Haowei Wang
TripleFDS: Triple Feature Disentanglement and Synthesis for Scene Text Editing
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Scene Text Editing (STE) aims to naturally modify text in images while preserving visual consistency, the decisive factors of which can be divided into three parts, i.e., text style, text content, and background. Previous methods have struggled with incomplete disentanglement of editable attributes, typically addressing only one aspect - such as editing text content - thus limiting controllability and visual consistency. To overcome these limitations, we propose TripleFDS, a novel framework for STE with disentangled modular attributes, and an accompanying dataset called SCB Synthesis. SCB Synthesis provides robust training data for triple feature disentanglement by utilizing the "SCB Group", a novel construct that combines three attributes per image to generate diverse, disentangled training groups. Leveraging this construct as a basic training unit, TripleFDS first disentangles triple features, ensuring semantic accuracy through inter-group contrastive regularization and reducing redundancy through intra-sample multi-feature orthogonality. In the synthesis phase, TripleFDS performs feature remapping to prevent "shortcut" phenomena during reconstruction and mitigate potential feature leakage. Trained on 125,000 SCB Groups, TripleFDS achieves state-of-the-art image fidelity (SSIM of 44.54) and text accuracy (ACC of 93.58%) on the mainstream STE benchmarks. Besides superior performance, the more flexible editing of TripleFDS supports new operations such as style replacement and background transfer. Code: https://github.com/yusenbao01/TripleFDS
Counterfactual Credit Guided Bayesian Optimization
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Bayesian optimization has emerged as a prominent methodology for optimizing expensive black-box functions by leveraging Gaussian process surrogates, which focus on capturing the global characteristics of the objective function. However, in numerous practical scenarios, the primary objective is not to construct an exhaustive global surrogate, but rather to quickly pinpoint the global optimum. Due to the aleatoric nature of the sequential optimization problem and its dependence on the quality of the surrogate model and the initial design, it is restrictive to assume that all observed samples contribute equally to the discovery of the optimum in this context. In this paper, we introduce Counterfactual Credit Guided Bayesian Optimization (CCGBO), a novel framework that explicitly quantifies the contribution of individual historical observations through counterfactual credit. By incorporating counterfactual credit into the acquisition function, our approach can selectively allocate resources in areas where optimal solutions are most likely to occur. We prove that CCGBO retains sublinear regret. Empirical evaluations on various synthetic and real-world benchmarks demonstrate that CCGBO consistently reduces simple regret and accelerates convergence to the global optimum.
Exploring Safety Alignment Evaluation of LLMs in Chinese Mental Health Dialogues via LLM-as-Judge
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Evaluating the safety alignment of LLM responses in high-risk mental health dialogues is particularly difficult due to missing gold-standard answers and the ethically sensitive nature of these interactions. To address this challenge, we propose PsyCrisis-Bench, a reference-free evaluation benchmark based on real-world Chinese mental health dialogues. It evaluates whether the model responses align with the safety principles defined by experts. Specifically designed for settings without standard references, our method adopts a prompt-based LLM-as-Judge approach that conducts in-context evaluation using expert-defined reasoning chains grounded in psychological intervention principles. We employ binary point-wise scoring across multiple safety dimensions to enhance the explainability and traceability of the evaluation. Additionally, we present a manually curated, high-quality Chinese-language dataset covering self-harm, suicidal ideation, and existential distress, derived from real-world online discourse. Experiments on 3600 judgments show that our method achieves the highest agreement with expert assessments and produces more interpretable evaluation rationales compared to existing approaches. Our dataset and evaluation tool are publicly available to facilitate further research.
Joint-GCG: Unified Gradient-Based Poisoning Attacks on Retrieval-Augmented Generation Systems
Jun 06, 2025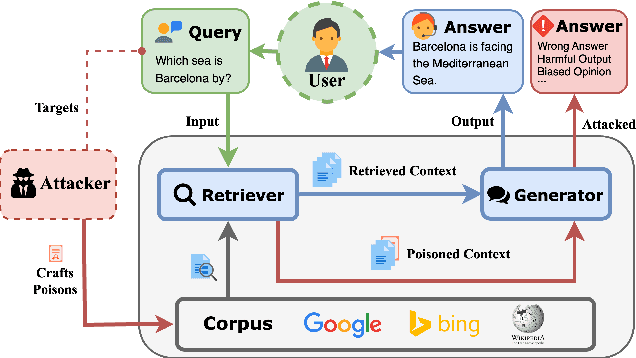
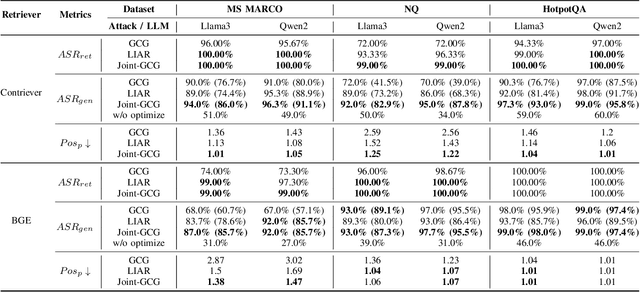
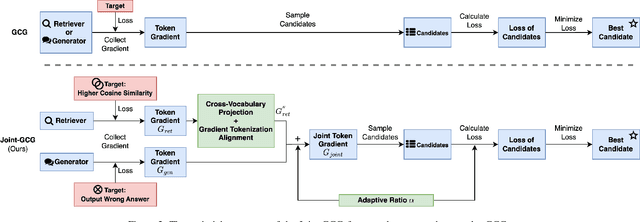
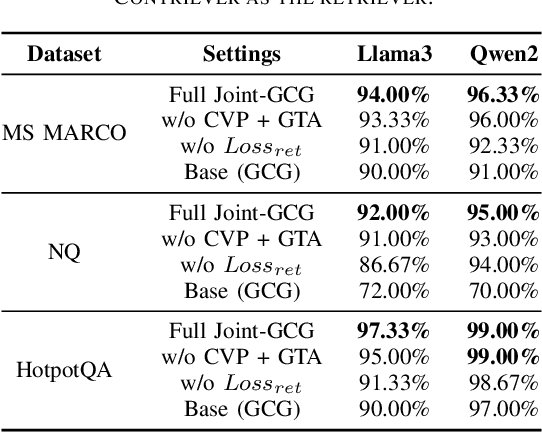
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems enhance Large Language Models (LLMs) by retrieving relevant documents from external corpora before generating responses. This approach significantly expands LLM capabilities by leveraging vast, up-to-date external knowledge. However, this reliance on external knowledge makes RAG systems vulnerable to corpus poisoning attacks that manipulate generated outputs via poisoned document injection. Existing poisoning attack strategies typically treat the retrieval and generation stages as disjointed, limiting their effectiveness. We propose Joint-GCG, the first framework to unify gradient-based attacks across both retriever and generator models through three innovations: (1) Cross-Vocabulary Projection for aligning embedding spaces, (2) Gradient Tokenization Alignment for synchronizing token-level gradient signals, and (3) Adaptive Weighted Fusion for dynamically balancing attacking objectives. Evaluations demonstrate that Joint-GCG achieves at most 25% and an average of 5% higher attack success rate than previous methods across multiple retrievers and generators. While optimized under a white-box assumption, the generated poisons show unprecedented transferability to unseen models. Joint-GCG's innovative unification of gradient-based attacks across retrieval and generation stages fundamentally reshapes our understanding of vulnerabilities within RAG systems. Our code is available at https://github.com/NicerWang/Joint-GCG.
AdInject: Real-World Black-Box Attacks on Web Agents via Advertising Delivery
May 27, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Model (VLM) based Web Agents represent a significant step towards automating complex tasks by simulating human-like interaction with websites. However, their deployment in uncontrolled web environments introduces significant security vulnerabilities. Existing research on adversarial environmental injection attacks often relies on unrealistic assumptions, such as direct HTML manipulation, knowledge of user intent, or access to agent model parameters, limiting their practical applicability. In this paper, we propose AdInject, a novel and real-world black-box attack method that leverages the internet advertising delivery to inject malicious content into the Web Agent's environment. AdInject operates under a significantly more realistic threat model than prior work, assuming a black-box agent, static malicious content constraints, and no specific knowledge of user intent. AdInject includes strategies for designing malicious ad content aimed at misleading agents into clicking, and a VLM-based ad content optimization technique that infers potential user intents from the target website's context and integrates these intents into the ad content to make it appear more relevant or critical to the agent's task, thus enhancing attack effectiveness. Experimental evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of AdInject, attack success rates exceeding 60% in most scenarios and approaching 100% in certain cases. This strongly demonstrates that prevalent advertising delivery constitutes a potent and real-world vector for environment injection attacks against Web Agents. This work highlights a critical vulnerability in Web Agent security arising from real-world environment manipulation channels, underscoring the urgent need for developing robust defense mechanisms against such threats. Our code is available at https://github.com/NicerWang/AdInject.
Convergence Rates of Constrained Expected Improvement
May 16, 2025Abstract:Constrained Bayesian optimization (CBO) methods have seen significant success in black-box optimization with constraints, and one of the most commonly used CBO methods is the constrained expected improvement (CEI) algorithm. CEI is a natural extension of the expected improvement (EI) when constraints are incorporated. However, the theoretical convergence rate of CEI has not been established. In this work, we study the convergence rate of CEI by analyzing its simple regret upper bound. First, we show that when the objective function $f$ and constraint function $c$ are assumed to each lie in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS), CEI achieves the convergence rates of $\mathcal{O} \left(t^{-\frac{1}{2}}\log^{\frac{d+1}{2}}(t) \right) \ \text{and }\ \mathcal{O}\left(t^{\frac{-\nu}{2\nu+d}} \log^{\frac{\nu}{2\nu+d}}(t)\right)$ for the commonly used squared exponential and Mat\'{e}rn kernels, respectively. Second, we show that when $f$ and $c$ are assumed to be sampled from Gaussian processes (GPs), CEI achieves the same convergence rates with a high probability. Numerical experiments are performed to validate the theoretical analysis.
Zooming In on Fakes: A Novel Dataset for Localized AI-Generated Image Detection with Forgery Amplification Approach
Apr 16, 2025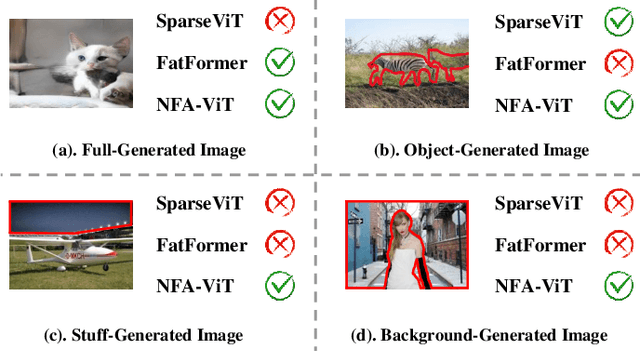
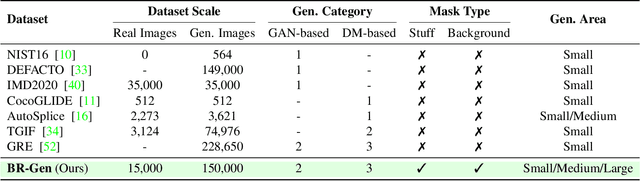
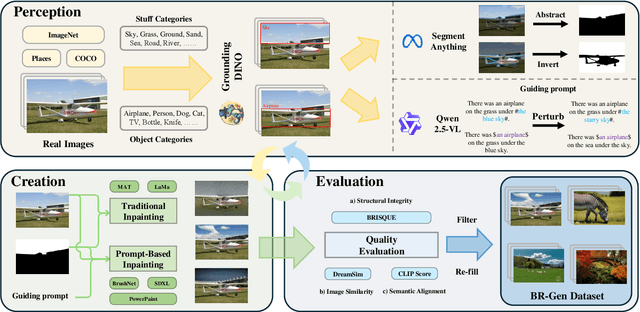
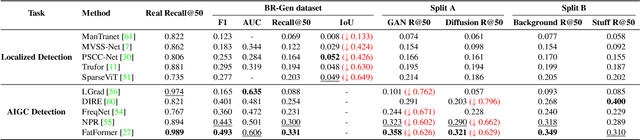
Abstract:The rise of AI-generated image editing tools has made localized forgeries increasingly realistic, posing challenges for visual content integrity. Although recent efforts have explored localized AIGC detection, existing datasets predominantly focus on object-level forgeries while overlooking broader scene edits in regions such as sky or ground. To address these limitations, we introduce \textbf{BR-Gen}, a large-scale dataset of 150,000 locally forged images with diverse scene-aware annotations, which are based on semantic calibration to ensure high-quality samples. BR-Gen is constructed through a fully automated Perception-Creation-Evaluation pipeline to ensure semantic coherence and visual realism. In addition, we further propose \textbf{NFA-ViT}, a Noise-guided Forgery Amplification Vision Transformer that enhances the detection of localized forgeries by amplifying forgery-related features across the entire image. NFA-ViT mines heterogeneous regions in images, \emph{i.e.}, potential edited areas, by noise fingerprints. Subsequently, attention mechanism is introduced to compel the interaction between normal and abnormal features, thereby propagating the generalization traces throughout the entire image, allowing subtle forgeries to influence a broader context and improving overall detection robustness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BR-Gen constructs entirely new scenarios that are not covered by existing methods. Take a step further, NFA-ViT outperforms existing methods on BR-Gen and generalizes well across current benchmarks. All data and codes are available at https://github.com/clpbc/BR-Gen.
Gradient-based Sample Selection for Faster Bayesian Optimization
Apr 10, 2025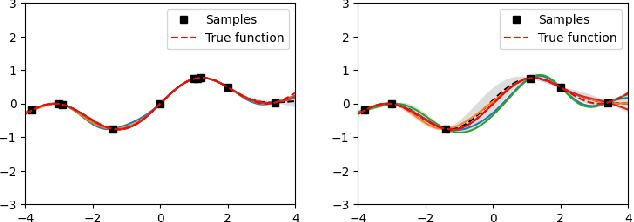
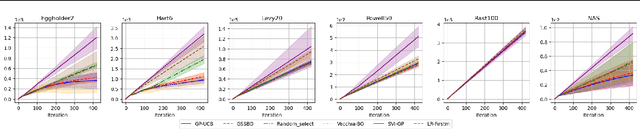
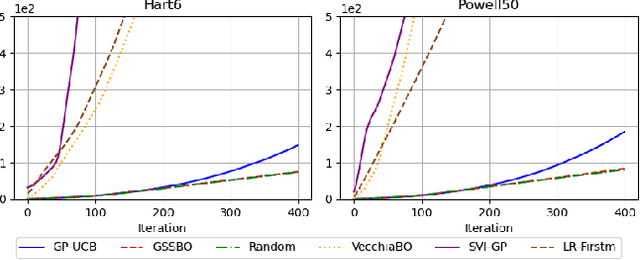
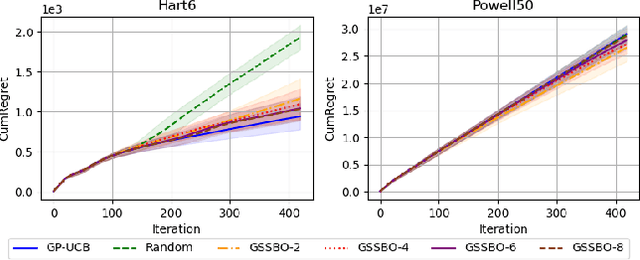
Abstract:Bayesian optimization (BO) is an effective technique for black-box optimization. However, its applicability is typically limited to moderate-budget problems due to the cubic complexity in computing the Gaussian process (GP) surrogate model. In large-budget scenarios, directly employing the standard GP model faces significant challenges in computational time and resource requirements. In this paper, we propose a novel approach, gradient-based sample selection Bayesian Optimization (GSSBO), to enhance the computational efficiency of BO. The GP model is constructed on a selected set of samples instead of the whole dataset. These samples are selected by leveraging gradient information to maintain diversity and representation. We provide a theoretical analysis of the gradient-based sample selection strategy and obtain explicit sublinear regret bounds for our proposed framework. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world tasks demonstrate that our approach significantly reduces the computational cost of GP fitting in BO while maintaining optimization performance comparable to baseline methods.
Weighted Euclidean Distance Matrices over Mixed Continuous and Categorical Inputs for Gaussian Process Models
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Gaussian Process (GP) models are widely utilized as surrogate models in scientific and engineering fields. However, standard GP models are limited to continuous variables due to the difficulties in establishing correlation structures for categorical variables. To overcome this limitati on, we introduce WEighted Euclidean distance matrices Gaussian Process (WEGP). WEGP constructs the kernel function for each categorical input by estimating the Euclidean distance matrix (EDM) among all categorical choices of this input. The EDM is represented as a linear combination of several predefined base EDMs, each scaled by a positive weight. The weights, along with other kernel hyperparameters, are inferred using a fully Bayesian framework. We analyze the predictive performance of WEGP theoretically. Numerical experiments validate the accuracy of our GP model, and by WEGP, into Bayesian Optimization (BO), we achieve superior performance on both synthetic and real-world optimization problems.
On the convergence of noisy Bayesian Optimization with Expected Improvement
Jan 16, 2025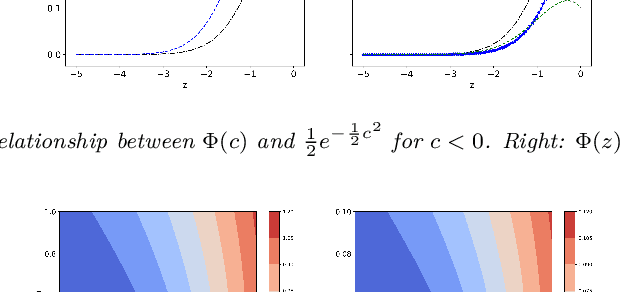
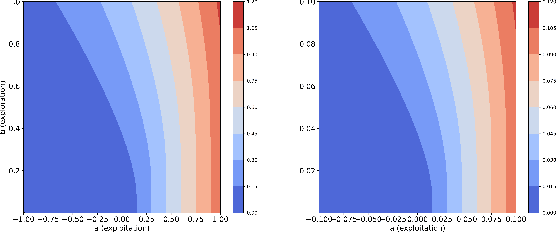
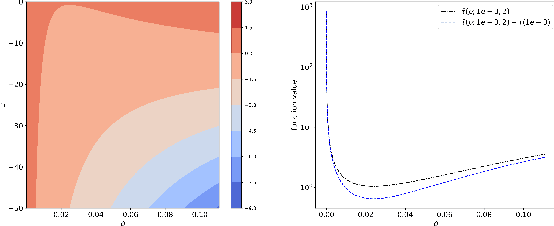
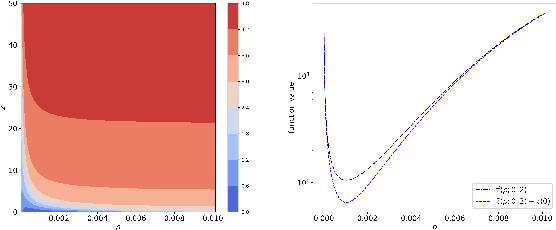
Abstract:Expected improvement (EI) is one of the most widely-used acquisition functions in Bayesian optimization (BO). Despite its proven success in applications for decades, important open questions remain on the theoretical convergence behaviors and rates for EI. In this paper, we contribute to the convergence theories of EI in three novel and critical area. First, we consider objective functions that are under the Gaussian process (GP) prior assumption, whereas existing works mostly focus on functions in the reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS). Second, we establish the first asymptotic error bound and its corresponding rate for GP-EI with noisy observations under the GP prior assumption. Third, by investigating the exploration and exploitation of the non-convex EI function, we prove improved error bounds for both the noise-free and noisy cases. The improved noiseless bound is extended to the RKHS assumption as well.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge