Wei Qiu
Towards Skilled Population Curriculum for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Feb 07, 2023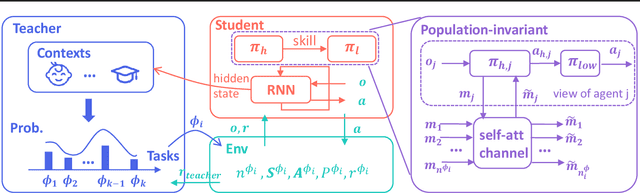
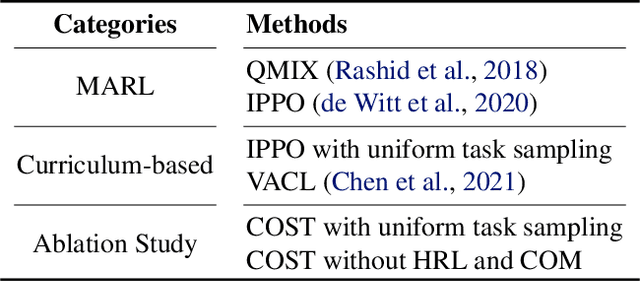
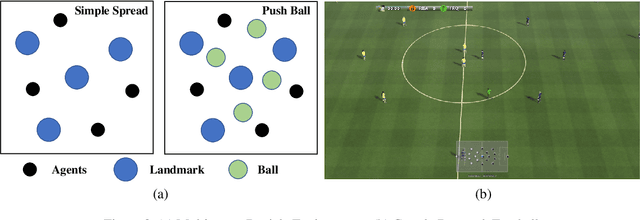

Abstract:Recent advances in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) allow agents to coordinate their behaviors in complex environments. However, common MARL algorithms still suffer from scalability and sparse reward issues. One promising approach to resolving them is automatic curriculum learning (ACL). ACL involves a student (curriculum learner) training on tasks of increasing difficulty controlled by a teacher (curriculum generator). Despite its success, ACL's applicability is limited by (1) the lack of a general student framework for dealing with the varying number of agents across tasks and the sparse reward problem, and (2) the non-stationarity of the teacher's task due to ever-changing student strategies. As a remedy for ACL, we introduce a novel automatic curriculum learning framework, Skilled Population Curriculum (SPC), which adapts curriculum learning to multi-agent coordination. Specifically, we endow the student with population-invariant communication and a hierarchical skill set, allowing it to learn cooperation and behavior skills from distinct tasks with varying numbers of agents. In addition, we model the teacher as a contextual bandit conditioned by student policies, enabling a team of agents to change its size while still retaining previously acquired skills. We also analyze the inherent non-stationarity of this multi-agent automatic curriculum teaching problem and provide a corresponding regret bound. Empirical results show that our method improves the performance, scalability and sample efficiency in several MARL environments.
Learning to Maximize Mutual Information for Dynamic Feature Selection
Jan 02, 2023



Abstract:Feature selection helps reduce data acquisition costs in ML, but the standard approach is to train models with static feature subsets. Here, we consider the dynamic feature selection (DFS) problem where a model sequentially queries features based on the presently available information. DFS is often addressed with reinforcement learning (RL), but we explore a simpler approach of greedily selecting features based on their conditional mutual information. This method is theoretically appealing but requires oracle access to the data distribution, so we develop a learning approach based on amortized optimization. The proposed method is shown to recover the greedy policy when trained to optimality and outperforms numerous existing feature selection methods in our experiments, thus validating it as a simple but powerful approach for this problem.
CELLS: A Parallel Corpus for Biomedical Lay Language Generation
Nov 07, 2022
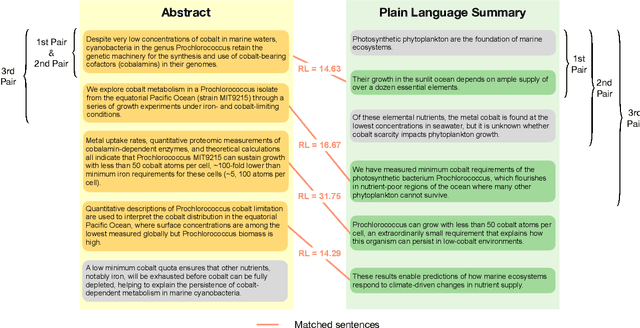
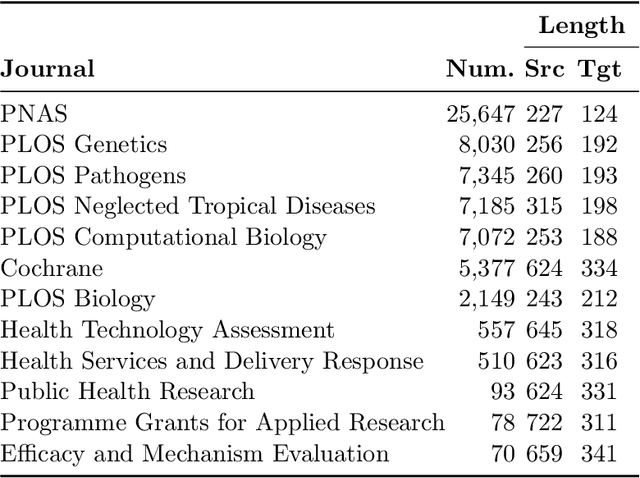
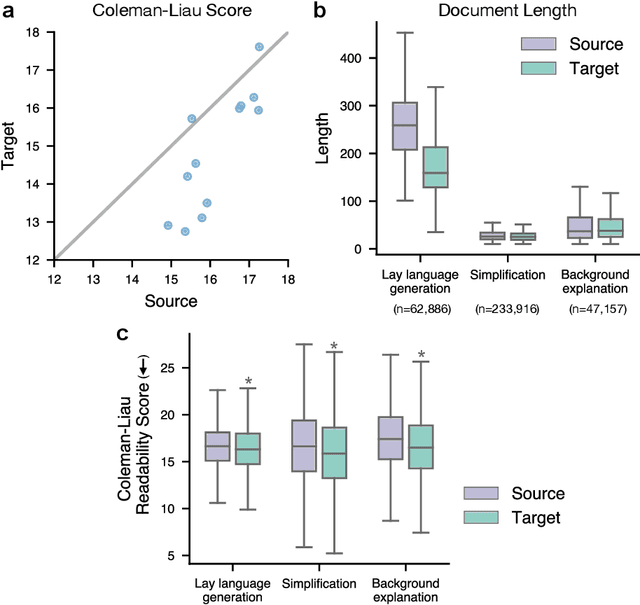
Abstract:Recent lay language generation systems have used Transformer models trained on a parallel corpus to increase health information accessibility. However, the applicability of these models is constrained by the limited size and topical breadth of available corpora. We introduce CELLS, the largest (63k pairs) and broadest-ranging (12 journals) parallel corpus for lay language generation. The abstract and the corresponding lay language summary are written by domain experts, assuring the quality of our dataset. Furthermore, qualitative evaluation of expert-authored plain language summaries has revealed background explanation as a key strategy to increase accessibility. Such explanation is challenging for neural models to generate because it goes beyond simplification by adding content absent from the source. We derive two specialized paired corpora from CELLS to address key challenges in lay language generation: generating background explanations and simplifying the original abstract. We adopt retrieval-augmented models as an intuitive fit for the task of background explanation generation, and show improvements in summary quality and simplicity while maintaining factual correctness. Taken together, this work presents the first comprehensive study of background explanation for lay language generation, paving the path for disseminating scientific knowledge to a broader audience. CELLS is publicly available at: https://github.com/LinguisticAnomalies/pls_retrieval.
RPM: Generalizable Behaviors for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Oct 18, 2022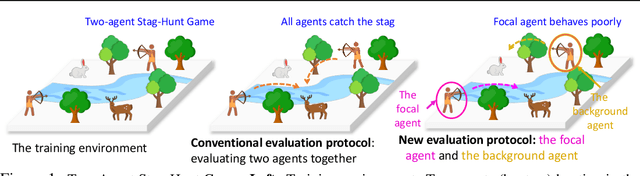
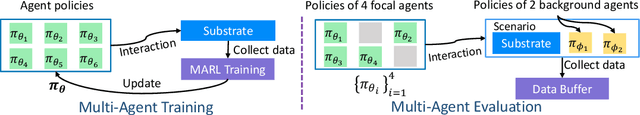
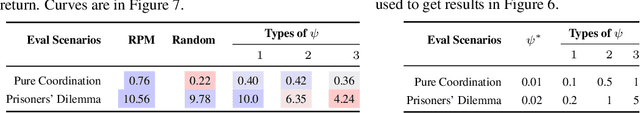
Abstract:Despite the recent advancement in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), the MARL agents easily overfit the training environment and perform poorly in the evaluation scenarios where other agents behave differently. Obtaining generalizable policies for MARL agents is thus necessary but challenging mainly due to complex multi-agent interactions. In this work, we model the problem with Markov Games and propose a simple yet effective method, ranked policy memory (RPM), to collect diverse multi-agent trajectories for training MARL policies with good generalizability. The main idea of RPM is to maintain a look-up memory of policies. In particular, we try to acquire various levels of behaviors by saving policies via ranking the training episode return, i.e., the episode return of agents in the training environment; when an episode starts, the learning agent can then choose a policy from the RPM as the behavior policy. This innovative self-play training framework leverages agents' past policies and guarantees the diversity of multi-agent interaction in the training data. We implement RPM on top of MARL algorithms and conduct extensive experiments on Melting Pot. It has been demonstrated that RPM enables MARL agents to interact with unseen agents in multi-agent generalization evaluation scenarios and complete given tasks, and it significantly boosts the performance up to 402% on average.
Off-Beat Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
May 27, 2022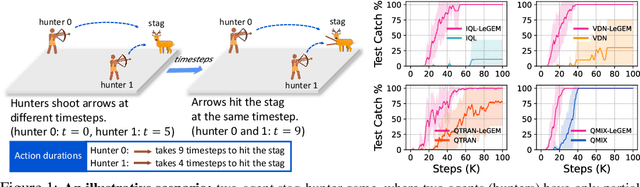
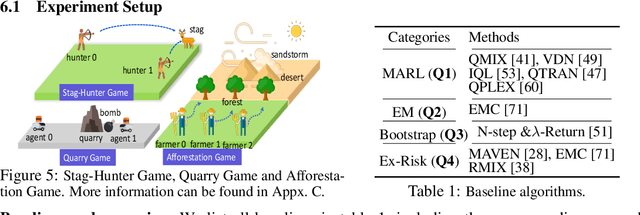

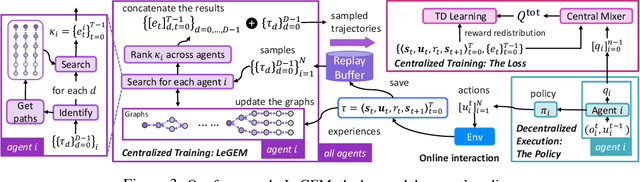
Abstract:We investigate model-free multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) in environments where off-beat actions are prevalent, i.e., all actions have pre-set execution durations. During execution durations, the environment changes are influenced by, but not synchronised with, action execution. Such a setting is ubiquitous in many real-world problems. However, most MARL methods assume actions are executed immediately after inference, which is often unrealistic and can lead to catastrophic failure for multi-agent coordination with off-beat actions. In order to fill this gap, we develop an algorithmic framework for MARL with off-beat actions. We then propose a novel episodic memory, LeGEM, for model-free MARL algorithms. LeGEM builds agents' episodic memories by utilizing agents' individual experiences. It boosts multi-agent learning by addressing the challenging temporal credit assignment problem raised by the off-beat actions via our novel reward redistribution scheme, alleviating the issue of non-Markovian reward. We evaluate LeGEM on various multi-agent scenarios with off-beat actions, including Stag-Hunter Game, Quarry Game, Afforestation Game, and StarCraft II micromanagement tasks. Empirical results show that LeGEM significantly boosts multi-agent coordination and achieves leading performance and improved sample efficiency.
Mis-spoke or mis-lead: Achieving Robustness in Multi-Agent Communicative Reinforcement Learning
Aug 09, 2021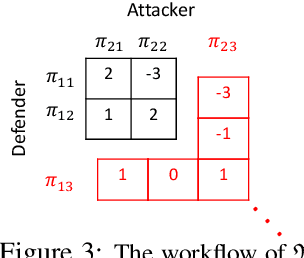
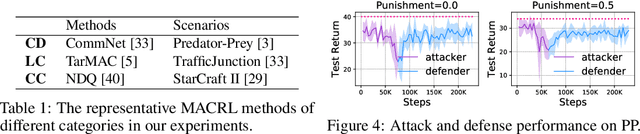
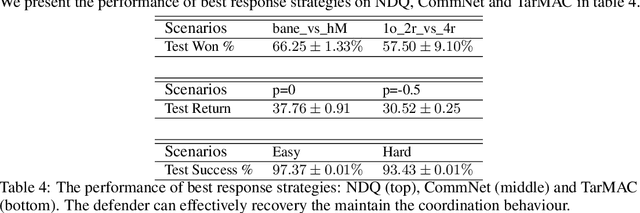
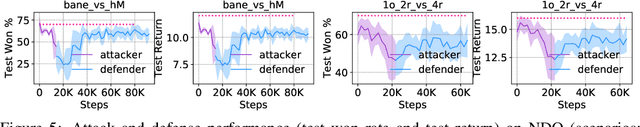
Abstract:Recent studies in multi-agent communicative reinforcement learning (MACRL) demonstrate that multi-agent coordination can be significantly improved when communication between agents is allowed. Meanwhile, advances in adversarial machine learning (ML) have shown that ML and reinforcement learning (RL) models are vulnerable to a variety of attacks that significantly degrade the performance of learned behaviours. However, despite the obvious and growing importance, the combination of adversarial ML and MACRL remains largely uninvestigated. In this paper, we make the first step towards conducting message attacks on MACRL methods. In our formulation, one agent in the cooperating group is taken over by an adversary and can send malicious messages to disrupt a deployed MACRL-based coordinated strategy during the deployment phase. We further our study by developing a defence method via message reconstruction. Finally, we address the resulting arms race, i.e., we consider the ability of the malicious agent to adapt to the changing and improving defensive communicative policies of the benign agents. Specifically, we model the adversarial MACRL problem as a two-player zero-sum game and then utilize Policy-Space Response Oracle to achieve communication robustness. Empirically, we demonstrate that MACRL methods are vulnerable to message attacks while our defence method the game-theoretic framework can effectively improve the robustness of MACRL.
Contingency-Aware Influence Maximization: A Reinforcement Learning Approach
Jun 13, 2021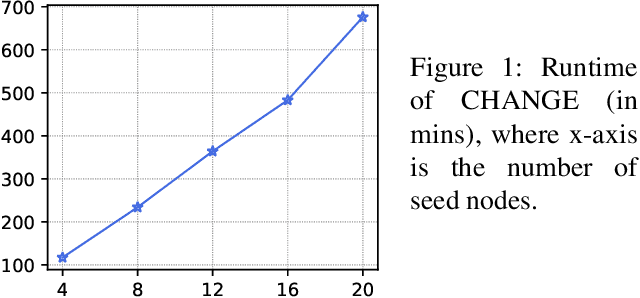
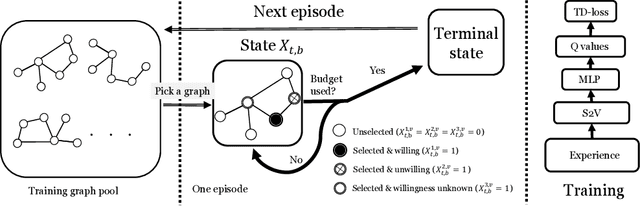
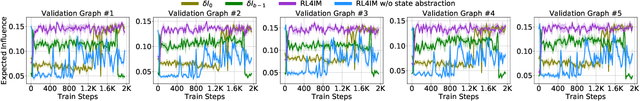
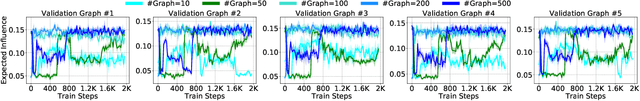
Abstract:The influence maximization (IM) problem aims at finding a subset of seed nodes in a social network that maximize the spread of influence. In this study, we focus on a sub-class of IM problems, where whether the nodes are willing to be the seeds when being invited is uncertain, called contingency-aware IM. Such contingency aware IM is critical for applications for non-profit organizations in low resource communities (e.g., spreading awareness of disease prevention). Despite the initial success, a major practical obstacle in promoting the solutions to more communities is the tremendous runtime of the greedy algorithms and the lack of high performance computing (HPC) for the non-profits in the field -- whenever there is a new social network, the non-profits usually do not have the HPCs to recalculate the solutions. Motivated by this and inspired by the line of works that use reinforcement learning (RL) to address combinatorial optimization on graphs, we formalize the problem as a Markov Decision Process (MDP), and use RL to learn an IM policy over historically seen networks, and generalize to unseen networks with negligible runtime at test phase. To fully exploit the properties of our targeted problem, we propose two technical innovations that improve the existing methods, including state-abstraction and theoretically grounded reward shaping. Empirical results show that our method achieves influence as high as the state-of-the-art methods for contingency-aware IM, while having negligible runtime at test phase.
RMIX: Learning Risk-Sensitive Policies for Cooperative Reinforcement Learning Agents
Feb 17, 2021
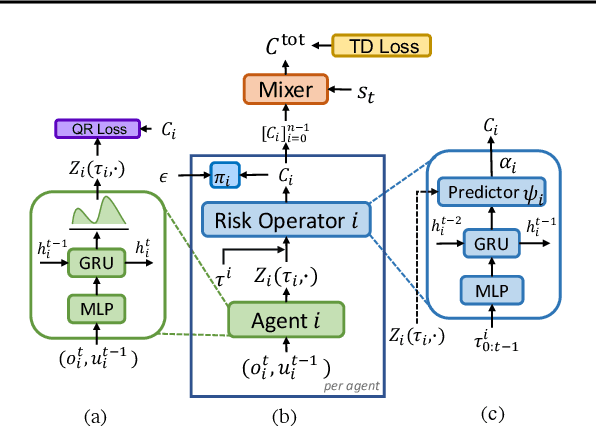
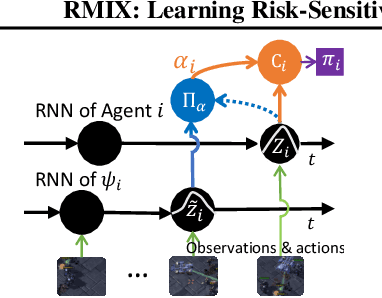
Abstract:Current value-based multi-agent reinforcement learning methods optimize individual Q values to guide individuals' behaviours via centralized training with decentralized execution (CTDE). However, such expected, i.e., risk-neutral, Q value is not sufficient even with CTDE due to the randomness of rewards and the uncertainty in environments, which causes the failure of these methods to train coordinating agents in complex environments. To address these issues, we propose RMIX, a novel cooperative MARL method with the Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR) measure over the learned distributions of individuals' Q values. Specifically, we first learn the return distributions of individuals to analytically calculate CVaR for decentralized execution. Then, to handle the temporal nature of the stochastic outcomes during executions, we propose a dynamic risk level predictor for risk level tuning. Finally, we optimize the CVaR policies with CVaR values used to estimate the target in TD error during centralized training and the CVaR values are used as auxiliary local rewards to update the local distribution via Quantile Regression loss. Empirically, we show that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on challenging StarCraft II tasks, demonstrating enhanced coordination and improved sample efficiency.
IFGAN: Missing Value Imputation using Feature-specific Generative Adversarial Networks
Dec 23, 2020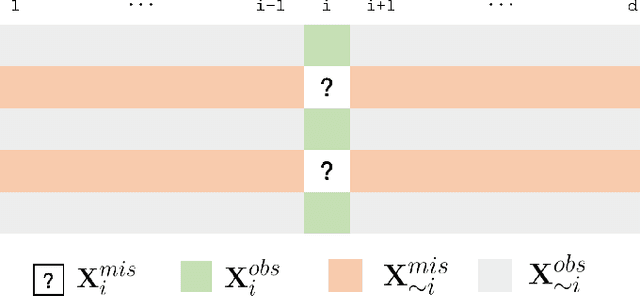
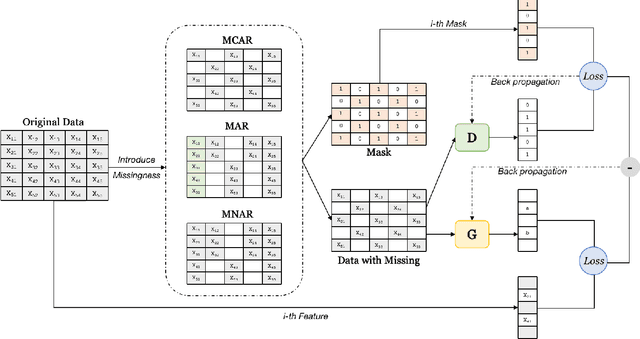
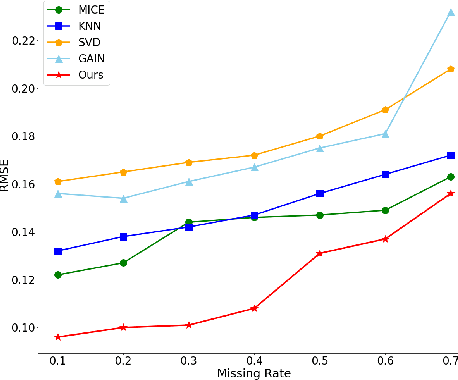
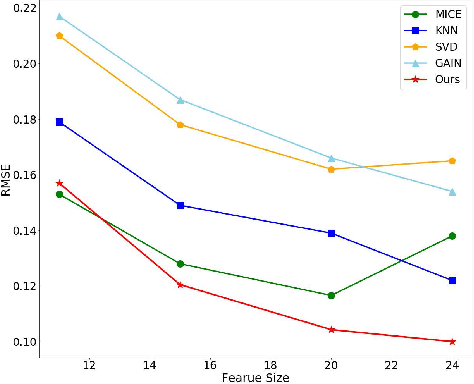
Abstract:Missing value imputation is a challenging and well-researched topic in data mining. In this paper, we propose IFGAN, a missing value imputation algorithm based on Feature-specific Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN). Our idea is intuitive yet effective: a feature-specific generator is trained to impute missing values, while a discriminator is expected to distinguish the imputed values from observed ones. The proposed architecture is capable of handling different data types, data distributions, missing mechanisms, and missing rates. It also improves post-imputation analysis by preserving inter-feature correlations. We empirically show on several real-life datasets that IFGAN outperforms current state-of-the-art algorithm under various missing conditions.
Automated Lay Language Summarization of Biomedical Scientific Reviews
Dec 23, 2020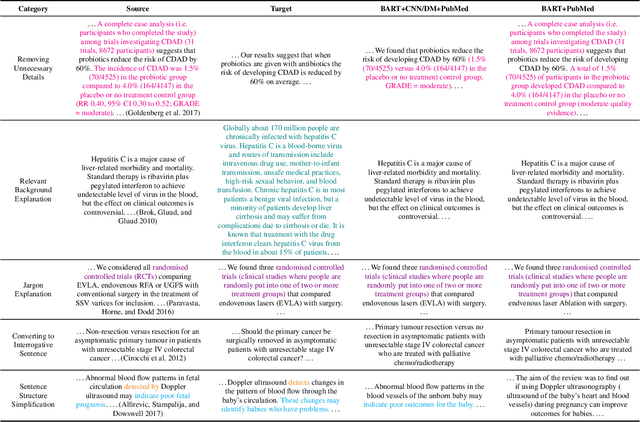
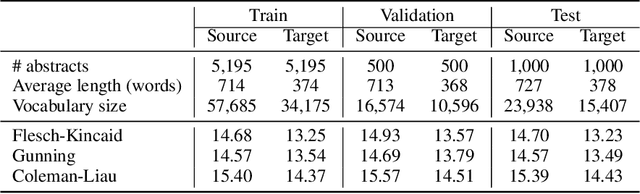
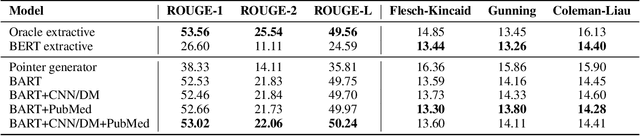
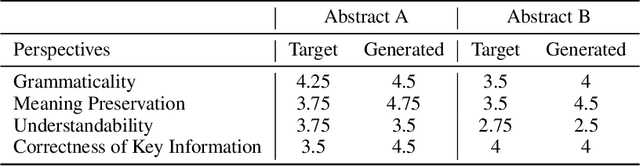
Abstract:Health literacy has emerged as a crucial factor in making appropriate health decisions and ensuring treatment outcomes. However, medical jargon and the complex structure of professional language in this domain make health information especially hard to interpret. Thus, there is an urgent unmet need for automated methods to enhance the accessibility of the biomedical literature to the general population. This problem can be framed as a type of translation problem between the language of healthcare professionals, and that of the general public. In this paper, we introduce the novel task of automated generation of lay language summaries of biomedical scientific reviews, and construct a dataset to support the development and evaluation of automated methods through which to enhance the accessibility of the biomedical literature. We conduct analyses of the various challenges in solving this task, including not only summarization of the key points but also explanation of background knowledge and simplification of professional language. We experiment with state-of-the-art summarization models as well as several data augmentation techniques, and evaluate their performance using both automated metrics and human assessment. Results indicate that automatically generated summaries produced using contemporary neural architectures can achieve promising quality and readability as compared with reference summaries developed for the lay public by experts (best ROUGE-L of 50.24 and Flesch-Kincaid readability score of 13.30). We also discuss the limitations of the current attempt, providing insights and directions for future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge