Yilan Dong
School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, Department of Forensic and Neurodevelopmental Science, Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience, King's College London, London, United Kingdom
DanceChat: Large Language Model-Guided Music-to-Dance Generation
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Music-to-dance generation aims to synthesize human dance motion conditioned on musical input. Despite recent progress, significant challenges remain due to the semantic gap between music and dance motion, as music offers only abstract cues, such as melody, groove, and emotion, without explicitly specifying the physical movements. Moreover, a single piece of music can produce multiple plausible dance interpretations. This one-to-many mapping demands additional guidance, as music alone provides limited information for generating diverse dance movements. The challenge is further amplified by the scarcity of paired music and dance data, which restricts the model\^a\u{A}\'Zs ability to learn diverse dance patterns. In this paper, we introduce DanceChat, a Large Language Model (LLM)-guided music-to-dance generation approach. We use an LLM as a choreographer that provides textual motion instructions, offering explicit, high-level guidance for dance generation. This approach goes beyond implicit learning from music alone, enabling the model to generate dance that is both more diverse and better aligned with musical styles. Our approach consists of three components: (1) an LLM-based pseudo instruction generation module that produces textual dance guidance based on music style and structure, (2) a multi-modal feature extraction and fusion module that integrates music, rhythm, and textual guidance into a shared representation, and (3) a diffusion-based motion synthesis module together with a multi-modal alignment loss, which ensures that the generated dance is aligned with both musical and textual cues. Extensive experiments on AIST++ and human evaluations show that DanceChat outperforms state-of-the-art methods both qualitatively and quantitatively.
HandSplat: Embedding-Driven Gaussian Splatting for High-Fidelity Hand Rendering
Mar 18, 2025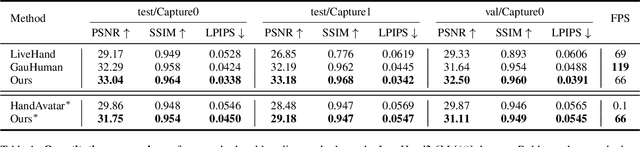
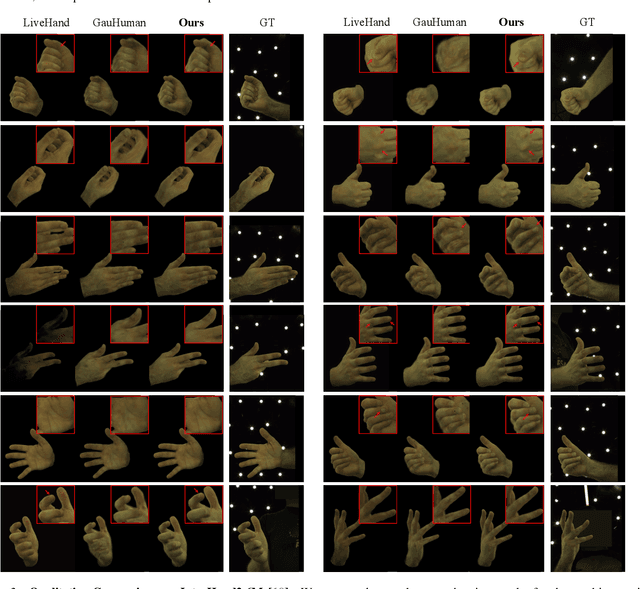
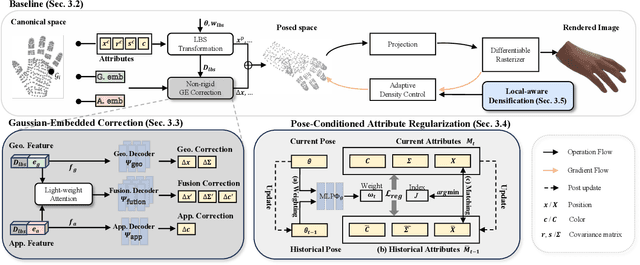
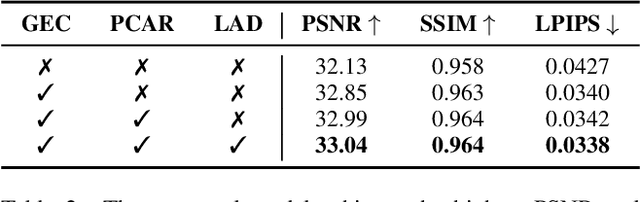

Abstract:Existing 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) methods for hand rendering rely on rigid skeletal motion with an oversimplified non-rigid motion model, which fails to capture fine geometric and appearance details. Additionally, they perform densification based solely on per-point gradients and process poses independently, ignoring spatial and temporal correlations. These limitations lead to geometric detail loss, temporal instability, and inefficient point distribution. To address these issues, we propose HandSplat, a novel Gaussian Splatting-based framework that enhances both fidelity and stability for hand rendering. To improve fidelity, we extend standard 3DGS attributes with implicit geometry and appearance embeddings for finer non-rigid motion modeling while preserving the static hand characteristic modeled by original 3DGS attributes. Additionally, we introduce a local gradient-aware densification strategy that dynamically refines Gaussian density in high-variation regions. To improve stability, we incorporate pose-conditioned attribute regularization to encourage attribute consistency across similar poses, mitigating temporal artifacts. Extensive experiments on InterHand2.6M demonstrate that HandSplat surpasses existing methods in fidelity and stability while achieving real-time performance. We will release the code and pre-trained models upon acceptance.
Automatic 8-tissue Segmentation for 6-month Infant Brains
Aug 27, 2024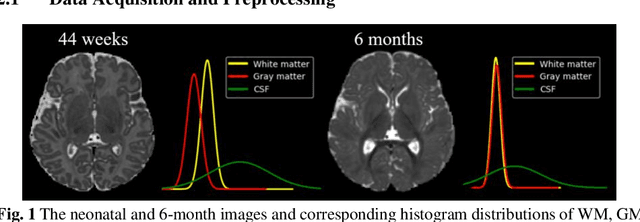
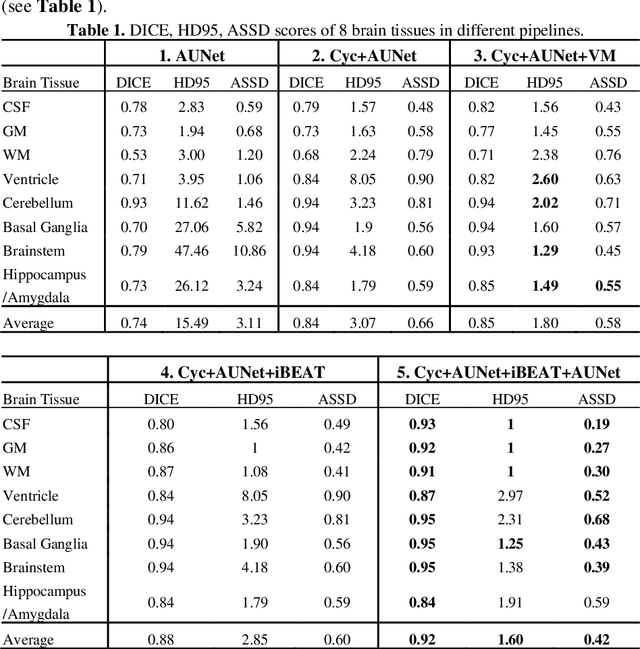
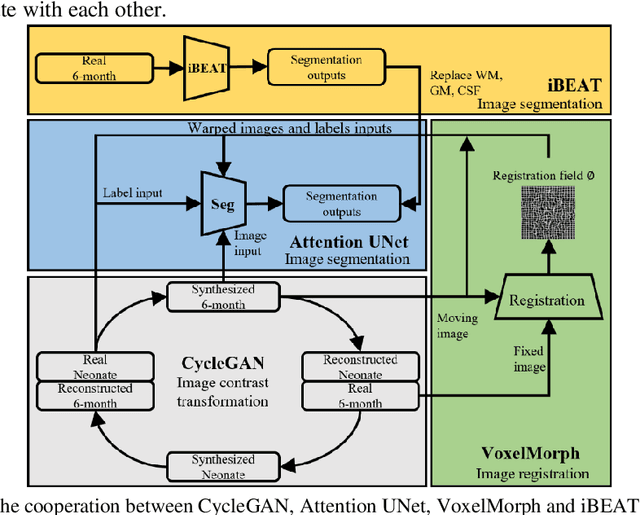
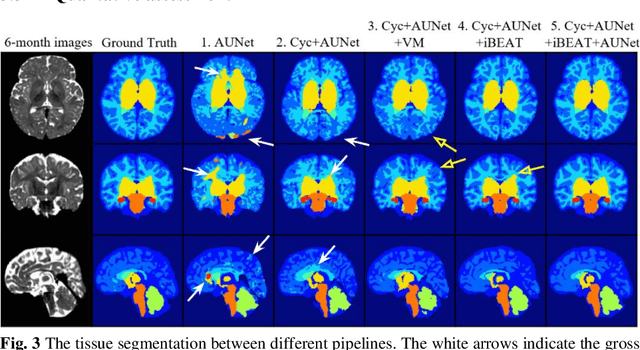
Abstract:Numerous studies have highlighted that atypical brain development, particularly during infancy and toddlerhood, is linked to an increased likelihood of being diagnosed with a neurodevelopmental condition, such as autism. Accurate brain tissue segmentations for morphological analysis are essential in numerous infant studies. However, due to ongoing white matter (WM) myelination changing tissue contrast in T1- and T2-weighted images, automatic tissue segmentation in 6-month infants is particularly difficult. On the other hand, manual labelling by experts is time-consuming and labor-intensive. In this study, we propose the first 8-tissue segmentation pipeline for six-month-old infant brains. This pipeline utilizes domain adaptation (DA) techniques to leverage our longitudinal data, including neonatal images segmented with the neonatal Developing Human Connectome Project structural pipeline. Our pipeline takes raw 6-month images as inputs and generates the 8-tissue segmentation as outputs, forming an end-to-end segmentation pipeline. The segmented tissues include WM, gray matter (GM), cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), ventricles, cerebellum, basal ganglia, brainstem, and hippocampus/amygdala. Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Network (CycleGAN) and Attention U-Net were employed to achieve the image contrast transformation between neonatal and 6-month images and perform tissue segmentation on the synthesized 6-month images (neonatal images with 6-month intensity contrast), respectively. Moreover, we incorporated the segmentation outputs from Infant Brain Extraction and Analysis Toolbox (iBEAT) and another Attention U-Net to further enhance the performance and construct the end-to-end segmentation pipeline. Our evaluation with real 6-month images achieved a DICE score of 0.92, an HD95 of 1.6, and an ASSD of 0.42.
HybridGait: A Benchmark for Spatial-Temporal Cloth-Changing Gait Recognition with Hybrid Explorations
Dec 30, 2023Abstract:Existing gait recognition benchmarks mostly include minor clothing variations in the laboratory environments, but lack persistent changes in appearance over time and space. In this paper, we propose the first in-the-wild benchmark CCGait for cloth-changing gait recognition, which incorporates diverse clothing changes, indoor and outdoor scenes, and multi-modal statistics over 92 days. To further address the coupling effect of clothing and viewpoint variations, we propose a hybrid approach HybridGait that exploits both temporal dynamics and the projected 2D information of 3D human meshes. Specifically, we introduce a Canonical Alignment Spatial-Temporal Transformer (CA-STT) module to encode human joint position-aware features, and fully exploit 3D dense priors via a Silhouette-guided Deformation with 3D-2D Appearance Projection (SilD) strategy. Our contributions are twofold: we provide a challenging benchmark CCGait that captures realistic appearance changes across an expanded and space, and we propose a hybrid framework HybridGait that outperforms prior works on CCGait and Gait3D benchmarks. Our project page is available at https://github.com/HCVLab/HybridGait.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge