Yanfei Wang
Uncertainty-Aware Machine-Learning Framework for Predicting Dislocation Plasticity and Stress-Strain Response in FCC Alloys
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:Machine learning has significantly advanced the understanding and application of structural materials, with an increasing emphasis on integrating existing data and quantifying uncertainties in predictive modeling. This study presents a comprehensive methodology utilizing a mixed density network (MDN) model, trained on extensive experimental data from literature. This approach uniquely predicts the distribution of dislocation density, inferred as a latent variable, and the resulting stress distribution at the grain level. The incorporation of statistical parameters of those predicted distributions into a dislocation-mediated plasticity model allows for accurate stress-strain predictions with explicit uncertainty quantification. This strategy not only improves the accuracy and reliability of mechanical property predictions but also plays a vital role in optimizing alloy design, thereby facilitating the development of new materials in a rapidly evolving industry.
scDrugMap: Benchmarking Large Foundation Models for Drug Response Prediction
May 08, 2025Abstract:Drug resistance presents a major challenge in cancer therapy. Single cell profiling offers insights into cellular heterogeneity, yet the application of large-scale foundation models for predicting drug response in single cell data remains underexplored. To address this, we developed scDrugMap, an integrated framework featuring both a Python command-line interface and a web server for drug response prediction. scDrugMap evaluates a wide range of foundation models, including eight single-cell models and two large language models, using a curated dataset of over 326,000 cells in the primary collection and 18,800 cells in the validation set, spanning 36 datasets and diverse tissue and cancer types. We benchmarked model performance under pooled-data and cross-data evaluation settings, employing both layer freezing and Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) fine-tuning strategies. In the pooled-data scenario, scFoundation achieved the best performance, with mean F1 scores of 0.971 (layer freezing) and 0.947 (fine-tuning), outperforming the lowest-performing model by over 50%. In the cross-data setting, UCE excelled post fine-tuning (mean F1: 0.774), while scGPT led in zero-shot learning (mean F1: 0.858). Overall, scDrugMap provides the first large-scale benchmark of foundation models for drug response prediction in single-cell data and serves as a user-friendly, flexible platform for advancing drug discovery and translational research.
SysNoise: Exploring and Benchmarking Training-Deployment System Inconsistency
Jul 01, 2023Abstract:Extensive studies have shown that deep learning models are vulnerable to adversarial and natural noises, yet little is known about model robustness on noises caused by different system implementations. In this paper, we for the first time introduce SysNoise, a frequently occurred but often overlooked noise in the deep learning training-deployment cycle. In particular, SysNoise happens when the source training system switches to a disparate target system in deployments, where various tiny system mismatch adds up to a non-negligible difference. We first identify and classify SysNoise into three categories based on the inference stage; we then build a holistic benchmark to quantitatively measure the impact of SysNoise on 20+ models, comprehending image classification, object detection, instance segmentation and natural language processing tasks. Our extensive experiments revealed that SysNoise could bring certain impacts on model robustness across different tasks and common mitigations like data augmentation and adversarial training show limited effects on it. Together, our findings open a new research topic and we hope this work will raise research attention to deep learning deployment systems accounting for model performance. We have open-sourced the benchmark and framework at https://modeltc.github.io/systemnoise_web.
* Proceedings of Machine Learning and Systems. 2023 Mar 18
Towards Unified INT8 Training for Convolutional Neural Network
Dec 29, 2019
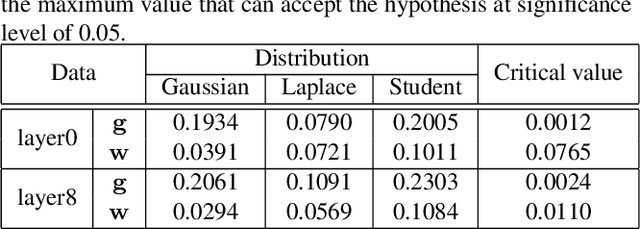
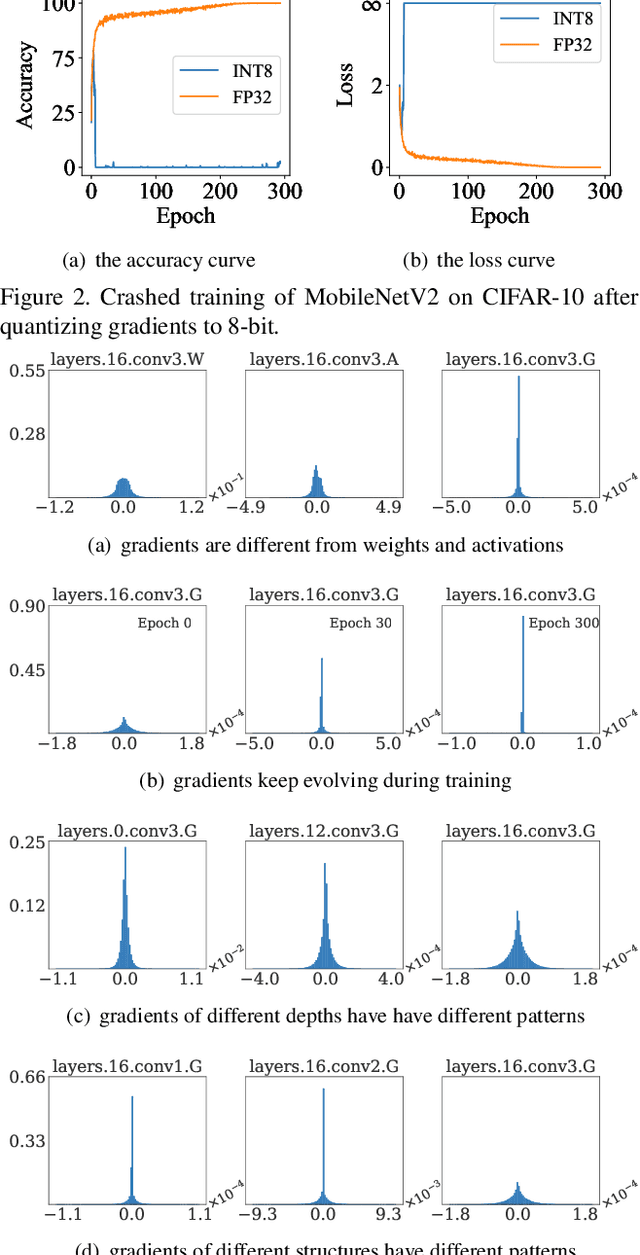

Abstract:Recently low-bit (e.g., 8-bit) network quantization has been extensively studied to accelerate the inference. Besides inference, low-bit training with quantized gradients can further bring more considerable acceleration, since the backward process is often computation-intensive. Unfortunately, the inappropriate quantization of backward propagation usually makes the training unstable and even crash. There lacks a successful unified low-bit training framework that can support diverse networks on various tasks. In this paper, we give an attempt to build a unified 8-bit (INT8) training framework for common convolutional neural networks from the aspects of both accuracy and speed. First, we empirically find the four distinctive characteristics of gradients, which provide us insightful clues for gradient quantization. Then, we theoretically give an in-depth analysis of the convergence bound and derive two principles for stable INT8 training. Finally, we propose two universal techniques, including Direction Sensitive Gradient Clipping that reduces the direction deviation of gradients and Deviation Counteractive Learning Rate Scaling that avoids illegal gradient update along the wrong direction. The experiments show that our unified solution promises accurate and efficient INT8 training for a variety of networks and tasks, including MobileNetV2, InceptionV3 and object detection that prior studies have never succeeded. Moreover, it enjoys a strong flexibility to run on off-the-shelf hardware, and reduces the training time by 22% on Pascal GPU without too much optimization effort. We believe that this pioneering study will help lead the community towards a fully unified INT8 training for convolutional neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge