmarks including GSM8K and MATH500, with the fine-tuned model achieving a substantial improvement on competition-level problems like AIME24. Code will be open-sourced.
Refinement Provenance Inference: Detecting LLM-Refined Training Prompts from Model Behavior
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Instruction tuning increasingly relies on LLM-based prompt refinement, where prompts in the training corpus are selectively rewritten by an external refiner to improve clarity and instruction alignment. This motivates an instance-level audit problem: for a fine-tuned model and a training prompt-response pair, can we infer whether the model was trained on the original prompt or its LLM-refined version within a mixed corpus? This matters for dataset governance and dispute resolution when training data are contested. However, it is non-trivial in practice: refined and raw instances are interleaved in the training corpus with unknown, source-dependent mixture ratios, making it harder to develop provenance methods that generalize across models and training setups. In this paper, we formalize this audit task as Refinement Provenance Inference (RPI) and show that prompt refinement yields stable, detectable shifts in teacher-forced token distributions, even when semantic differences are not obvious. Building on this phenomenon, we propose RePro, a logit-based provenance framework that fuses teacher-forced likelihood features with logit-ranking signals. During training, RePro learns a transferable representation via shadow fine-tuning, and uses a lightweight linear head to infer provenance on unseen victims without training-data access. Empirically, RePro consistently attains strong performance and transfers well across refiners, suggesting that it exploits refiner-agnostic distribution shifts rather than rewrite-style artifacts.
3SGen: Unified Subject, Style, and Structure-Driven Image Generation with Adaptive Task-specific Memory
Dec 22, 2025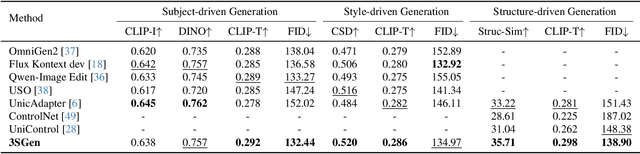
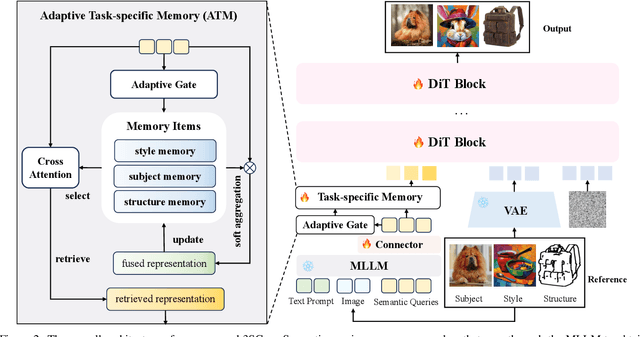
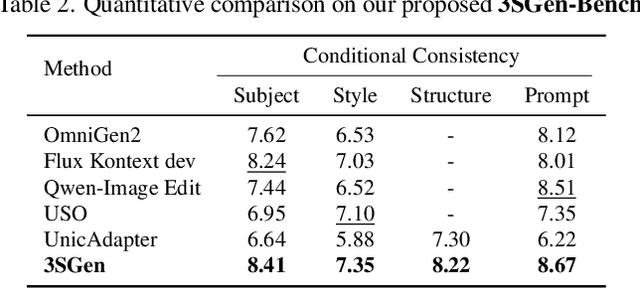
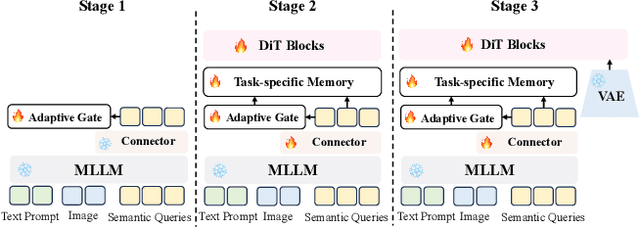
Abstract:Recent image generation approaches often address subject, style, and structure-driven conditioning in isolation, leading to feature entanglement and limited task transferability. In this paper, we introduce 3SGen, a task-aware unified framework that performs all three conditioning modes within a single model. 3SGen employs an MLLM equipped with learnable semantic queries to align text-image semantics, complemented by a VAE branch that preserves fine-grained visual details. At its core, an Adaptive Task-specific Memory (ATM) module dynamically disentangles, stores, and retrieves condition-specific priors, such as identity for subjects, textures for styles, and spatial layouts for structures, via a lightweight gating mechanism along with several scalable memory items. This design mitigates inter-task interference and naturally scales to compositional inputs. In addition, we propose 3SGen-Bench, a unified image-driven generation benchmark with standardized metrics for evaluating cross-task fidelity and controllability. Extensive experiments on our proposed 3SGen-Bench and other public benchmarks demonstrate our superior performance across diverse image-driven generation tasks.
TTP: Test-Time Padding for Adversarial Detection and Robust Adaptation on Vision-Language Models
Dec 18, 2025



Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs), such as CLIP, have achieved impressive zero-shot recognition performance but remain highly susceptible to adversarial perturbations, posing significant risks in safety-critical scenarios. Previous training-time defenses rely on adversarial fine-tuning, which requires labeled data and costly retraining, while existing test-time strategies fail to reliably distinguish between clean and adversarial inputs, thereby preventing both adversarial robustness and clean accuracy from reaching their optimum. To address these limitations, we propose Test-Time Padding (TTP), a lightweight defense framework that performs adversarial detection followed by targeted adaptation at inference. TTP identifies adversarial inputs via the cosine similarity shift between CLIP feature embeddings computed before and after spatial padding, yielding a universal threshold for reliable detection across architectures and datasets. For detected adversarial cases, TTP employs trainable padding to restore disrupted attention patterns, coupled with a similarity-aware ensemble strategy for a more robust final prediction. For clean inputs, TTP leaves them unchanged by default or optionally integrates existing test-time adaptation techniques for further accuracy gains. Comprehensive experiments on diverse CLIP backbones and fine-grained benchmarks show that TTP consistently surpasses state-of-the-art test-time defenses, delivering substantial improvements in adversarial robustness without compromising clean accuracy. The code for this paper will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge