Yen-Ting Lin
An Intelligent AI glasses System with Multi-Agent Architecture for Real-Time Voice Processing and Task Execution
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:This paper presents an AI glasses system that integrates real-time voice processing, artificial intelligence(AI) agents, and cross-network streaming capabilities. The system employs dual-agent architecture where Agent 01 handles Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and Agent 02 manages AI processing through local Large Language Models (LLMs), Model Context Protocol (MCP) tools, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). The system supports real-time RTSP streaming for voice and video data transmission, eye tracking data collection, and remote task execution through RabbitMQ messaging. Implementation demonstrates successful voice command processing with multilingual support and cross-platform task execution capabilities.
Step-KTO: Optimizing Mathematical Reasoning through Stepwise Binary Feedback
Jan 18, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have recently demonstrated remarkable success in mathematical reasoning. Despite progress in methods like chain-of-thought prompting and self-consistency sampling, these advances often focus on final correctness without ensuring that the underlying reasoning process is coherent and reliable. This paper introduces Step-KTO, a training framework that combines process-level and outcome-level binary feedback to guide LLMs toward more trustworthy reasoning trajectories. By providing binary evaluations for both the intermediate reasoning steps and the final answer, Step-KTO encourages the model to adhere to logical progressions rather than relying on superficial shortcuts. Our experiments on challenging mathematical benchmarks show that Step-KTO significantly improves both final answer accuracy and the quality of intermediate reasoning steps. For example, on the MATH-500 dataset, Step-KTO achieves a notable improvement in Pass@1 accuracy over strong baselines. These results highlight the promise of integrating stepwise process feedback into LLM training, paving the way toward more interpretable and dependable reasoning capabilities.
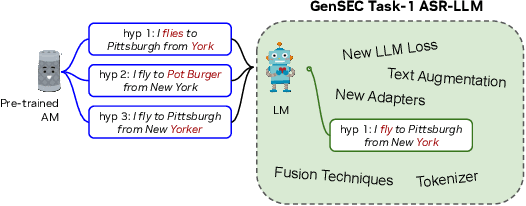
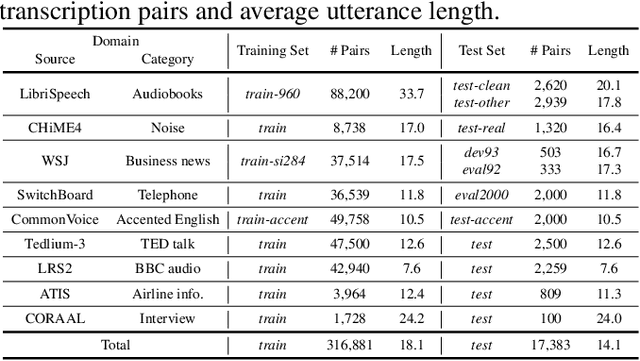
NeKo: Toward Post Recognition Generative Correction Large Language Models with Task-Oriented Experts
Nov 08, 2024
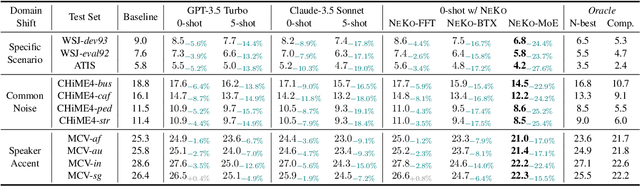
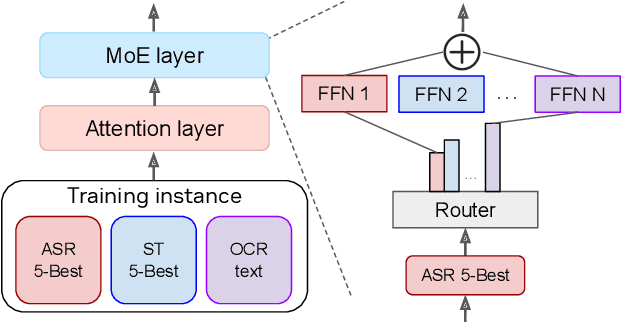
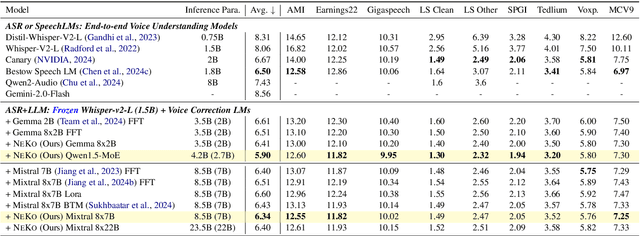
Abstract:Construction of a general-purpose post-recognition error corrector poses a crucial question: how can we most effectively train a model on a large mixture of domain datasets? The answer would lie in learning dataset-specific features and digesting their knowledge in a single model. Previous methods achieve this by having separate correction language models, resulting in a significant increase in parameters. In this work, we present Mixture-of-Experts as a solution, highlighting that MoEs are much more than a scalability tool. We propose a Multi-Task Correction MoE, where we train the experts to become an ``expert'' of speech-to-text, language-to-text and vision-to-text datasets by learning to route each dataset's tokens to its mapped expert. Experiments on the Open ASR Leaderboard show that we explore a new state-of-the-art performance by achieving an average relative $5.0$% WER reduction and substantial improvements in BLEU scores for speech and translation tasks. On zero-shot evaluation, NeKo outperforms GPT-3.5 and Claude-Opus with $15.5$% to $27.6$% relative WER reduction in the Hyporadise benchmark. NeKo performs competitively on grammar and post-OCR correction as a multi-task model.
Large Language Model Based Generative Error Correction: A Challenge and Baselines for Speech Recognition, Speaker Tagging, and Emotion Recognition
Sep 17, 2024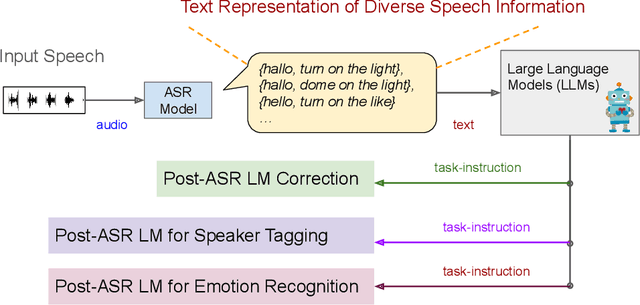
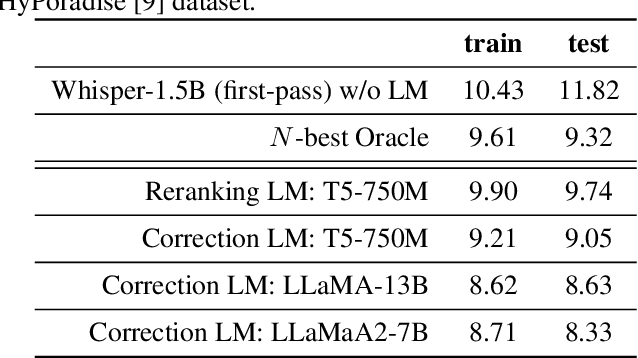
Abstract:Given recent advances in generative AI technology, a key question is how large language models (LLMs) can enhance acoustic modeling tasks using text decoding results from a frozen, pretrained automatic speech recognition (ASR) model. To explore new capabilities in language modeling for speech processing, we introduce the generative speech transcription error correction (GenSEC) challenge. This challenge comprises three post-ASR language modeling tasks: (i) post-ASR transcription correction, (ii) speaker tagging, and (iii) emotion recognition. These tasks aim to emulate future LLM-based agents handling voice-based interfaces while remaining accessible to a broad audience by utilizing open pretrained language models or agent-based APIs. We also discuss insights from baseline evaluations, as well as lessons learned for designing future evaluations.
A Survey of Data Synthesis Approaches
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:This paper provides a detailed survey of synthetic data techniques. We first discuss the expected goals of using synthetic data in data augmentation, which can be divided into four parts: 1) Improving Diversity, 2) Data Balancing, 3) Addressing Domain Shift, and 4) Resolving Edge Cases. Synthesizing data are closely related to the prevailing machine learning techniques at the time, therefore, we summarize the domain of synthetic data techniques into four categories: 1) Expert-knowledge, 2) Direct Training, 3) Pre-train then Fine-tune, and 4) Foundation Models without Fine-tuning. Next, we categorize the goals of synthetic data filtering into four types for discussion: 1) Basic Quality, 2) Label Consistency, and 3) Data Distribution. In section 5 of this paper, we also discuss the future directions of synthetic data and state three direction that we believe is important: 1) focus more on quality, 2) the evaluation of synthetic data, and 3) multi-model data augmentation.
A Survey of Useful LLM Evaluation
Jun 03, 2024Abstract:LLMs have gotten attention across various research domains due to their exceptional performance on a wide range of complex tasks. Therefore, refined methods to evaluate the capabilities of LLMs are needed to determine the tasks and responsibility they should undertake. Our study mainly discussed how LLMs, as useful tools, should be effectively assessed. We proposed the two-stage framework: from ``core ability'' to ``agent'', clearly explaining how LLMs can be applied based on their specific capabilities, along with the evaluation methods in each stage. Core ability refers to the capabilities that LLMs need in order to generate high-quality natural language texts. After confirming LLMs possess core ability, they can solve real-world and complex tasks as agent. In the "core ability" stage, we discussed the reasoning ability, societal impact, and domain knowledge of LLMs. In the ``agent'' stage, we demonstrated embodied action, planning, and tool learning of LLMs agent applications. Finally, we examined the challenges currently confronting the evaluation methods for LLMs, as well as the directions for future development.
Measuring Taiwanese Mandarin Language Understanding
Mar 29, 2024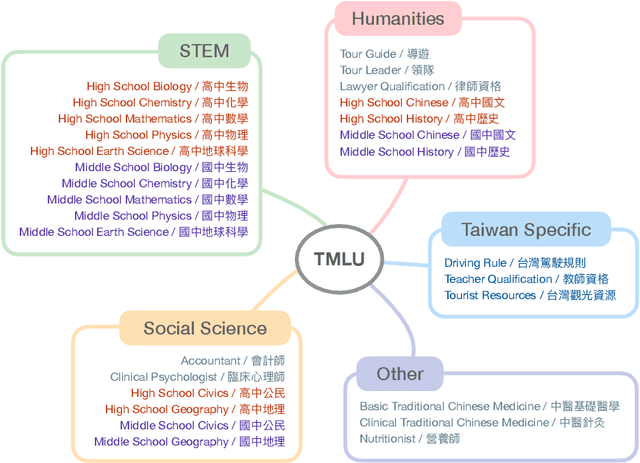
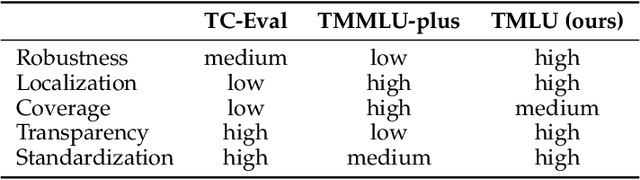
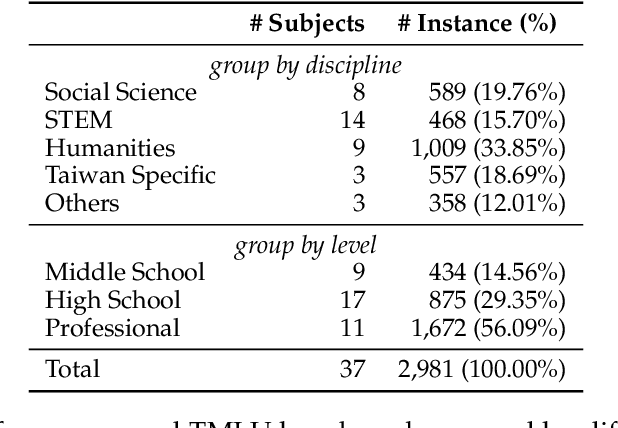

Abstract:The evaluation of large language models (LLMs) has drawn substantial attention in the field recently. This work focuses on evaluating LLMs in a Chinese context, specifically, for Traditional Chinese which has been largely underrepresented in existing benchmarks. We present TMLU, a holistic evaluation suit tailored for assessing the advanced knowledge and reasoning capability in LLMs, under the context of Taiwanese Mandarin. TMLU consists of an array of 37 subjects across social science, STEM, humanities, Taiwan-specific content, and others, ranging from middle school to professional levels. In addition, we curate chain-of-thought-like few-shot explanations for each subject to facilitate the evaluation of complex reasoning skills. To establish a comprehensive baseline, we conduct extensive experiments and analysis on 24 advanced LLMs. The results suggest that Chinese open-weight models demonstrate inferior performance comparing to multilingual proprietary ones, and open-weight models tailored for Taiwanese Mandarin lag behind the Simplified-Chinese counterparts. The findings indicate great headrooms for improvement, and emphasize the goal of TMLU to foster the development of localized Taiwanese-Mandarin LLMs. We release the benchmark and evaluation scripts for the community to promote future research.
Taiwan LLM: Bridging the Linguistic Divide with a Culturally Aligned Language Model
Nov 29, 2023Abstract:In the realm of language models, the nuanced linguistic and cultural intricacies of Traditional Chinese, as spoken in Taiwan, have been largely overlooked. This paper introduces Taiwan LLM, a pioneering Large Language Model that specifically caters to the Traditional Chinese language, with a focus on the variant used in Taiwan. Leveraging a comprehensive pretraining corpus and instruction-finetuning datasets, we have developed a model that not only understands the complexities of Traditional Chinese but also embodies the cultural context of Taiwan. Taiwan LLM represents the first of its kind, a model that is not only linguistically accurate but also culturally resonant with its user base. Our evaluations demonstrate that Taiwan LLM achieves superior performance in understanding and generating Traditional Chinese text, outperforming existing models that are predominantly trained on Simplified Chinese or English. The open-source release of Taiwan LLM invites collaboration and further innovation, ensuring that the linguistic diversity of Chinese speakers is embraced and well-served. The model, datasets, and further resources are made publicly available to foster ongoing research and development in this field.
VoiceBank-2023: A Multi-Speaker Mandarin Speech Corpus for Constructing Personalized TTS Systems for the Speech Impaired
Aug 27, 2023Abstract:Services of personalized TTS systems for the Mandarin-speaking speech impaired are rarely mentioned. Taiwan started the VoiceBanking project in 2020, aiming to build a complete set of services to deliver personalized Mandarin TTS systems to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. This paper reports the corpus design, corpus recording, data purging and correction for the corpus, and evaluations of the developed personalized TTS systems, for the VoiceBanking project. The developed corpus is named after the VoiceBank-2023 speech corpus because of its release year. The corpus contains 29.78 hours of utterances with prompts of short paragraphs and common phrases spoken by 111 native Mandarin speakers. The corpus is labeled with information about gender, degree of speech impairment, types of users, transcription, SNRs, and speaking rates. The VoiceBank-2023 is available by request for non-commercial use and welcomes all parties to join the VoiceBanking project to improve the services for the speech impaired.
LLM-Eval: Unified Multi-Dimensional Automatic Evaluation for Open-Domain Conversations with Large Language Models
May 23, 2023Abstract:We propose LLM-Eval, a unified multi-dimensional automatic evaluation method for open-domain conversations with large language models (LLMs). Existing evaluation methods often rely on human annotations, ground-truth responses, or multiple LLM prompts, which can be expensive and time-consuming. To address these issues, we design a single prompt-based evaluation method that leverages a unified evaluation schema to cover multiple dimensions of conversation quality in a single model call. We extensively evaluate the performance of LLM-Eval on various benchmark datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness, efficiency, and adaptability compared to state-of-the-art evaluation methods. Our analysis also highlights the importance of choosing suitable LLMs and decoding strategies for accurate evaluation results. LLM-Eval offers a versatile and robust solution for evaluating open-domain conversation systems, streamlining the evaluation process and providing consistent performance across diverse scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge