Qiyu Wei
MemAdapter: Fast Alignment across Agent Memory Paradigms via Generative Subgraph Retrieval
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Memory mechanism is a core component of LLM-based agents, enabling reasoning and knowledge discovery over long-horizon contexts. Existing agent memory systems are typically designed within isolated paradigms (e.g., explicit, parametric, or latent memory) with tightly coupled retrieval methods that hinder cross-paradigm generalization and fusion. In this work, we take a first step toward unifying heterogeneous memory paradigms within a single memory system. We propose MemAdapter, a memory retrieval framework that enables fast alignment across agent memory paradigms. MemAdapter adopts a two-stage training strategy: (1) training a generative subgraph retriever from the unified memory space, and (2) adapting the retriever to unseen memory paradigms by training a lightweight alignment module through contrastive learning. This design improves the flexibility for memory retrieval and substantially reduces alignment cost across paradigms. Comprehensive experiments on three public evaluation benchmarks demonstrate that the generative subgraph retriever consistently outperforms five strong agent memory systems across three memory paradigms and agent model scales. Notably, MemAdapter completes cross-paradigm alignment within 13 minutes on a single GPU, achieving superior performance over original memory retrievers with less than 5% of training compute. Furthermore, MemAdapter enables effective zero-shot fusion across memory paradigms, highlighting its potential as a plug-and-play solution for agent memory systems.
Implicit Graph, Explicit Retrieval: Towards Efficient and Interpretable Long-horizon Memory for Large Language Models
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Long-horizon applications increasingly require large language models (LLMs) to answer queries when relevant evidence is sparse and dispersed across very long contexts. Existing memory systems largely follow two paradigms: explicit structured memories offer interpretability but often become brittle under long-context overload, while latent memory mechanisms are efficient and stable yet difficult to inspect. We propose LatentGraphMem, a memory framework that combines implicit graph memory with explicit subgraph retrieval. LatentGraphMem stores a graph-structured memory in latent space for stability and efficiency, and exposes a task-specific subgraph retrieval interface that returns a compact symbolic subgraph under a fixed budget for downstream reasoning and human inspection. During training, an explicit graph view is materialized to interface with a frozen reasoner for question-answering supervision. At inference time, retrieval is performed in latent space and only the retrieved subgraph is externalized. Experiments on long-horizon benchmarks across multiple model scales show that LatentGraphMem consistently outperforms representative explicit-graph and latent-memory baselines, while enabling parameter-efficient adaptation and flexible scaling to larger reasoners without introducing large symbolic artifacts.
Counterfactual Credit Guided Bayesian Optimization
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Bayesian optimization has emerged as a prominent methodology for optimizing expensive black-box functions by leveraging Gaussian process surrogates, which focus on capturing the global characteristics of the objective function. However, in numerous practical scenarios, the primary objective is not to construct an exhaustive global surrogate, but rather to quickly pinpoint the global optimum. Due to the aleatoric nature of the sequential optimization problem and its dependence on the quality of the surrogate model and the initial design, it is restrictive to assume that all observed samples contribute equally to the discovery of the optimum in this context. In this paper, we introduce Counterfactual Credit Guided Bayesian Optimization (CCGBO), a novel framework that explicitly quantifies the contribution of individual historical observations through counterfactual credit. By incorporating counterfactual credit into the acquisition function, our approach can selectively allocate resources in areas where optimal solutions are most likely to occur. We prove that CCGBO retains sublinear regret. Empirical evaluations on various synthetic and real-world benchmarks demonstrate that CCGBO consistently reduces simple regret and accelerates convergence to the global optimum.
Gradient-based Sample Selection for Faster Bayesian Optimization
Apr 10, 2025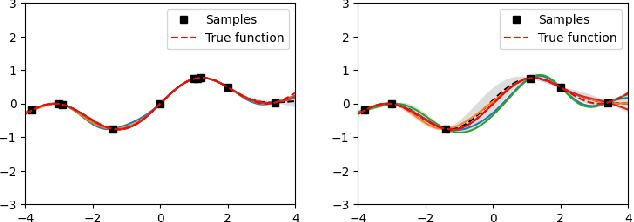
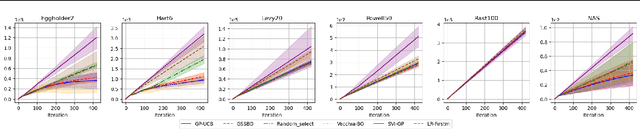
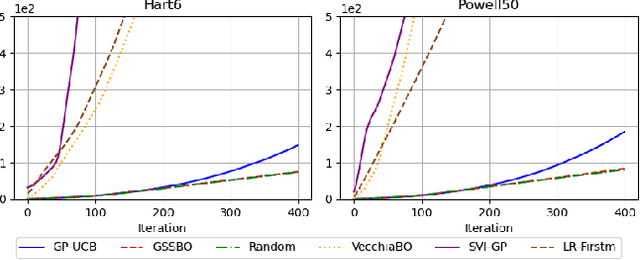
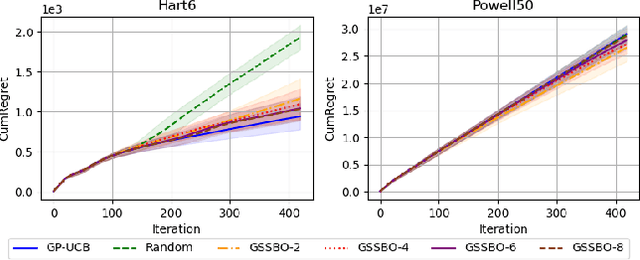
Abstract:Bayesian optimization (BO) is an effective technique for black-box optimization. However, its applicability is typically limited to moderate-budget problems due to the cubic complexity in computing the Gaussian process (GP) surrogate model. In large-budget scenarios, directly employing the standard GP model faces significant challenges in computational time and resource requirements. In this paper, we propose a novel approach, gradient-based sample selection Bayesian Optimization (GSSBO), to enhance the computational efficiency of BO. The GP model is constructed on a selected set of samples instead of the whole dataset. These samples are selected by leveraging gradient information to maintain diversity and representation. We provide a theoretical analysis of the gradient-based sample selection strategy and obtain explicit sublinear regret bounds for our proposed framework. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world tasks demonstrate that our approach significantly reduces the computational cost of GP fitting in BO while maintaining optimization performance comparable to baseline methods.
SynGraph: A Dynamic Graph-LLM Synthesis Framework for Sparse Streaming User Sentiment Modeling
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:User reviews on e-commerce platforms exhibit dynamic sentiment patterns driven by temporal and contextual factors. Traditional sentiment analysis methods focus on static reviews, failing to capture the evolving temporal relationship between user sentiment rating and textual content. Sentiment analysis on streaming reviews addresses this limitation by modeling and predicting the temporal evolution of user sentiments. However, it suffers from data sparsity, manifesting in temporal, spatial, and combined forms. In this paper, we introduce SynGraph, a novel framework designed to address data sparsity in sentiment analysis on streaming reviews. SynGraph alleviates data sparsity by categorizing users into mid-tail, long-tail, and extreme scenarios and incorporating LLM-augmented enhancements within a dynamic graph-based structure. Experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate its effectiveness in addressing sparsity and improving sentiment modeling in streaming reviews.
Utilizing the Mean Teacher with Supcontrast Loss for Wafer Pattern Recognition
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:The patterns on wafer maps play a crucial role in helping engineers identify the causes of production issues during semiconductor manufacturing. In order to reduce costs and improve accuracy, automation technology is essential, and recent developments in deep learning have led to impressive results in wafer map pattern recognition. In this context, inspired by the effectiveness of semi-supervised learning and contrastive learning methods, we introduce an innovative approach that integrates the Mean Teacher framework with the supervised contrastive learning loss for enhanced wafer map pattern recognition. Our methodology not only addresses the nuances of wafer patterns but also tackles challenges arising from limited labeled data. To further refine the process, we address data imbalance in the wafer dataset by employing SMOTE and under-sampling techniques. We conduct a comprehensive analysis of our proposed method and demonstrate its effectiveness through experiments using real-world dataset WM811K obtained from semiconductor manufacturers. Compared to the baseline method, our method has achieved 5.46%, 6.68%, 5.42%, and 4.53% improvements in Accuracy, Precision, Recall, and F1 score, respectively.
A Deeply Supervised Semantic Segmentation Method Based on GAN
Oct 06, 2023Abstract:In recent years, the field of intelligent transportation has witnessed rapid advancements, driven by the increasing demand for automation and efficiency in transportation systems. Traffic safety, one of the tasks integral to intelligent transport systems, requires accurately identifying and locating various road elements, such as road cracks, lanes, and traffic signs. Semantic segmentation plays a pivotal role in achieving this task, as it enables the partition of images into meaningful regions with accurate boundaries. In this study, we propose an improved semantic segmentation model that combines the strengths of adversarial learning with state-of-the-art semantic segmentation techniques. The proposed model integrates a generative adversarial network (GAN) framework into the traditional semantic segmentation model, enhancing the model's performance in capturing complex and subtle features in transportation images. The effectiveness of our approach is demonstrated by a significant boost in performance on the road crack dataset compared to the existing methods, \textit{i.e.,} SEGAN. This improvement can be attributed to the synergistic effect of adversarial learning and semantic segmentation, which leads to a more refined and accurate representation of road structures and conditions. The enhanced model not only contributes to better detection of road cracks but also to a wide range of applications in intelligent transportation, such as traffic sign recognition, vehicle detection, and lane segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge