Ke Hu
FedTopo: Topology-Informed Representation Alignment in Federated Learning under Non-I.I.D. Conditions
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Current federated-learning models deteriorate under heterogeneous (non-I.I.D.) client data, as their feature representations diverge and pixel- or patch-level objectives fail to capture the global topology which is essential for high-dimensional visual tasks. We propose FedTopo, a framework that integrates Topological-Guided Block Screening (TGBS) and Topological Embedding (TE) to leverage topological information, yielding coherently aligned cross-client representations by Topological Alignment Loss (TAL). First, Topology-Guided Block Screening (TGBS) automatically selects the most topology-informative block, i.e., the one with maximal topological separability, whose persistence-based signatures best distinguish within- versus between-class pairs, ensuring that subsequent analysis focuses on topology-rich features. Next, this block yields a compact Topological Embedding, which quantifies the topological information for each client. Finally, a Topological Alignment Loss (TAL) guides clients to maintain topological consistency with the global model during optimization, reducing representation drift across rounds. Experiments on Fashion-MNIST, CIFAR-10, and CIFAR-100 under four non-I.I.D. partitions show that FedTopo accelerates convergence and improves accuracy over strong baselines.
GenPO: Generative Diffusion Models Meet On-Policy Reinforcement Learning
May 24, 2025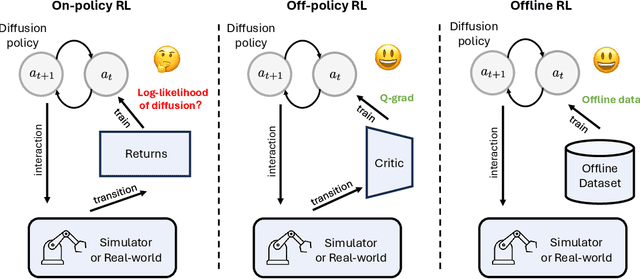
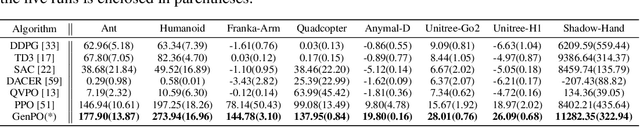
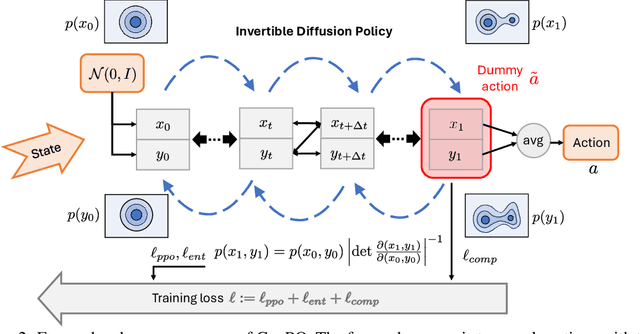
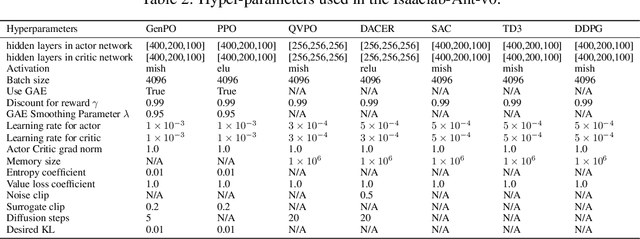
Abstract:Recent advances in reinforcement learning (RL) have demonstrated the powerful exploration capabilities and multimodality of generative diffusion-based policies. While substantial progress has been made in offline RL and off-policy RL settings, integrating diffusion policies into on-policy frameworks like PPO remains underexplored. This gap is particularly significant given the widespread use of large-scale parallel GPU-accelerated simulators, such as IsaacLab, which are optimized for on-policy RL algorithms and enable rapid training of complex robotic tasks. A key challenge lies in computing state-action log-likelihoods under diffusion policies, which is straightforward for Gaussian policies but intractable for flow-based models due to irreversible forward-reverse processes and discretization errors (e.g., Euler-Maruyama approximations). To bridge this gap, we propose GenPO, a generative policy optimization framework that leverages exact diffusion inversion to construct invertible action mappings. GenPO introduces a novel doubled dummy action mechanism that enables invertibility via alternating updates, resolving log-likelihood computation barriers. Furthermore, we also use the action log-likelihood for unbiased entropy and KL divergence estimation, enabling KL-adaptive learning rates and entropy regularization in on-policy updates. Extensive experiments on eight IsaacLab benchmarks, including legged locomotion (Ant, Humanoid, Anymal-D, Unitree H1, Go2), dexterous manipulation (Shadow Hand), aerial control (Quadcopter), and robotic arm tasks (Franka), demonstrate GenPO's superiority over existing RL baselines. Notably, GenPO is the first method to successfully integrate diffusion policies into on-policy RL, unlocking their potential for large-scale parallelized training and real-world robotic deployment.
Efficient and Direct Duplex Modeling for Speech-to-Speech Language Model
May 21, 2025
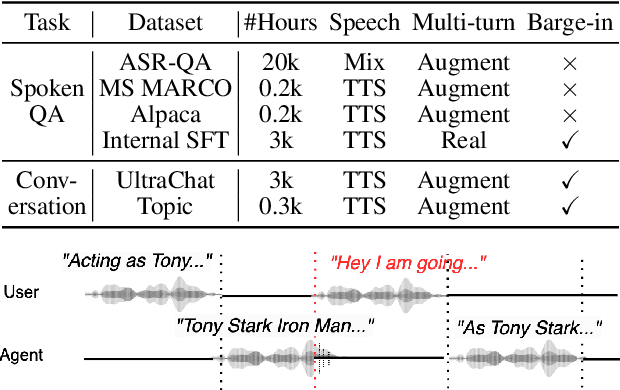
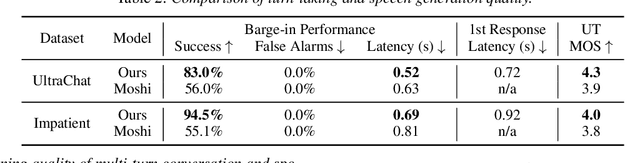

Abstract:Spoken dialogue is an intuitive form of human-computer interaction, yet current speech language models often remain constrained to turn-based exchanges, lacking real-time adaptability such as user barge-in. We propose a novel duplex speech to speech (S2S) architecture featuring continuous user inputs and codec agent outputs with channel fusion that directly models simultaneous user and agent streams. Using a pretrained streaming encoder for user input enables the first duplex S2S model without requiring speech pretrain. Separate architectures for agent and user modeling facilitate codec fine-tuning for better agent voices and halve the bitrate (0.6 kbps) compared to previous works. Experimental results show that the proposed model outperforms previous duplex models in reasoning, turn-taking, and barge-in abilities. The model requires significantly less speech data, as speech pretrain is skipped, which markedly simplifies the process of building a duplex S2S model from any LLMs. Finally, it is the first openly available duplex S2S model with training and inference code to foster reproducibility.
Word Level Timestamp Generation for Automatic Speech Recognition and Translation
May 21, 2025
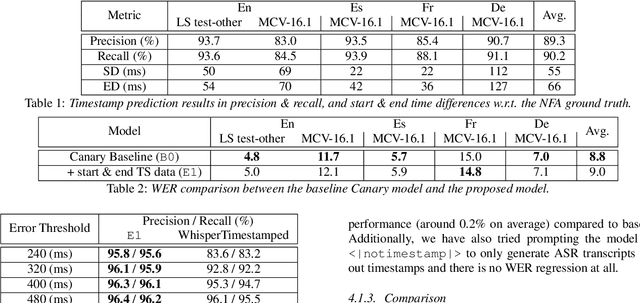
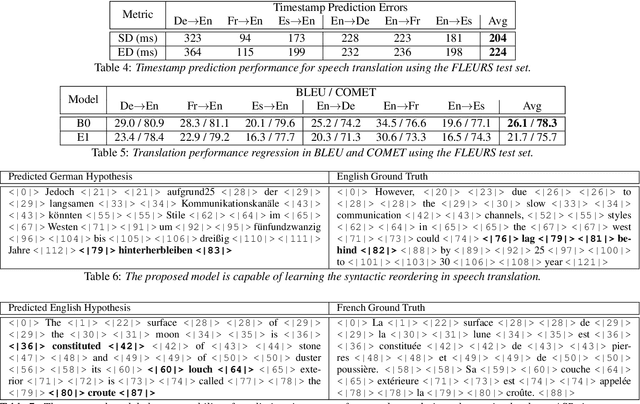
Abstract:We introduce a data-driven approach for enabling word-level timestamp prediction in the Canary model. Accurate timestamp information is crucial for a variety of downstream tasks such as speech content retrieval and timed subtitles. While traditional hybrid systems and end-to-end (E2E) models may employ external modules for timestamp prediction, our approach eliminates the need for separate alignment mechanisms. By leveraging the NeMo Forced Aligner (NFA) as a teacher model, we generate word-level timestamps and train the Canary model to predict timestamps directly. We introduce a new <|timestamp|> token, enabling the Canary model to predict start and end timestamps for each word. Our method demonstrates precision and recall rates between 80% and 90%, with timestamp prediction errors ranging from 20 to 120 ms across four languages, with minimal WER degradation. Additionally, we extend our system to automatic speech translation (AST) tasks, achieving timestamp prediction errors around 200 milliseconds.
Training and Inference Efficiency of Encoder-Decoder Speech Models
Mar 07, 2025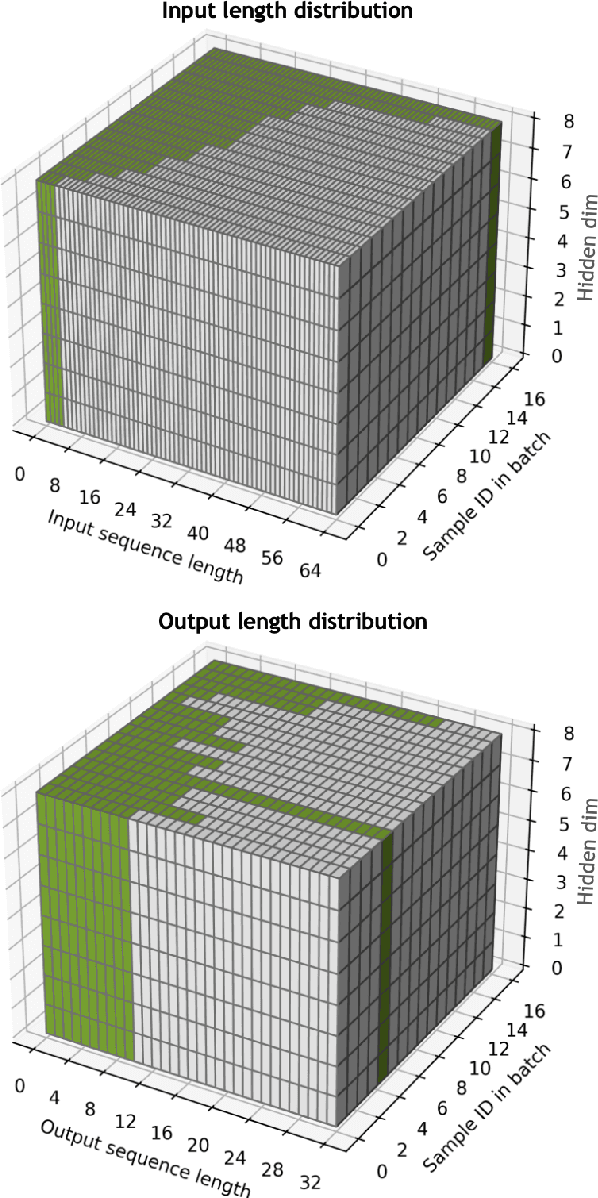

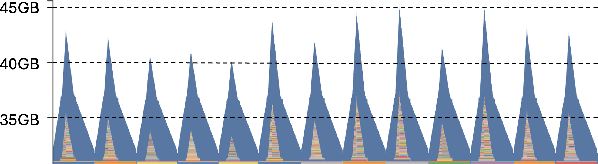
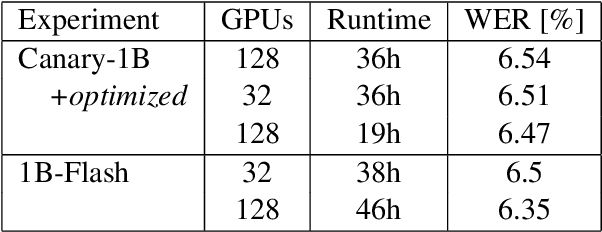
Abstract:Attention encoder-decoder model architecture is the backbone of several recent top performing foundation speech models: Whisper, Seamless, OWSM, and Canary-1B. However, the reported data and compute requirements for their training are prohibitive for many in the research community. In this work, we focus on the efficiency angle and ask the questions of whether we are training these speech models efficiently, and what can we do to improve? We argue that a major, if not the most severe, detrimental factor for training efficiency is related to the sampling strategy of sequential data. We show that negligence in mini-batch sampling leads to more than 50% computation being spent on padding. To that end, we study, profile, and optimize Canary-1B training to show gradual improvement in GPU utilization leading up to 5x increase in average batch sizes versus its original training settings. This in turn allows us to train an equivalent model using 4x less GPUs in the same wall time, or leverage the original resources and train it in 2x shorter wall time. Finally, we observe that the major inference bottleneck lies in the autoregressive decoder steps. We find that adjusting the model architecture to transfer model parameters from the decoder to the encoder results in a 3x inference speedup as measured by inverse real-time factor (RTFx) while preserving the accuracy and compute requirements for convergence. The training code and models will be available as open-source.
NeKo: Toward Post Recognition Generative Correction Large Language Models with Task-Oriented Experts
Nov 08, 2024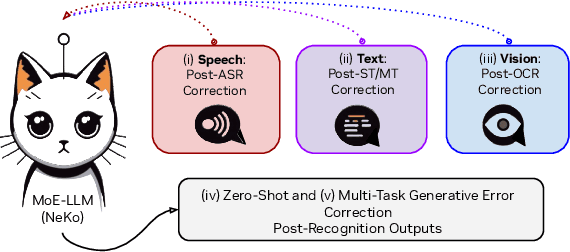
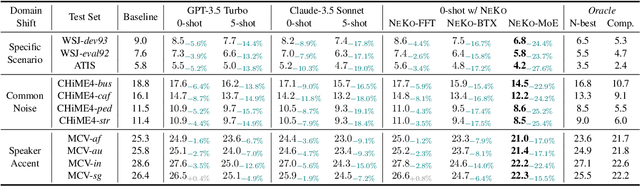
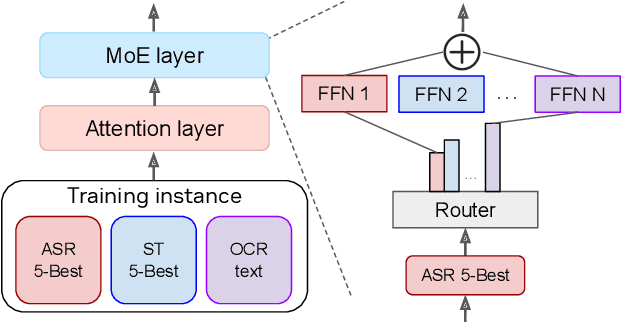
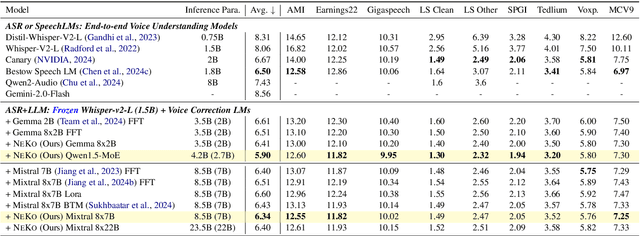
Abstract:Construction of a general-purpose post-recognition error corrector poses a crucial question: how can we most effectively train a model on a large mixture of domain datasets? The answer would lie in learning dataset-specific features and digesting their knowledge in a single model. Previous methods achieve this by having separate correction language models, resulting in a significant increase in parameters. In this work, we present Mixture-of-Experts as a solution, highlighting that MoEs are much more than a scalability tool. We propose a Multi-Task Correction MoE, where we train the experts to become an ``expert'' of speech-to-text, language-to-text and vision-to-text datasets by learning to route each dataset's tokens to its mapped expert. Experiments on the Open ASR Leaderboard show that we explore a new state-of-the-art performance by achieving an average relative $5.0$% WER reduction and substantial improvements in BLEU scores for speech and translation tasks. On zero-shot evaluation, NeKo outperforms GPT-3.5 and Claude-Opus with $15.5$% to $27.6$% relative WER reduction in the Hyporadise benchmark. NeKo performs competitively on grammar and post-OCR correction as a multi-task model.
VoiceTextBlender: Augmenting Large Language Models with Speech Capabilities via Single-Stage Joint Speech-Text Supervised Fine-Tuning
Oct 23, 2024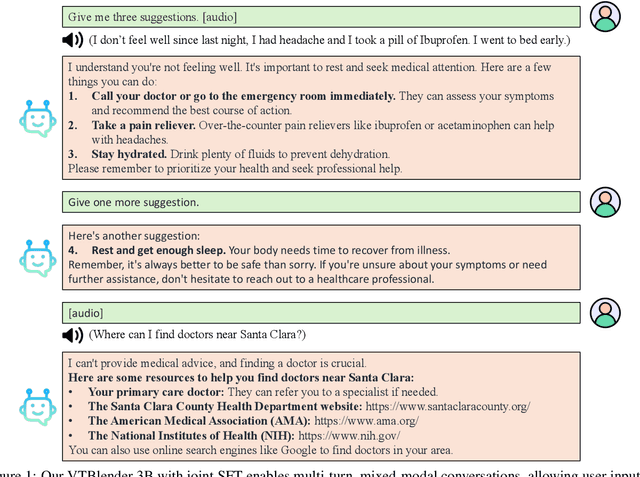
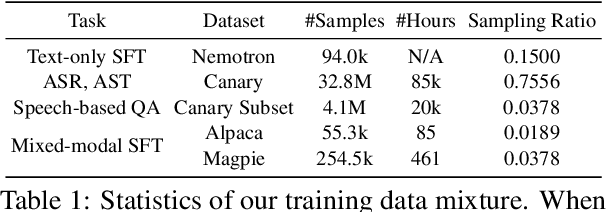
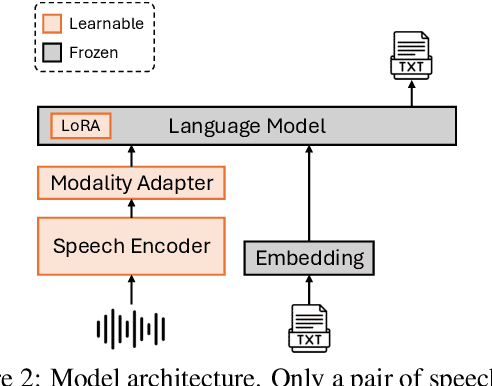
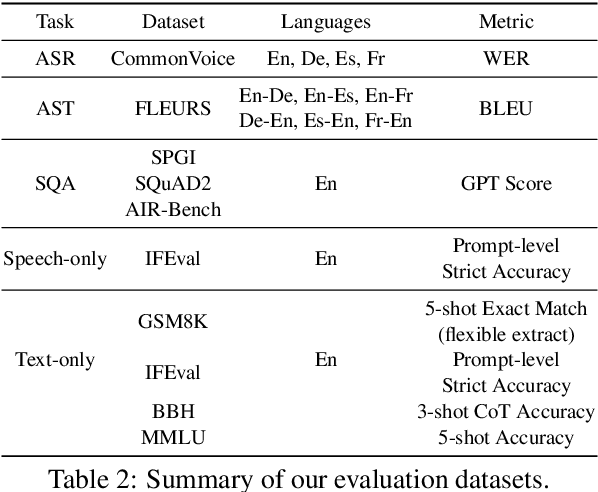
Abstract:Recent studies have augmented large language models (LLMs) with speech capabilities, leading to the development of speech language models (SpeechLMs). Earlier SpeechLMs focused on single-turn speech-based question answering (QA), where user input comprised a speech context and a text question. More recent studies have extended this to multi-turn conversations, though they often require complex, multi-stage supervised fine-tuning (SFT) with diverse data. Another critical challenge with SpeechLMs is catastrophic forgetting-where models optimized for speech tasks suffer significant degradation in text-only performance. To mitigate these issues, we propose a novel single-stage joint speech-text SFT approach on the low-rank adaptation (LoRA) of the LLM backbone. Our joint SFT combines text-only SFT data with three types of speech-related data: speech recognition and translation, speech-based QA, and mixed-modal SFT. Compared to previous SpeechLMs with 7B or 13B parameters, our 3B model demonstrates superior performance across various speech benchmarks while preserving the original capabilities on text-only tasks. Furthermore, our model shows emergent abilities of effectively handling previously unseen prompts and tasks, including multi-turn, mixed-modal inputs.
Chain-of-Thought Prompting for Speech Translation
Sep 17, 2024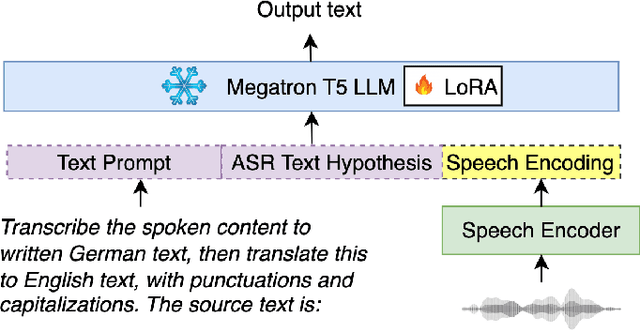
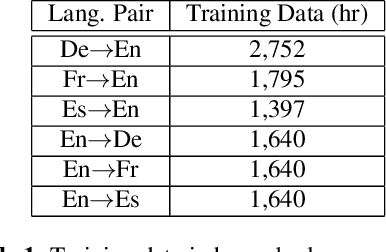
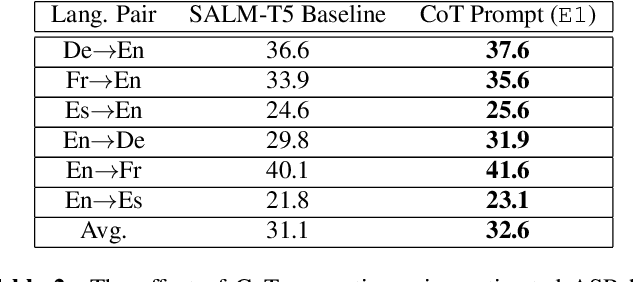
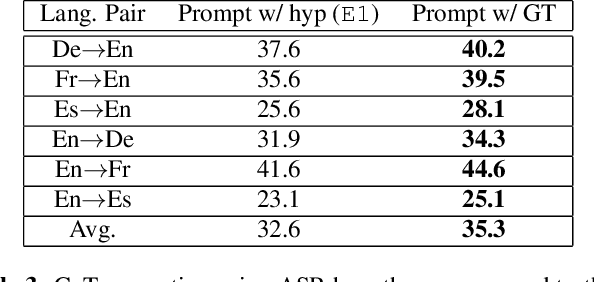
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable advancements in language understanding and generation. Building on the success of text-based LLMs, recent research has adapted these models to use speech embeddings for prompting, resulting in Speech-LLM models that exhibit strong performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and automatic speech translation (AST). In this work, we propose a novel approach to leverage ASR transcripts as prompts for AST in a Speech-LLM built on an encoder-decoder text LLM. The Speech-LLM model consists of a speech encoder and an encoder-decoder structure Megatron-T5. By first decoding speech to generate ASR transcripts and subsequently using these transcripts along with encoded speech for prompting, we guide the speech translation in a two-step process like chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting. Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) is used for the T5 LLM for model adaptation and shows superior performance to full model fine-tuning. Experimental results show that the proposed CoT prompting significantly improves AST performance, achieving an average increase of 2.4 BLEU points across 6 En->X or X->En AST tasks compared to speech prompting alone. Additionally, compared to a related CoT prediction method that predicts a concatenated sequence of ASR and AST transcripts, our method performs better by an average of 2 BLEU points.
Robust Principal Component Analysis via Discriminant Sample Weight Learning
Aug 22, 2024



Abstract:Principal component analysis (PCA) is a classical feature extraction method, but it may be adversely affected by outliers, resulting in inaccurate learning of the projection matrix. This paper proposes a robust method to estimate both the data mean and the PCA projection matrix by learning discriminant sample weights from data containing outliers. Each sample in the dataset is assigned a weight, and the proposed algorithm iteratively learns the weights, the mean, and the projection matrix, respectively. Specifically, when the mean and the projection matrix are available, via fine-grained analysis of outliers, a weight for each sample is learned hierarchically so that outliers have small weights while normal samples have large weights. With the learned weights available, a weighted optimization problem is solved to estimate both the data mean and the projection matrix. Because the learned weights discriminate outliers from normal samples, the adverse influence of outliers is mitigated due to the corresponding small weights. Experiments on toy data, UCI dataset, and face dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in estimating the mean and the projection matrix from the data containing outliers.
Diffusion-based Reinforcement Learning via Q-weighted Variational Policy Optimization
May 25, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have garnered widespread attention in Reinforcement Learning (RL) for their powerful expressiveness and multimodality. It has been verified that utilizing diffusion policies can significantly improve the performance of RL algorithms in continuous control tasks by overcoming the limitations of unimodal policies, such as Gaussian policies, and providing the agent with enhanced exploration capabilities. However, existing works mainly focus on the application of diffusion policies in offline RL, while their incorporation into online RL is less investigated. The training objective of the diffusion model, known as the variational lower bound, cannot be optimized directly in online RL due to the unavailability of 'good' actions. This leads to difficulties in conducting diffusion policy improvement. To overcome this, we propose a novel model-free diffusion-based online RL algorithm, Q-weighted Variational Policy Optimization (QVPO). Specifically, we introduce the Q-weighted variational loss, which can be proved to be a tight lower bound of the policy objective in online RL under certain conditions. To fulfill these conditions, the Q-weight transformation functions are introduced for general scenarios. Additionally, to further enhance the exploration capability of the diffusion policy, we design a special entropy regularization term. We also develop an efficient behavior policy to enhance sample efficiency by reducing the variance of the diffusion policy during online interactions. Consequently, the QVPO algorithm leverages the exploration capabilities and multimodality of diffusion policies, preventing the RL agent from converging to a sub-optimal policy. To verify the effectiveness of QVPO, we conduct comprehensive experiments on MuJoCo benchmarks. The final results demonstrate that QVPO achieves state-of-the-art performance on both cumulative reward and sample efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge