Yi Zhao
Zetavision AI Lab
Quantifying the Knowledge Proximity Between Academic and Industry Research: An Entity and Semantic Perspective
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:The academia and industry are characterized by a reciprocal shaping and dynamic feedback mechanism. Despite distinct institutional logics, they have adapted closely in collaborative publishing and talent mobility, demonstrating tension between institutional divergence and intensive collaboration. Existing studies on their knowledge proximity mainly rely on macro indicators such as the number of collaborative papers or patents, lacking an analysis of knowledge units in the literature. This has led to an insufficient grasp of fine-grained knowledge proximity between industry and academia, potentially undermining collaboration frameworks and resource allocation efficiency. To remedy the limitation, this study quantifies the trajectory of academia-industry co-evolution through fine-grained entities and semantic space. In the entity measurement part, we extract fine-grained knowledge entities via pre-trained models, measure sequence overlaps using cosine similarity, and analyze topological features through complex network analysis. At the semantic level, we employ unsupervised contrastive learning to quantify convergence in semantic spaces by measuring cross-institutional textual similarities. Finally, we use citation distribution patterns to examine correlations between bidirectional knowledge flows and similarity. Analysis reveals that knowledge proximity between academia and industry rises, particularly following technological change. This provides textual evidence of bidirectional adaptation in co-evolution. Additionally, academia's knowledge dominance weakens during technological paradigm shifts. The dataset and code for this paper can be accessed at https://github.com/tinierZhao/Academic-Industrial-associations.
Sparsely Supervised Diffusion
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Diffusion models have shown remarkable success across a wide range of generative tasks. However, they often suffer from spatially inconsistent generation, arguably due to the inherent locality of their denoising mechanisms. This can yield samples that are locally plausible but globally inconsistent. To mitigate this issue, we propose sparsely supervised learning for diffusion models, a simple yet effective masking strategy that can be implemented with only a few lines of code. Interestingly, the experiments show that it is safe to mask up to 98\% of pixels during diffusion model training. Our method delivers competitive FID scores across experiments and, most importantly, avoids training instability on small datasets. Moreover, the masking strategy reduces memorization and promotes the use of essential contextual information during generation.
ShapLoRA: Allocation of Low-rank Adaption on Large Language Models via Shapley Value Inspired Importance Estimation
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Low-rank adaption (LoRA) is a representative method in the field of parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT), and is key to Democratizating the modern large language models (LLMs). The vanilla LoRA is implemented with uniform ranks, and the recent literature have found that properly allocating ranks on the LLM backbones results in performance boosts. However, the previous rank allocation methods have limitations since they rely on inexplanable and unreliable importance measures for the LoRA ranks. To address the above issues, we propose the ShapLoRA framework. Inspired by the explanable attribution measure Shapley Value, we combine the sensitivity-based measures with the idea of coalitions in the collaborative games among LoRA ranks, and propose a more explainable importance measure called Shapley sensitivity. In addition, we optimize the workflow of the existing works by: (a) calculating Shapley sensitivity on a separate validation set; (b) Setting up the allocating-retraining procedures for fair comparisons. We have conducted experiments on various challenging tasks, and the experimental results demonstrate that our ShapLoRA method can outperform the recent baselines with comparable tunable parameters.\footnote{Codes and fine-tuned models will be open-sourced to facilitate future research.
DPWriter: Reinforcement Learning with Diverse Planning Branching for Creative Writing
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL)-based enhancement of large language models (LLMs) often leads to reduced output diversity, undermining their utility in open-ended tasks like creative writing. Current methods lack explicit mechanisms for guiding diverse exploration and instead prioritize optimization efficiency and performance over diversity. This paper proposes an RL framework structured around a semi-structured long Chain-of-Thought (CoT), in which the generation process is decomposed into explicitly planned intermediate steps. We introduce a Diverse Planning Branching method that strategically introduces divergence at the planning phase based on diversity variation, alongside a group-aware diversity reward to encourage distinct trajectories. Experimental results on creative writing benchmarks demonstrate that our approach significantly improves output diversity without compromising generation quality, consistently outperforming existing baselines.
The Effect of Gender Diversity on Scientific Team Impact: A Team Roles Perspective
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:The influence of gender diversity on the success of scientific teams is of great interest to academia. However, prior findings remain inconsistent, and most studies operationalize diversity in aggregate terms, overlooking internal role differentiation. This limitation obscures a more nuanced understanding of how gender diversity shapes team impact. In particular, the effect of gender diversity across different team roles remains poorly understood. To this end, we define a scientific team as all coauthors of a paper and measure team impact through five-year citation counts. Using author contribution statements, we classified members into leadership and support roles. Drawing on more than 130,000 papers from PLOS journals, most of which are in biomedical-related disciplines, we employed multivariable regression to examine the association between gender diversity in these roles and team impact. Furthermore, we apply a threshold regression model to investigate how team size moderates this relationship. The results show that (1) the relationship between gender diversity and team impact follows an inverted U-shape for both leadership and support groups; (2) teams with an all-female leadership group and an all-male support group achieve higher impact than other team types. Interestingly, (3) the effect of leadership-group gender diversity is significantly negative for small teams but becomes positive and statistically insignificant in large teams. In contrast, the estimates for support-group gender diversity remain significant and positive, regardless of team size.
Prefix Probing: Lightweight Harmful Content Detection for Large Language Models
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Large language models often face a three-way trade-off among detection accuracy, inference latency, and deployment cost when used in real-world safety-sensitive applications. This paper introduces Prefix Probing, a black-box harmful content detection method that compares the conditional log-probabilities of "agreement/execution" versus "refusal/safety" opening prefixes and leverages prefix caching to reduce detection overhead to near first-token latency. During inference, the method requires only a single log-probability computation over the probe prefixes to produce a harmfulness score and apply a threshold, without invoking any additional models or multi-stage inference. To further enhance the discriminative power of the prefixes, we design an efficient prefix construction algorithm that automatically discovers highly informative prefixes, substantially improving detection performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Prefix Probing achieves detection effectiveness comparable to mainstream external safety models while incurring only minimal computational cost and requiring no extra model deployment, highlighting its strong practicality and efficiency.
Design, Results and Industry Implications of the World's First Insurance Large Language Model Evaluation Benchmark
Nov 11, 2025
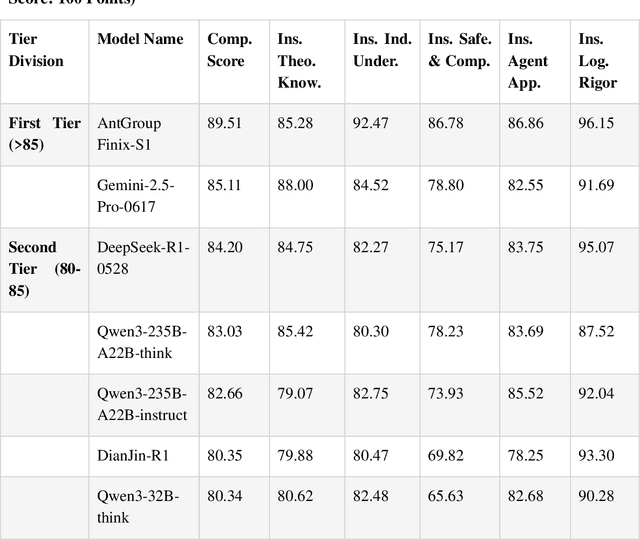
Abstract:This paper comprehensively elaborates on the construction methodology, multi-dimensional evaluation system, and underlying design philosophy of CUFEInse v1.0. Adhering to the principles of "quantitative-oriented, expert-driven, and multi-validation," the benchmark establishes an evaluation framework covering 5 core dimensions, 54 sub-indicators, and 14,430 high-quality questions, encompassing insurance theoretical knowledge, industry understanding, safety and compliance, intelligent agent application, and logical rigor. Based on this benchmark, a comprehensive evaluation was conducted on 11 mainstream large language models. The evaluation results reveal that general-purpose models suffer from common bottlenecks such as weak actuarial capabilities and inadequate compliance adaptation. High-quality domain-specific training demonstrates significant advantages in insurance vertical scenarios but exhibits shortcomings in business adaptation and compliance. The evaluation also accurately identifies the common bottlenecks of current large models in professional scenarios such as insurance actuarial, underwriting and claim settlement reasoning, and compliant marketing copywriting. The establishment of CUFEInse not only fills the gap in professional evaluation benchmarks for the insurance field, providing academia and industry with a professional, systematic, and authoritative evaluation tool, but also its construction concept and methodology offer important references for the evaluation paradigm of large models in vertical fields, serving as an authoritative reference for academic model optimization and industrial model selection. Finally, the paper looks forward to the future iteration direction of the evaluation benchmark and the core development direction of "domain adaptation + reasoning enhancement" for insurance large models.
Generative World Modelling for Humanoids: 1X World Model Challenge Technical Report
Oct 08, 2025



Abstract:World models are a powerful paradigm in AI and robotics, enabling agents to reason about the future by predicting visual observations or compact latent states. The 1X World Model Challenge introduces an open-source benchmark of real-world humanoid interaction, with two complementary tracks: sampling, focused on forecasting future image frames, and compression, focused on predicting future discrete latent codes. For the sampling track, we adapt the video generation foundation model Wan-2.2 TI2V-5B to video-state-conditioned future frame prediction. We condition the video generation on robot states using AdaLN-Zero, and further post-train the model using LoRA. For the compression track, we train a Spatio-Temporal Transformer model from scratch. Our models achieve 23.0 dB PSNR in the sampling task and a Top-500 CE of 6.6386 in the compression task, securing 1st place in both challenges.
EasySize: Elastic Analog Circuit Sizing via LLM-Guided Heuristic Search
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Analog circuit design is a time-consuming, experience-driven task in chip development. Despite advances in AI, developing universal, fast, and stable gate sizing methods for analog circuits remains a significant challenge. Recent approaches combine Large Language Models (LLMs) with heuristic search techniques to enhance generalizability, but they often depend on large model sizes and lack portability across different technology nodes. To overcome these limitations, we propose EasySize, the first lightweight gate sizing framework based on a finetuned Qwen3-8B model, designed for universal applicability across process nodes, design specifications, and circuit topologies. EasySize exploits the varying Ease of Attainability (EOA) of performance metrics to dynamically construct task-specific loss functions, enabling efficient heuristic search through global Differential Evolution (DE) and local Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) within a feedback-enhanced flow. Although finetuned solely on 350nm node data, EasySize achieves strong performance on 5 operational amplifier (Op-Amp) netlists across 180nm, 45nm, and 22nm technology nodes without additional targeted training, and outperforms AutoCkt, a widely-used Reinforcement Learning based sizing framework, on 86.67\% of tasks with more than 96.67\% of simulation resources reduction. We argue that EasySize can significantly reduce the reliance on human expertise and computational resources in gate sizing, thereby accelerating and simplifying the analog circuit design process. EasySize will be open-sourced at a later date.
Slot Attention with Re-Initialization and Self-Distillation
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:Unlike popular solutions based on dense feature maps, Object-Centric Learning (OCL) represents visual scenes as sub-symbolic object-level feature vectors, termed slots, which are highly versatile for tasks involving visual modalities. OCL typically aggregates object superpixels into slots by iteratively applying competitive cross attention, known as Slot Attention, with the slots as the query. However, once initialized, these slots are reused naively, causing redundant slots to compete with informative ones for representing objects. This often results in objects being erroneously segmented into parts. Additionally, mainstream methods derive supervision signals solely from decoding slots into the input's reconstruction, overlooking potential supervision based on internal information. To address these issues, we propose Slot Attention with re-Initialization and self-Distillation (DIAS): $\emph{i)}$ We reduce redundancy in the aggregated slots and re-initialize extra aggregation to update the remaining slots; $\emph{ii)}$ We drive the bad attention map at the first aggregation iteration to approximate the good at the last iteration to enable self-distillation. Experiments demonstrate that DIAS achieves state-of-the-art on OCL tasks like object discovery and recognition, while also improving advanced visual prediction and reasoning. Our code is available on https://github.com/Genera1Z/DIAS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge