Nathan White
Designing Parent-child-robot Interactions to Facilitate In-Home Parental Math Talk with Young Children
May 04, 2023


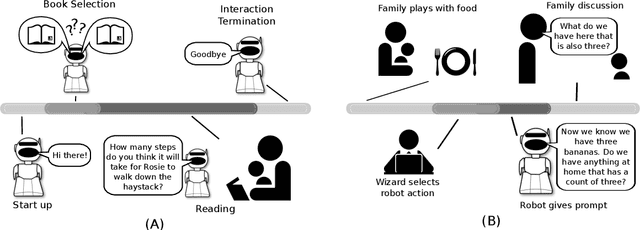
Abstract:Parent-child interaction is critical for child development, yet parents may need guidance in some aspects of their engagement with their children. Current research on educational math robots focuses on child-robot interactions but falls short of including the parents and integrating the critical role they play in children's learning. We explore how educational robots can be designed to facilitate parent-child conversations, focusing on math talk, a predictor of later math ability in children. We prototyped capabilities for a social robot to support math talk via reading and play activities and conducted an exploratory Wizard-of-Oz in-home study for parent-child interactions facilitated by a robot. Our findings yield insights into how parents were inspired by the robot's prompts, their desired interaction styles and methods for the robot, and how they wanted to include the robot in the activities, leading to guidelines for the design of parent-child-robot interaction in educational contexts.
Learning to Maximize Mutual Information for Dynamic Feature Selection
Jan 02, 2023



Abstract:Feature selection helps reduce data acquisition costs in ML, but the standard approach is to train models with static feature subsets. Here, we consider the dynamic feature selection (DFS) problem where a model sequentially queries features based on the presently available information. DFS is often addressed with reinforcement learning (RL), but we explore a simpler approach of greedily selecting features based on their conditional mutual information. This method is theoretically appealing but requires oracle access to the data distribution, so we develop a learning approach based on amortized optimization. The proposed method is shown to recover the greedy policy when trained to optimality and outperforms numerous existing feature selection methods in our experiments, thus validating it as a simple but powerful approach for this problem.
Understanding Factors that Shape Children's Long Term Engagement with an In-Home Learning Companion Robot
May 18, 2022
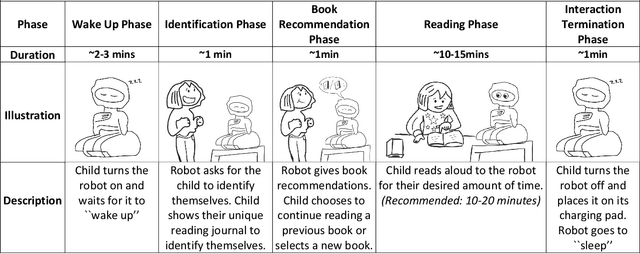
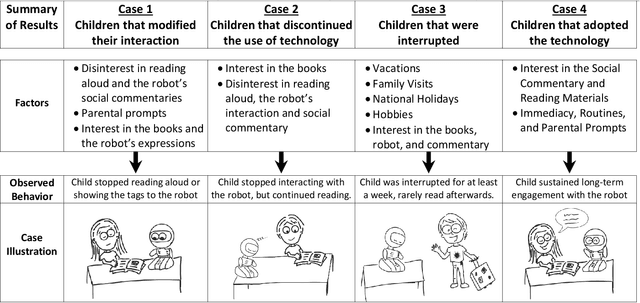
Abstract:Social robots are emerging as learning companions for children, and research shows that they facilitate the development of interest and learning even through brief interactions. However, little is known about how such technologies might support these goals in authentic environments over long-term periods of use and interaction. We designed a learning companion robot capable of supporting children reading popular-science books by expressing social and informational commentaries. We deployed the robot in homes of 14 families with children aged 10-12 for four weeks during the summer. Our analysis revealed critical factors that affected children's long-term engagement and adoption of the robot, including external factors such as vacations, family visits, and extracurricular activities; family/parental involvement; and children's individual interests. We present four in-depth cases that illustrate these factors and demonstrate their impact on children's reading experiences and discuss the implications of our findings for robot design.
Socially Inspired Communication in Swarm Robotics
Jun 03, 2019
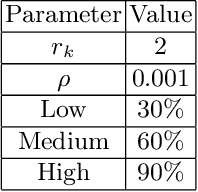

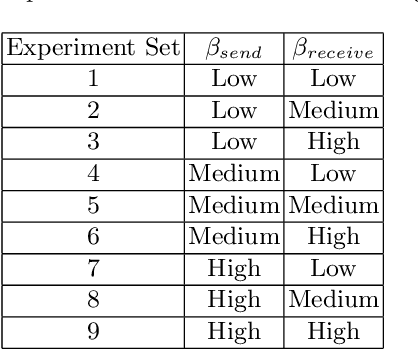
Abstract:Localized communication in swarms has been shown to increase swarm effectiveness in some situations by allowing for additional opportunities for cooperation. However, communication and utilization of potentially outdated information is also a concern. We present an explicit non-directional goal-based communication model and message accept/reject scheme, and test our model in a set of object gathering experiments with a swarm of robots. The results of the experiments indicate that even low levels of communication regarding the swarm's goal outperform high levels of random information communication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge