Mingyu Lu
SurrogateSHAP: Training-Free Contributor Attribution for Text-to-Image (T2I) Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:As Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models are increasingly used in real-world creative workflows, a principled framework for valuing contributors who provide a collection of data is essential for fair compensation and sustainable data marketplaces. While the Shapley value offers a theoretically grounded approach to attribution, it faces a dual computational bottleneck: (i) the prohibitive cost of exhaustive model retraining for each sampled subset of players (i.e., data contributors) and (ii) the combinatorial number of subsets needed to estimate marginal contributions due to contributor interactions. To this end, we propose SurrogateSHAP, a retraining-free framework that approximates the expensive retraining game through inference from a pretrained model. To further improve efficiency, we employ a gradient-boosted tree to approximate the utility function and derive Shapley values analytically from the tree-based model. We evaluate SurrogateSHAP across three diverse attribution tasks: (i) image quality for DDPM-CFG on CIFAR-20, (ii) aesthetics for Stable Diffusion on Post-Impressionist artworks, and (iii) product diversity for FLUX.1 on Fashion-Product data. Across settings, SurrogateSHAP outperforms prior methods while substantially reducing computational overhead, consistently identifying influential contributors across multiple utility metrics. Finally, we demonstrate that SurrogateSHAP effectively localizes data sources responsible for spurious correlations in clinical images, providing a scalable path toward auditing safety-critical generative models.
Swin-BERT: A Feature Fusion System designed for Speech-based Alzheimer's Dementia Detection
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:Speech is usually used for constructing an automatic Alzheimer's dementia (AD) detection system, as the acoustic and linguistic abilities show a decline in people living with AD at the early stages. However, speech includes not only AD-related local and global information but also other information unrelated to cognitive status, such as age and gender. In this paper, we propose a speech-based system named Swin-BERT for automatic dementia detection. For the acoustic part, the shifted windows multi-head attention that proposed to extract local and global information from images, is used for designing our acoustic-based system. To decouple the effect of age and gender on acoustic feature extraction, they are used as an extra input of the designed acoustic system. For the linguistic part, the rhythm-related information, which varies significantly between people living with and without AD, is removed while transcribing the audio recordings into transcripts. To compensate for the removed rhythm-related information, the character-level transcripts are proposed to be used as the extra input of a word-level BERT-style system. Finally, the Swin-BERT combines the acoustic features learned from our proposed acoustic-based system with our linguistic-based system. The experiments are based on the two datasets provided by the international dementia detection challenges: the ADReSS and ADReSSo. The results show that both the proposed acoustic and linguistic systems can be better or comparable with previous research on the two datasets. Superior results are achieved by the proposed Swin-BERT system on the ADReSS and ADReSSo datasets, which are 85.58\% F-score and 87.32\% F-score respectively.
TKwinFormer: Top k Window Attention in Vision Transformers for Feature Matching
Aug 29, 2023



Abstract:Local feature matching remains a challenging task, primarily due to difficulties in matching sparse keypoints and low-texture regions. The key to solving this problem lies in effectively and accurately integrating global and local information. To achieve this goal, we introduce an innovative local feature matching method called TKwinFormer. Our approach employs a multi-stage matching strategy to optimize the efficiency of information interaction. Furthermore, we propose a novel attention mechanism called Top K Window Attention, which facilitates global information interaction through window tokens prior to patch-level matching, resulting in improved matching accuracy. Additionally, we design an attention block to enhance attention between channels. Experimental results demonstrate that TKwinFormer outperforms state-of-the-art methods on various benchmarks. Code is available at: https://github.com/LiaoYun0x0/TKwinFormer.
Learning to Maximize Mutual Information for Dynamic Feature Selection
Jan 02, 2023



Abstract:Feature selection helps reduce data acquisition costs in ML, but the standard approach is to train models with static feature subsets. Here, we consider the dynamic feature selection (DFS) problem where a model sequentially queries features based on the presently available information. DFS is often addressed with reinforcement learning (RL), but we explore a simpler approach of greedily selecting features based on their conditional mutual information. This method is theoretically appealing but requires oracle access to the data distribution, so we develop a learning approach based on amortized optimization. The proposed method is shown to recover the greedy policy when trained to optimality and outperforms numerous existing feature selection methods in our experiments, thus validating it as a simple but powerful approach for this problem.
A Deep Bayesian Bandits Approach for Anticancer Therapy: Exploration via Functional Prior
May 05, 2022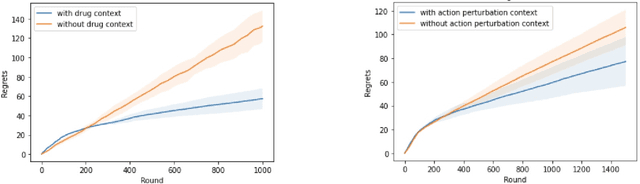
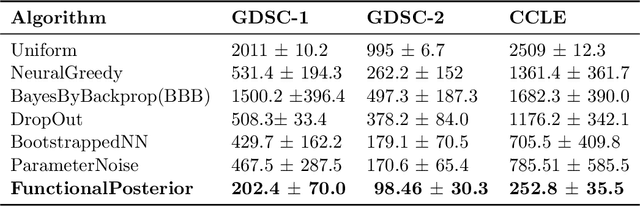
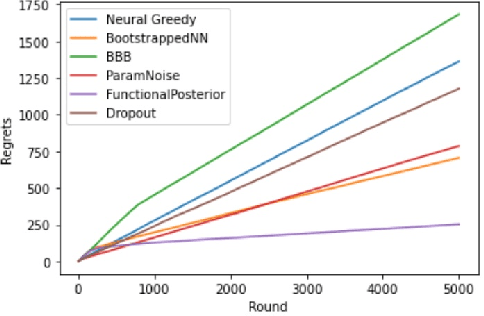
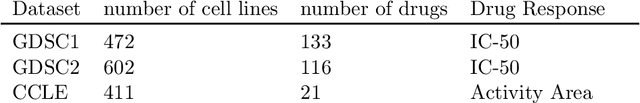
Abstract:Learning personalized cancer treatment with machine learning holds great promise to improve cancer patients' chance of survival. Despite recent advances in machine learning and precision oncology, this approach remains challenging as collecting data in preclinical/clinical studies for modeling multiple treatment efficacies is often an expensive, time-consuming process. Moreover, the randomization in treatment allocation proves to be suboptimal since some participants/samples are not receiving the most appropriate treatments during the trial. To address this challenge, we formulate drug screening study as a "contextual bandit" problem, in which an algorithm selects anticancer therapeutics based on contextual information about cancer cell lines while adapting its treatment strategy to maximize treatment response in an "online" fashion. We propose using a novel deep Bayesian bandits framework that uses functional prior to approximate posterior for drug response prediction based on multi-modal information consisting of genomic features and drug structure. We empirically evaluate our method on three large-scale in vitro pharmacogenomic datasets and show that our approach outperforms several benchmarks in identifying optimal treatment for a given cell line.
G-Net: A Deep Learning Approach to G-computation for Counterfactual Outcome Prediction Under Dynamic Treatment Regimes
Mar 23, 2020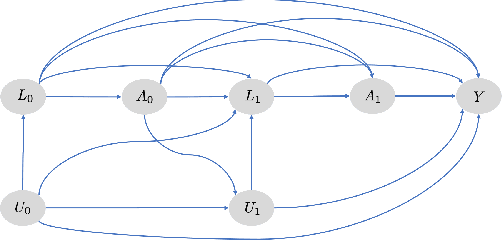
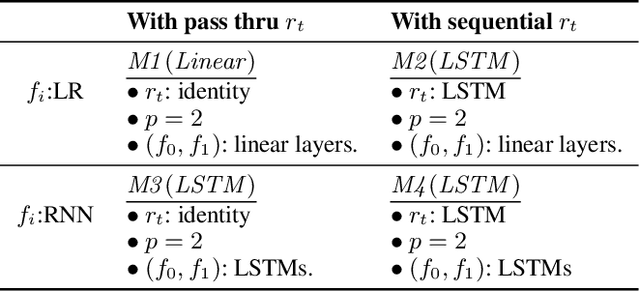
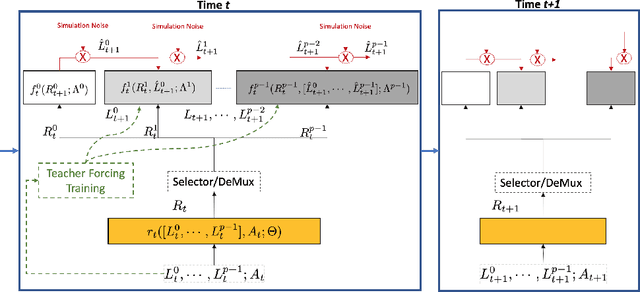
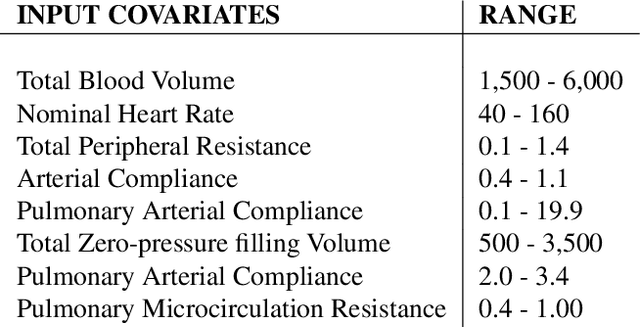
Abstract:Counterfactual prediction is a fundamental task in decision-making. G-computation is a method for estimating expected counterfactual outcomes under dynamic time-varying treatment strategies. Existing G-computation implementations have mostly employed classical regression models with limited capacity to capture complex temporal and nonlinear dependence structures. This paper introduces G-Net, a novel sequential deep learning framework for G-computation that can handle complex time series data while imposing minimal modeling assumptions and provide estimates of individual or population-level time varying treatment effects. We evaluate alternative G-Net implementations using realistically complex temporal simulated data obtained from CVSim, a mechanistic model of the cardiovascular system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge