Nan Wang
University of California, Santa Cruz
Can Vision-Language Models Handle Long-Context Code? An Empirical Study on Visual Compression
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle with long-context code due to window limitations. Existing textual code compression methods mitigate this via selective filtering but often disrupt dependency closure, causing semantic fragmentation. To address this, we introduce LongCodeOCR, a visual compression framework that renders code into compressed two-dimensional image sequences for Vision-Language Models (VLMs). By preserving a global view, this approach avoids the dependency breakage inherent in filtering. We systematically evaluate LongCodeOCR against the state-of-the-art LongCodeZip across four benchmarks spanning code summarization, code question answering, and code completion. Our results demonstrate that visual code compression serves as a viable alternative for tasks requiring global understanding. At comparable compression ratios ($\sim$1.7$\times$), LongCodeOCR improves CompScore on Long Module Summarization by 36.85 points over LongCodeZip. At a 1M-token context length with Glyph (a specialized 9B VLM), LongCodeOCR maintains higher accuracy than LongCodeZip while operating at about 4$\times$ higher compression. Moreover, compared with LongCodeZip, LongCodeOCR drastically reduces compression-stage overhead (reducing latency from $\sim$4.3 hours to $\sim$1 minute at 1M tokens). Finally, our results characterize a fundamental coverage--fidelity trade-off: visual code compression retains broader context coverage to support global dependencies, yet faces fidelity bottlenecks on exactness-critical tasks; by contrast, textual code compression preserves symbol-level precision while sacrificing structural coverage.
Innovator-VL: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Scientific Discovery
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:We present Innovator-VL, a scientific multimodal large language model designed to advance understanding and reasoning across diverse scientific domains while maintaining excellent performance on general vision tasks. Contrary to the trend of relying on massive domain-specific pretraining and opaque pipelines, our work demonstrates that principled training design and transparent methodology can yield strong scientific intelligence with substantially reduced data requirements. (i) First, we provide a fully transparent, end-to-end reproducible training pipeline, covering data collection, cleaning, preprocessing, supervised fine-tuning, reinforcement learning, and evaluation, along with detailed optimization recipes. This facilitates systematic extension by the community. (ii) Second, Innovator-VL exhibits remarkable data efficiency, achieving competitive performance on various scientific tasks using fewer than five million curated samples without large-scale pretraining. These results highlight that effective reasoning can be achieved through principled data selection rather than indiscriminate scaling. (iii) Third, Innovator-VL demonstrates strong generalization, achieving competitive performance on general vision, multimodal reasoning, and scientific benchmarks. This indicates that scientific alignment can be integrated into a unified model without compromising general-purpose capabilities. Our practices suggest that efficient, reproducible, and high-performing scientific multimodal models can be built even without large-scale data, providing a practical foundation for future research.
Mimic Human Cognition, Master Multi-Image Reasoning: A Meta-Action Framework for Enhanced Visual Understanding
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel at single-image understanding, they exhibit significantly degraded performance in multi-image reasoning scenarios. Multi-image reasoning presents fundamental challenges including complex inter-relationships between images and scattered critical information across image sets. Inspired by human cognitive processes, we propose the Cognition-Inspired Meta-Action Framework (CINEMA), a novel approach that decomposes multi-image reasoning into five structured meta-actions: Global, Focus, Hint, Think, and Answer which explicitly modeling the sequential cognitive steps humans naturally employ. For cold-start training, we introduce a Retrieval-Based Tree Sampling strategy that generates high-quality meta-action trajectories to bootstrap the model with reasoning patterns. During reinforcement learning, we adopt a two-stage paradigm: an exploration phase with Diversity-Preserving Strategy to avoid entropy collapse, followed by an annealed exploitation phase with DAPO to gradually strengthen exploitation. To train our model, we construct a dataset of 57k cold-start and 58k reinforcement learning instances spanning multi-image, multi-frame, and single-image tasks. We conduct extensive evaluations on multi-image reasoning benchmarks, video understanding benchmarks, and single-image benchmarks, achieving competitive state-of-the-art performance on several key benchmarks. Our model surpasses GPT-4o on the MUIR and MVMath benchmarks and notably outperforms specialized video reasoning models on video understanding benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness and generalizability of our human cognition-inspired reasoning framework.
Advanced Global Wildfire Activity Modeling with Hierarchical Graph ODE
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Wildfires, as an integral component of the Earth system, are governed by a complex interplay of atmospheric, oceanic, and terrestrial processes spanning a vast range of spatiotemporal scales. Modeling their global activity on large timescales is therefore a critical yet challenging task. While deep learning has recently achieved significant breakthroughs in global weather forecasting, its potential for global wildfire behavior prediction remains underexplored. In this work, we reframe this problem and introduce the Hierarchical Graph ODE (HiGO), a novel framework designed to learn the multi-scale, continuous-time dynamics of wildfires. Specifically, we represent the Earth system as a multi-level graph hierarchy and propose an adaptive filtering message passing mechanism for both intra- and inter-level information flow, enabling more effective feature extraction and fusion. Furthermore, we incorporate GNN-parameterized Neural ODE modules at multiple levels to explicitly learn the continuous dynamics inherent to each scale. Through extensive experiments on the SeasFire Cube dataset, we demonstrate that HiGO significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on long-range wildfire forecasting. Moreover, its continuous-time predictions exhibit strong observational consistency, highlighting its potential for real-world applications.
Diffusion Knows Transparency: Repurposing Video Diffusion for Transparent Object Depth and Normal Estimation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Transparent objects remain notoriously hard for perception systems: refraction, reflection and transmission break the assumptions behind stereo, ToF and purely discriminative monocular depth, causing holes and temporally unstable estimates. Our key observation is that modern video diffusion models already synthesize convincing transparent phenomena, suggesting they have internalized the optical rules. We build TransPhy3D, a synthetic video corpus of transparent/reflective scenes: 11k sequences rendered with Blender/Cycles. Scenes are assembled from a curated bank of category-rich static assets and shape-rich procedural assets paired with glass/plastic/metal materials. We render RGB + depth + normals with physically based ray tracing and OptiX denoising. Starting from a large video diffusion model, we learn a video-to-video translator for depth (and normals) via lightweight LoRA adapters. During training we concatenate RGB and (noisy) depth latents in the DiT backbone and co-train on TransPhy3D and existing frame-wise synthetic datasets, yielding temporally consistent predictions for arbitrary-length input videos. The resulting model, DKT, achieves zero-shot SOTA on real and synthetic video benchmarks involving transparency: ClearPose, DREDS (CatKnown/CatNovel), and TransPhy3D-Test. It improves accuracy and temporal consistency over strong image/video baselines, and a normal variant sets the best video normal estimation results on ClearPose. A compact 1.3B version runs at ~0.17 s/frame. Integrated into a grasping stack, DKT's depth boosts success rates across translucent, reflective and diffuse surfaces, outperforming prior estimators. Together, these results support a broader claim: "Diffusion knows transparency." Generative video priors can be repurposed, efficiently and label-free, into robust, temporally coherent perception for challenging real-world manipulation.
Fast Reconstruction of Motion-Corrupted Data with Mobile-GRAPPA: Motion and dB0 Inhomogeneity Correction Leveraging Efficient GRAPPA
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Advanced motion navigations now enable rapid tracking of subject motion and dB0-induced phase, but accurately incorporating this high-temporal-resolution information into SENSE (Aligned-SENSE) is often computationally prohibitive. We propose "Mobile-GRAPPA", a k-space "cleaning" approach that uses local GRAPPA operators to remove motion and dB0 related corruption so that the resulting data can be reconstructed with standard SENSE. We efficiently train a family of k-space-position-specific Mobile-GRAPPA kernels via a lightweight multilayer perceptron (MLP) and apply them across k-space to generate clean data. In experiments on highly motion-corrupted 1-mm whole-brain GRE (Tacq = 10 min; 1,620 motion/dB0 trackings) and EPTI (Tacq = 2 min; 544 trackings), Mobile-GRAPPA enabled accurate reconstruction with negligible time penalty, whereas full Aligned-SENSE was impractical (reconstruction times > 10 h for GRE and > 10 days for EPTI). These results show that Mobile-GRAPPA incorporates detailed motion and dB0 tracking into SENSE with minimal computational overhead, enabling fast, high-quality reconstructions of challenging data.
SciGPT: A Large Language Model for Scientific Literature Understanding and Knowledge Discovery
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Scientific literature is growing exponentially, creating a critical bottleneck for researchers to efficiently synthesize knowledge. While general-purpose Large Language Models (LLMs) show potential in text processing, they often fail to capture scientific domain-specific nuances (e.g., technical jargon, methodological rigor) and struggle with complex scientific tasks, limiting their utility for interdisciplinary research. To address these gaps, this paper presents SciGPT, a domain-adapted foundation model for scientific literature understanding and ScienceBench, an open source benchmark tailored to evaluate scientific LLMs. Built on the Qwen3 architecture, SciGPT incorporates three key innovations: (1) low-cost domain distillation via a two-stage pipeline to balance performance and efficiency; (2) a Sparse Mixture-of-Experts (SMoE) attention mechanism that cuts memory consumption by 55\% for 32,000-token long-document reasoning; and (3) knowledge-aware adaptation integrating domain ontologies to bridge interdisciplinary knowledge gaps. Experimental results on ScienceBench show that SciGPT outperforms GPT-4o in core scientific tasks including sequence labeling, generation, and inference. It also exhibits strong robustness in unseen scientific tasks, validating its potential to facilitate AI-augmented scientific discovery.
One View, Many Worlds: Single-Image to 3D Object Meets Generative Domain Randomization for One-Shot 6D Pose Estimation
Sep 09, 2025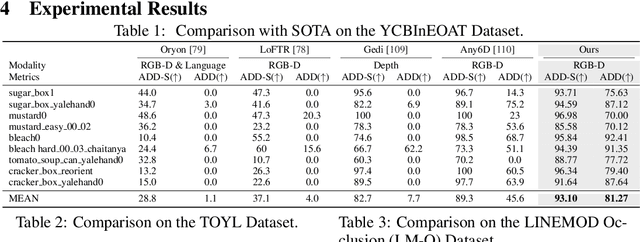
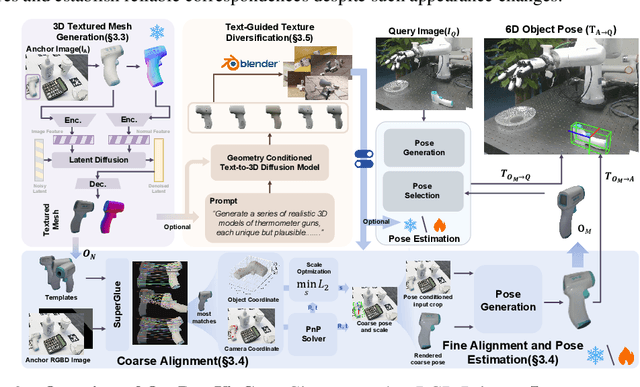
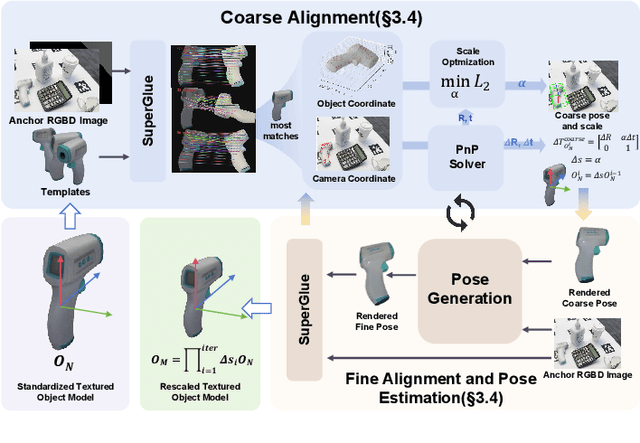
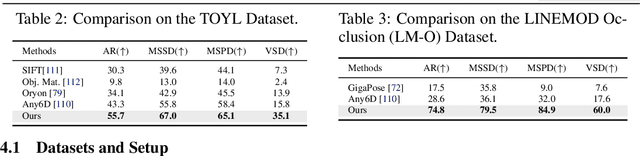
Abstract:Estimating the 6D pose of arbitrary unseen objects from a single reference image is critical for robotics operating in the long-tail of real-world instances. However, this setting is notoriously challenging: 3D models are rarely available, single-view reconstructions lack metric scale, and domain gaps between generated models and real-world images undermine robustness. We propose OnePoseViaGen, a pipeline that tackles these challenges through two key components. First, a coarse-to-fine alignment module jointly refines scale and pose by combining multi-view feature matching with render-and-compare refinement. Second, a text-guided generative domain randomization strategy diversifies textures, enabling effective fine-tuning of pose estimators with synthetic data. Together, these steps allow high-fidelity single-view 3D generation to support reliable one-shot 6D pose estimation. On challenging benchmarks (YCBInEOAT, Toyota-Light, LM-O), OnePoseViaGen achieves state-of-the-art performance far surpassing prior approaches. We further demonstrate robust dexterous grasping with a real robot hand, validating the practicality of our method in real-world manipulation. Project page: https://gzwsama.github.io/OnePoseviaGen.github.io/
zkUnlearner: A Zero-Knowledge Framework for Verifiable Unlearning with Multi-Granularity and Forgery-Resistance
Sep 08, 2025Abstract:As the demand for exercising the "right to be forgotten" grows, the need for verifiable machine unlearning has become increasingly evident to ensure both transparency and accountability. We present {\em zkUnlearner}, the first zero-knowledge framework for verifiable machine unlearning, specifically designed to support {\em multi-granularity} and {\em forgery-resistance}. First, we propose a general computational model that employs a {\em bit-masking} technique to enable the {\em selectivity} of existing zero-knowledge proofs of training for gradient descent algorithms. This innovation enables not only traditional {\em sample-level} unlearning but also more advanced {\em feature-level} and {\em class-level} unlearning. Our model can be translated to arithmetic circuits, ensuring compatibility with a broad range of zero-knowledge proof systems. Furthermore, our approach overcomes key limitations of existing methods in both efficiency and privacy. Second, forging attacks present a serious threat to the reliability of unlearning. Specifically, in Stochastic Gradient Descent optimization, gradients from unlearned data, or from minibatches containing it, can be forged using alternative data samples or minibatches that exclude it. We propose the first effective strategies to resist state-of-the-art forging attacks. Finally, we benchmark a zkSNARK-based instantiation of our framework and perform comprehensive performance evaluations to validate its practicality.
An Agentic Model Context Protocol Framework for Medical Concept Standardization
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:The Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership (OMOP) common data model (CDM) provides a standardized representation of heterogeneous health data to support large-scale, multi-institutional research. One critical step in data standardization using OMOP CDM is the mapping of source medical terms to OMOP standard concepts, a procedure that is resource-intensive and error-prone. While large language models (LLMs) have the potential to facilitate this process, their tendency toward hallucination makes them unsuitable for clinical deployment without training and expert validation. Here, we developed a zero-training, hallucination-preventive mapping system based on the Model Context Protocol (MCP), a standardized and secure framework allowing LLMs to interact with external resources and tools. The system enables explainable mapping and significantly improves efficiency and accuracy with minimal effort. It provides real-time vocabulary lookups and structured reasoning outputs suitable for immediate use in both exploratory and production environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge