Jingya Wang
Learning Semantic Atomic Skills for Multi-Task Robotic Manipulation
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:While imitation learning has shown impressive results in single-task robot manipulation, scaling it to multi-task settings remains a fundamental challenge due to issues such as suboptimal demonstrations, trajectory noise, and behavioral multi-modality. Existing skill-based methods attempt to address this by decomposing actions into reusable abstractions, but they often rely on fixed-length segmentation or environmental priors that limit semantic consistency and cross-task generalization. In this work, we propose AtomSkill, a novel multi-task imitation learning framework that learns and leverages a structured Atomic Skill Space for composable robot manipulation. Our approach is built on two key technical contributions. First, we construct a Semantically Grounded Atomic Skill Library by partitioning demonstrations into variable-length skills using gripper-state keyframe detection and vision-language model annotation. A contrastive learning objective ensures the resulting skill embeddings are both semantically consistent and temporally coherent. Second, we propose an Action Generation module with Keypose Imagination, which jointly predicts a skill's long-horizon terminal keypose and its immediate action sequence. This enables the policy to reason about overarching motion goals and fine-grained control simultaneously, facilitating robust skill chaining. Extensive experiments in simulated and real-world environments show that AtomSkill consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across diverse manipulation tasks.
InterAgent: Physics-based Multi-agent Command Execution via Diffusion on Interaction Graphs
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Humanoid agents are expected to emulate the complex coordination inherent in human social behaviors. However, existing methods are largely confined to single-agent scenarios, overlooking the physically plausible interplay essential for multi-agent interactions. To bridge this gap, we propose InterAgent, the first end-to-end framework for text-driven physics-based multi-agent humanoid control. At its core, we introduce an autoregressive diffusion transformer equipped with multi-stream blocks, which decouples proprioception, exteroception, and action to mitigate cross-modal interference while enabling synergistic coordination. We further propose a novel interaction graph exteroception representation that explicitly captures fine-grained joint-to-joint spatial dependencies to facilitate network learning. Additionally, within it we devise a sparse edge-based attention mechanism that dynamically prunes redundant connections and emphasizes critical inter-agent spatial relations, thereby enhancing the robustness of interaction modeling. Extensive experiments demonstrate that InterAgent consistently outperforms multiple strong baselines, achieving state-of-the-art performance. It enables producing coherent, physically plausible, and semantically faithful multi-agent behaviors from only text prompts. Our code and data will be released to facilitate future research.
Sample from What You See: Visuomotor Policy Learning via Diffusion Bridge with Observation-Embedded Stochastic Differential Equation
Dec 08, 2025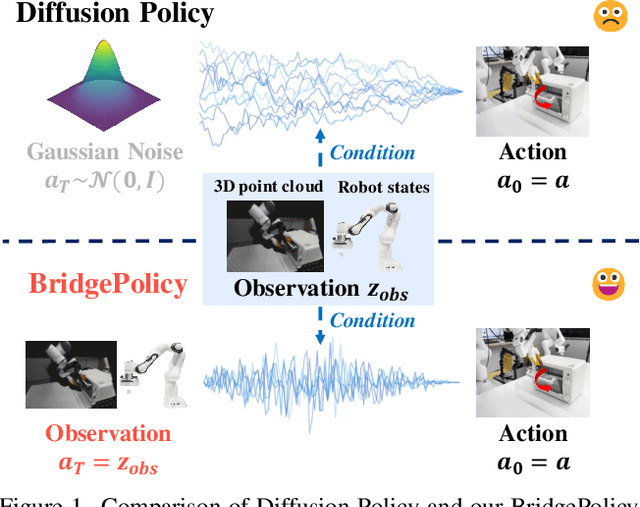
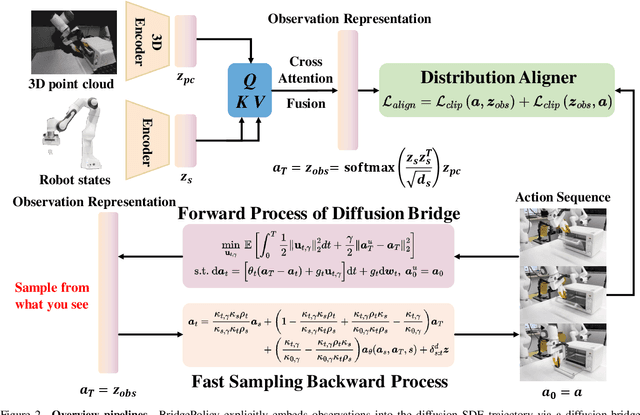
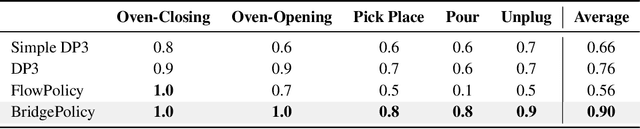
Abstract:Imitation learning with diffusion models has advanced robotic control by capturing multi-modal action distributions. However, existing approaches typically treat observations as high-level conditioning inputs to the denoising network, rather than integrating them into the stochastic dynamics of the diffusion process itself. As a result, sampling must begin from random Gaussian noise, weakening the coupling between perception and control and often yielding suboptimal performance. We introduce BridgePolicy, a generative visuomotor policy that explicitly embeds observations within the stochastic differential equation via a diffusion-bridge formulation. By constructing an observation-informed trajectory, BridgePolicy enables sampling to start from a rich, informative prior rather than random noise, substantially improving precision and reliability in control. A key challenge is that classical diffusion bridges connect distributions with matched dimensionality, whereas robotic observations are heterogeneous and multi-modal and do not naturally align with the action space. To address this, we design a multi-modal fusion module and a semantic aligner that unify visual and state inputs and align observation and action representations, making the bridge applicable to heterogeneous robot data. Extensive experiments across 52 simulation tasks on three benchmarks and five real-world tasks demonstrate that BridgePolicy consistently outperforms state-of-the-art generative policies.
Training-Free ANN-to-SNN Conversion for High-Performance Spiking Transformer
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Leveraging the event-driven paradigm, Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) offer a promising approach for constructing energy-efficient Transformer architectures. Compared to directly trained Spiking Transformers, ANN-to-SNN conversion methods bypass the high training costs. However, existing methods still suffer from notable limitations, failing to effectively handle nonlinear operations in Transformer architectures and requiring additional fine-tuning processes for pre-trained ANNs. To address these issues, we propose a high-performance and training-free ANN-to-SNN conversion framework tailored for Transformer architectures. Specifically, we introduce a Multi-basis Exponential Decay (MBE) neuron, which employs an exponential decay strategy and multi-basis encoding method to efficiently approximate various nonlinear operations. It removes the requirement for weight modifications in pre-trained ANNs. Extensive experiments across diverse tasks (CV, NLU, NLG) and mainstream Transformer architectures (ViT, RoBERTa, GPT-2) demonstrate that our method achieves near-lossless conversion accuracy with significantly lower latency. This provides a promising pathway for the efficient and scalable deployment of Spiking Transformers in real-world applications.
OpenHOI: Open-World Hand-Object Interaction Synthesis with Multimodal Large Language Model
May 25, 2025Abstract:Understanding and synthesizing realistic 3D hand-object interactions (HOI) is critical for applications ranging from immersive AR/VR to dexterous robotics. Existing methods struggle with generalization, performing well on closed-set objects and predefined tasks but failing to handle unseen objects or open-vocabulary instructions. We introduce OpenHOI, the first framework for open-world HOI synthesis, capable of generating long-horizon manipulation sequences for novel objects guided by free-form language commands. Our approach integrates a 3D Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) fine-tuned for joint affordance grounding and semantic task decomposition, enabling precise localization of interaction regions (e.g., handles, buttons) and breakdown of complex instructions (e.g., "Find a water bottle and take a sip") into executable sub-tasks. To synthesize physically plausible interactions, we propose an affordance-driven diffusion model paired with a training-free physics refinement stage that minimizes penetration and optimizes affordance alignment. Evaluations across diverse scenarios demonstrate OpenHOI's superiority over state-of-the-art methods in generalizing to novel object categories, multi-stage tasks, and complex language instructions. Our project page at \href{https://openhoi.github.io}
One Policy but Many Worlds: A Scalable Unified Policy for Versatile Humanoid Locomotion
May 24, 2025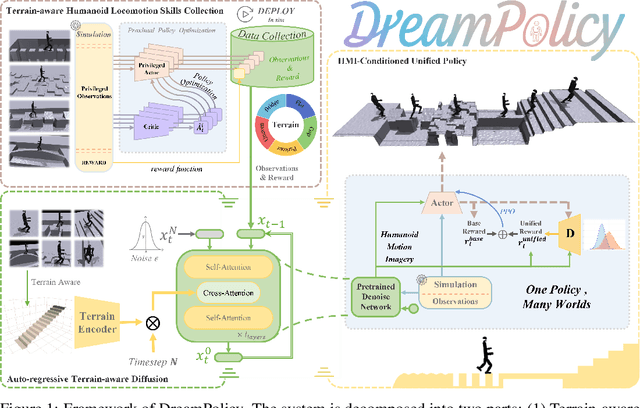
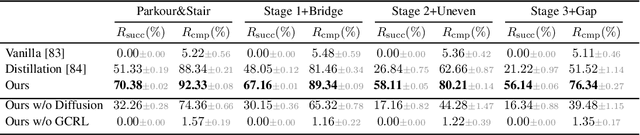
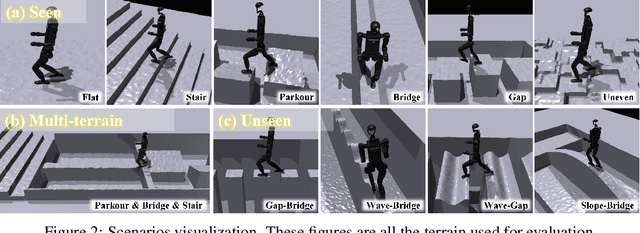
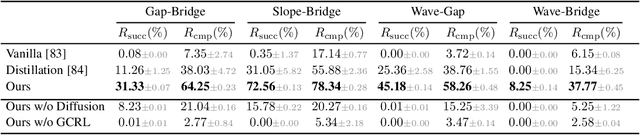
Abstract:Humanoid locomotion faces a critical scalability challenge: traditional reinforcement learning (RL) methods require task-specific rewards and struggle to leverage growing datasets, even as more training terrains are introduced. We propose DreamPolicy, a unified framework that enables a single policy to master diverse terrains and generalize zero-shot to unseen scenarios by systematically integrating offline data and diffusion-driven motion synthesis. At its core, DreamPolicy introduces Humanoid Motion Imagery (HMI) - future state predictions synthesized through an autoregressive terrain-aware diffusion planner curated by aggregating rollouts from specialized policies across various distinct terrains. Unlike human motion datasets requiring laborious retargeting, our data directly captures humanoid kinematics, enabling the diffusion planner to synthesize "dreamed" trajectories that encode terrain-specific physical constraints. These trajectories act as dynamic objectives for our HMI-conditioned policy, bypassing manual reward engineering and enabling cross-terrain generalization. DreamPolicy addresses the scalability limitations of prior methods: while traditional RL fails to exploit growing datasets, our framework scales seamlessly with more offline data. As the dataset expands, the diffusion prior learns richer locomotion skills, which the policy leverages to master new terrains without retraining. Experiments demonstrate that DreamPolicy achieves average 90% success rates in training environments and an average of 20% higher success on unseen terrains than the prevalent method. It also generalizes to perturbed and composite scenarios where prior approaches collapse. By unifying offline data, diffusion-based trajectory synthesis, and policy optimization, DreamPolicy overcomes the "one task, one policy" bottleneck, establishing a paradigm for scalable, data-driven humanoid control.
GenPO: Generative Diffusion Models Meet On-Policy Reinforcement Learning
May 24, 2025
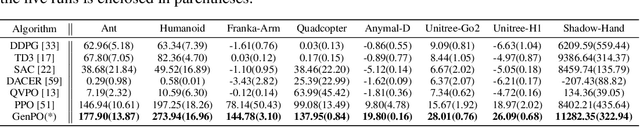
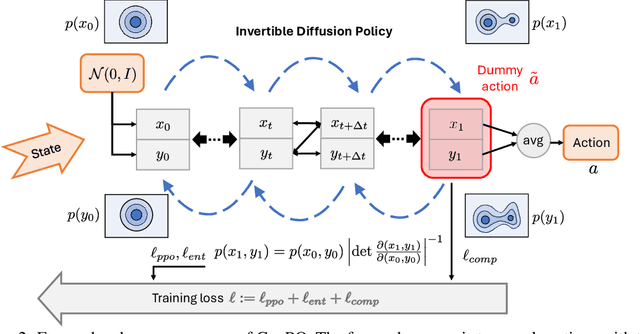
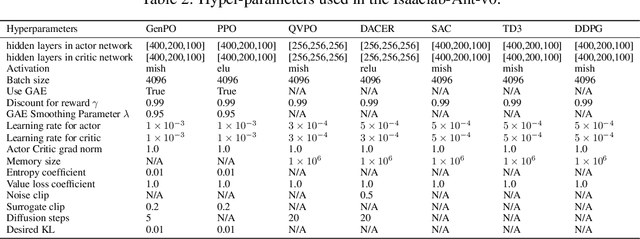
Abstract:Recent advances in reinforcement learning (RL) have demonstrated the powerful exploration capabilities and multimodality of generative diffusion-based policies. While substantial progress has been made in offline RL and off-policy RL settings, integrating diffusion policies into on-policy frameworks like PPO remains underexplored. This gap is particularly significant given the widespread use of large-scale parallel GPU-accelerated simulators, such as IsaacLab, which are optimized for on-policy RL algorithms and enable rapid training of complex robotic tasks. A key challenge lies in computing state-action log-likelihoods under diffusion policies, which is straightforward for Gaussian policies but intractable for flow-based models due to irreversible forward-reverse processes and discretization errors (e.g., Euler-Maruyama approximations). To bridge this gap, we propose GenPO, a generative policy optimization framework that leverages exact diffusion inversion to construct invertible action mappings. GenPO introduces a novel doubled dummy action mechanism that enables invertibility via alternating updates, resolving log-likelihood computation barriers. Furthermore, we also use the action log-likelihood for unbiased entropy and KL divergence estimation, enabling KL-adaptive learning rates and entropy regularization in on-policy updates. Extensive experiments on eight IsaacLab benchmarks, including legged locomotion (Ant, Humanoid, Anymal-D, Unitree H1, Go2), dexterous manipulation (Shadow Hand), aerial control (Quadcopter), and robotic arm tasks (Franka), demonstrate GenPO's superiority over existing RL baselines. Notably, GenPO is the first method to successfully integrate diffusion policies into on-policy RL, unlocking their potential for large-scale parallelized training and real-world robotic deployment.
Multi-modal Multi-platform Person Re-Identification: Benchmark and Method
Mar 21, 2025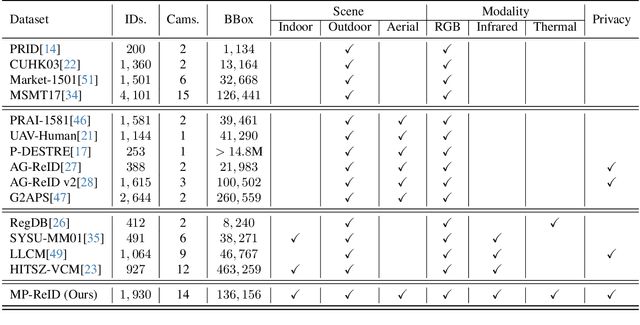

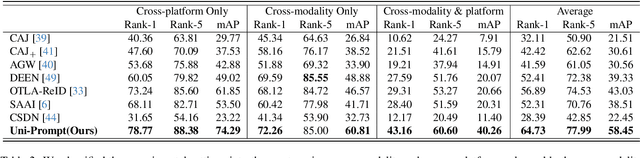
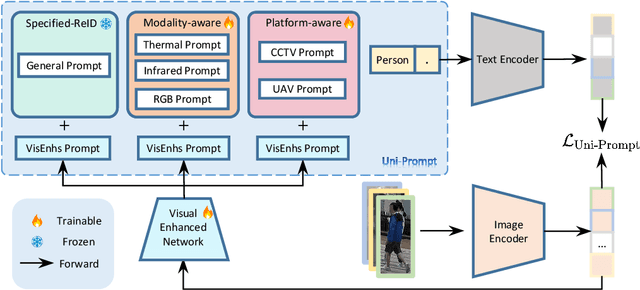
Abstract:Conventional person re-identification (ReID) research is often limited to single-modality sensor data from static cameras, which fails to address the complexities of real-world scenarios where multi-modal signals are increasingly prevalent. For instance, consider an urban ReID system integrating stationary RGB cameras, nighttime infrared sensors, and UAVs equipped with dynamic tracking capabilities. Such systems face significant challenges due to variations in camera perspectives, lighting conditions, and sensor modalities, hindering effective person ReID. To address these challenges, we introduce the MP-ReID benchmark, a novel dataset designed specifically for multi-modality and multi-platform ReID. This benchmark uniquely compiles data from 1,930 identities across diverse modalities, including RGB, infrared, and thermal imaging, captured by both UAVs and ground-based cameras in indoor and outdoor environments. Building on this benchmark, we introduce Uni-Prompt ReID, a framework with specific-designed prompts, tailored for cross-modality and cross-platform scenarios. Our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, establishing a robust foundation for future research in complex and dynamic ReID environments. Our dataset are available at:https://mp-reid.github.io/.
MouseGPT: A Large-scale Vision-Language Model for Mouse Behavior Analysis
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Analyzing animal behavior is crucial in advancing neuroscience, yet quantifying and deciphering its intricate dynamics remains a significant challenge. Traditional machine vision approaches, despite their ability to detect spontaneous behaviors, fall short due to limited interpretability and reliance on manual labeling, which restricts the exploration of the full behavioral spectrum. Here, we introduce MouseGPT, a Vision-Language Model (VLM) that integrates visual cues with natural language to revolutionize mouse behavior analysis. Built upon our first-of-its-kind dataset - incorporating pose dynamics and open-vocabulary behavioral annotations across over 42 million frames of diverse psychiatric conditions - MouseGPT provides a novel, context-rich method for comprehensive behavior interpretation. Our holistic analysis framework enables detailed behavior profiling, clustering, and novel behavior discovery, offering deep insights without the need for labor - intensive manual annotation. Evaluations reveal that MouseGPT surpasses existing models in precision, adaptability, and descriptive richness, positioning it as a transformative tool for ethology and for unraveling complex behavioral dynamics in animal models.
UniDB: A Unified Diffusion Bridge Framework via Stochastic Optimal Control
Feb 09, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion bridge models leverage Doob's $h$-transform to establish fixed endpoints between distributions, demonstrating promising results in image translation and restoration tasks. However, these approaches frequently produce blurred or excessively smoothed image details and lack a comprehensive theoretical foundation to explain these shortcomings. To address these limitations, we propose UniDB, a unified framework for diffusion bridges based on Stochastic Optimal Control (SOC). UniDB formulates the problem through an SOC-based optimization and derives a closed-form solution for the optimal controller, thereby unifying and generalizing existing diffusion bridge models. We demonstrate that existing diffusion bridges employing Doob's $h$-transform constitute a special case of our framework, emerging when the terminal penalty coefficient in the SOC cost function tends to infinity. By incorporating a tunable terminal penalty coefficient, UniDB achieves an optimal balance between control costs and terminal penalties, substantially improving detail preservation and output quality. Notably, UniDB seamlessly integrates with existing diffusion bridge models, requiring only minimal code modifications. Extensive experiments across diverse image restoration tasks validate the superiority and adaptability of the proposed framework. Our code is available at https://github.com/UniDB-SOC/UniDB/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge