Quanzheng Li
CAMCA, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School
Adaptation of Agentic AI
Dec 22, 2025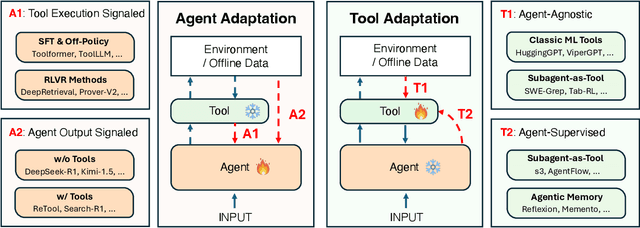
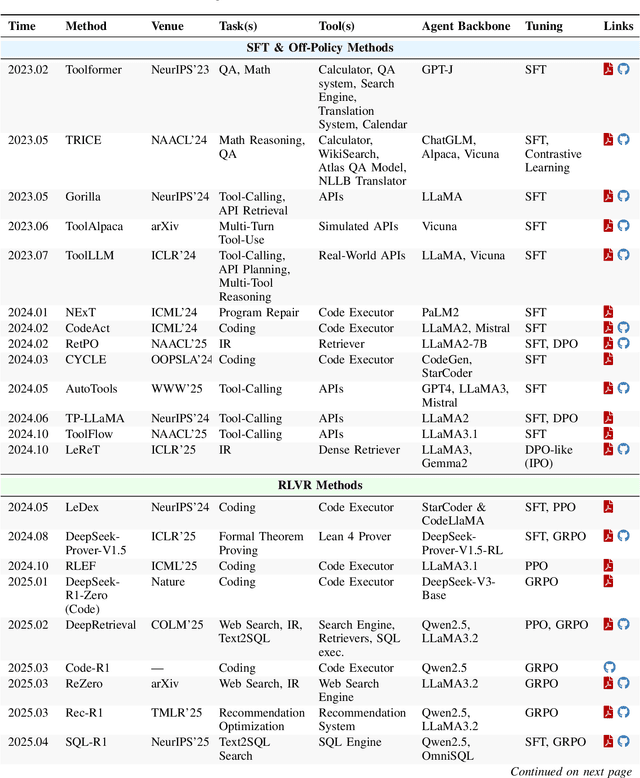
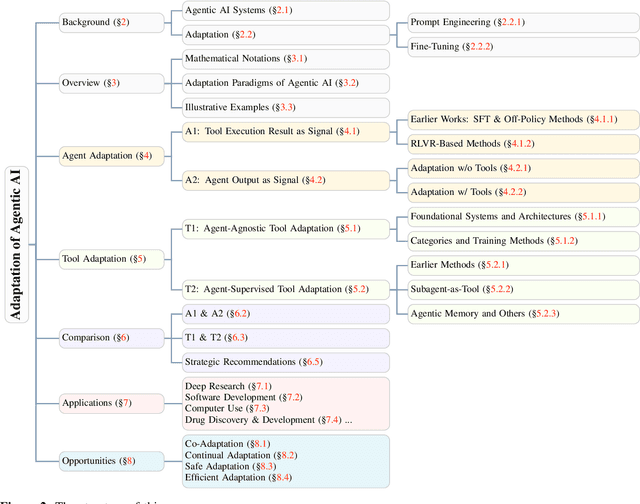
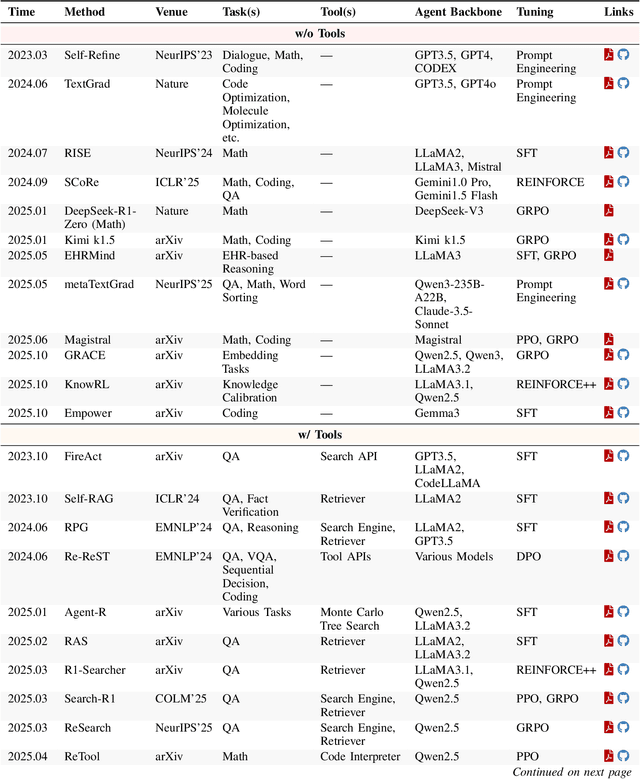
Abstract:Cutting-edge agentic AI systems are built on foundation models that can be adapted to plan, reason, and interact with external tools to perform increasingly complex and specialized tasks. As these systems grow in capability and scope, adaptation becomes a central mechanism for improving performance, reliability, and generalization. In this paper, we unify the rapidly expanding research landscape into a systematic framework that spans both agent adaptations and tool adaptations. We further decompose these into tool-execution-signaled and agent-output-signaled forms of agent adaptation, as well as agent-agnostic and agent-supervised forms of tool adaptation. We demonstrate that this framework helps clarify the design space of adaptation strategies in agentic AI, makes their trade-offs explicit, and provides practical guidance for selecting or switching among strategies during system design. We then review the representative approaches in each category, analyze their strengths and limitations, and highlight key open challenges and future opportunities. Overall, this paper aims to offer a conceptual foundation and practical roadmap for researchers and practitioners seeking to build more capable, efficient, and reliable agentic AI systems.
Projection Embedded Diffusion Bridge for CT Reconstruction from Incomplete Data
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing CT images from incomplete projection data remains challenging due to the ill-posed nature of the problem. Diffusion bridge models have recently shown promise in restoring clean images from their corresponding Filtered Back Projection (FBP) reconstructions, but incorporating data consistency into these models remains largely underexplored. Incorporating data consistency can improve reconstruction fidelity by aligning the reconstructed image with the observed projection data, and can enhance detail recovery by integrating structural information contained in the projections. In this work, we propose the Projection Embedded Diffusion Bridge (PEDB). PEDB introduces a novel reverse stochastic differential equation (SDE) to sample from the distribution of clean images conditioned on both the FBP reconstruction and the incomplete projection data. By explicitly conditioning on the projection data in sampling the clean images, PEDB naturally incorporates data consistency. We embed the projection data into the score function of the reverse SDE. Under certain assumptions, we derive a tractable expression for the posterior score. In addition, we introduce a free parameter to control the level of stochasticity in the reverse process. We also design a discretization scheme for the reverse SDE to mitigate discretization error. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PEDB achieves strong performance in CT reconstruction from three types of incomplete data, including sparse-view, limited-angle, and truncated projections. For each of these types, PEDB outperforms evaluated state-of-the-art diffusion bridge models across standard, noisy, and domain-shift evaluations.
RODS: Robust Optimization Inspired Diffusion Sampling for Detecting and Reducing Hallucination in Generative Models
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved state-of-the-art performance in generative modeling, yet their sampling procedures remain vulnerable to hallucinations, often stemming from inaccuracies in score approximation. In this work, we reinterpret diffusion sampling through the lens of optimization and introduce RODS (Robust Optimization-inspired Diffusion Sampler), a novel method that detects and corrects high-risk sampling steps using geometric cues from the loss landscape. RODS enforces smoother sampling trajectories and adaptively adjusts perturbations, reducing hallucinations without retraining and at minimal additional inference cost. Experiments on AFHQv2, FFHQ, and 11k-hands demonstrate that RODS improves both sampling fidelity and robustness, detecting over 70% of hallucinated samples and correcting more than 25%, all while avoiding the introduction of new artifacts.
Towards a general-purpose foundation model for fMRI analysis
Jun 11, 2025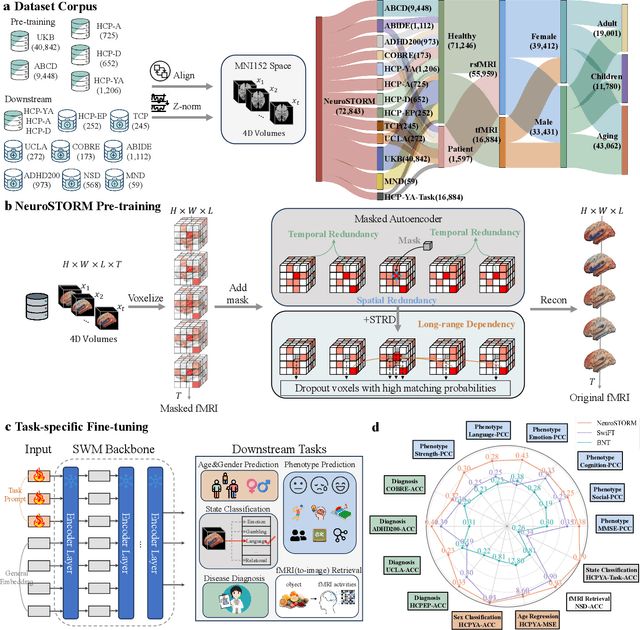

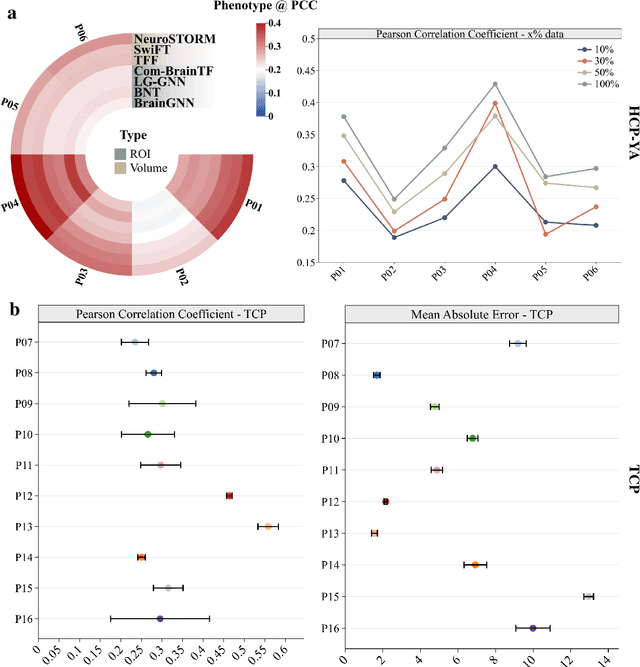
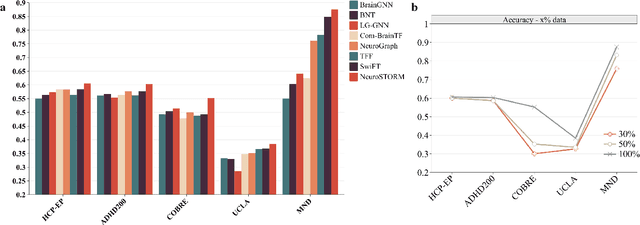
Abstract:Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) is essential for studying brain function and diagnosing neurological disorders, but current analysis methods face reproducibility and transferability issues due to complex pre-processing and task-specific models. We introduce NeuroSTORM (Neuroimaging Foundation Model with Spatial-Temporal Optimized Representation Modeling), a generalizable framework that directly learns from 4D fMRI volumes and enables efficient knowledge transfer across diverse applications. NeuroSTORM is pre-trained on 28.65 million fMRI frames (>9,000 hours) from over 50,000 subjects across multiple centers and ages 5 to 100. Using a Mamba backbone and a shifted scanning strategy, it efficiently processes full 4D volumes. We also propose a spatial-temporal optimized pre-training approach and task-specific prompt tuning to improve transferability. NeuroSTORM outperforms existing methods across five tasks: age/gender prediction, phenotype prediction, disease diagnosis, fMRI-to-image retrieval, and task-based fMRI classification. It demonstrates strong clinical utility on datasets from hospitals in the U.S., South Korea, and Australia, achieving top performance in disease diagnosis and cognitive phenotype prediction. NeuroSTORM provides a standardized, open-source foundation model to improve reproducibility and transferability in fMRI-based clinical research.
Surf2CT: Cascaded 3D Flow Matching Models for Torso 3D CT Synthesis from Skin Surface
May 29, 2025Abstract:We present Surf2CT, a novel cascaded flow matching framework that synthesizes full 3D computed tomography (CT) volumes of the human torso from external surface scans and simple demographic data (age, sex, height, weight). This is the first approach capable of generating realistic volumetric internal anatomy images solely based on external body shape and demographics, without any internal imaging. Surf2CT proceeds through three sequential stages: (1) Surface Completion, reconstructing a complete signed distance function (SDF) from partial torso scans using conditional 3D flow matching; (2) Coarse CT Synthesis, generating a low-resolution CT volume from the completed SDF and demographic information; and (3) CT Super-Resolution, refining the coarse volume into a high-resolution CT via a patch-wise conditional flow model. Each stage utilizes a 3D-adapted EDM2 backbone trained via flow matching. We trained our model on a combined dataset of 3,198 torso CT scans (approximately 1.13 million axial slices) sourced from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the AutoPET challenge. Evaluation on 700 paired torso surface-CT cases demonstrated strong anatomical fidelity: organ volumes exhibited small mean percentage differences (range from -11.1% to 4.4%), and muscle/fat body composition metrics matched ground truth with strong correlation (range from 0.67 to 0.96). Lung localization had minimal bias (mean difference -2.5 mm), and surface completion significantly improved metrics (Chamfer distance: from 521.8 mm to 2.7 mm; Intersection-over-Union: from 0.87 to 0.98). Surf2CT establishes a new paradigm for non-invasive internal anatomical imaging using only external data, opening opportunities for home-based healthcare, preventive medicine, and personalized clinical assessments without the risks associated with conventional imaging techniques.
Cascaded 3D Diffusion Models for Whole-body 3D 18-F FDG PET/CT synthesis from Demographics
May 28, 2025Abstract:We propose a cascaded 3D diffusion model framework to synthesize high-fidelity 3D PET/CT volumes directly from demographic variables, addressing the growing need for realistic digital twins in oncologic imaging, virtual trials, and AI-driven data augmentation. Unlike deterministic phantoms, which rely on predefined anatomical and metabolic templates, our method employs a two-stage generative process. An initial score-based diffusion model synthesizes low-resolution PET/CT volumes from demographic variables alone, providing global anatomical structures and approximate metabolic activity. This is followed by a super-resolution residual diffusion model that refines spatial resolution. Our framework was trained on 18-F FDG PET/CT scans from the AutoPET dataset and evaluated using organ-wise volume and standardized uptake value (SUV) distributions, comparing synthetic and real data between demographic subgroups. The organ-wise comparison demonstrated strong concordance between synthetic and real images. In particular, most deviations in metabolic uptake values remained within 3-5% of the ground truth in subgroup analysis. These findings highlight the potential of cascaded 3D diffusion models to generate anatomically and metabolically accurate PET/CT images, offering a robust alternative to traditional phantoms and enabling scalable, population-informed synthetic imaging for clinical and research applications.
OWT: A Foundational Organ-Wise Tokenization Framework for Medical Imaging
May 08, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in representation learning often rely on holistic, black-box embeddings that entangle multiple semantic components, limiting interpretability and generalization. These issues are especially critical in medical imaging. To address these limitations, we propose an Organ-Wise Tokenization (OWT) framework with a Token Group-based Reconstruction (TGR) training paradigm. Unlike conventional approaches that produce holistic features, OWT explicitly disentangles an image into separable token groups, each corresponding to a distinct organ or semantic entity. Our design ensures each token group encapsulates organ-specific information, boosting interpretability, generalization, and efficiency while allowing fine-grained control in downstream tasks. Experiments on CT and MRI datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of OWT in not only achieving strong image reconstruction and segmentation performance, but also enabling novel semantic-level generation and retrieval applications that are out of reach for standard holistic embedding methods. These findings underscore the potential of OWT as a foundational framework for semantically disentangled representation learning, offering broad scalability and applicability to real-world medical imaging scenarios and beyond.
MAST-Pro: Dynamic Mixture-of-Experts for Adaptive Segmentation of Pan-Tumors with Knowledge-Driven Prompts
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Accurate tumor segmentation is crucial for cancer diagnosis and treatment. While foundation models have advanced general-purpose segmentation, existing methods still struggle with: (1) limited incorporation of medical priors, (2) imbalance between generic and tumor-specific features, and (3) high computational costs for clinical adaptation. To address these challenges, we propose MAST-Pro (Mixture-of-experts for Adaptive Segmentation of pan-Tumors with knowledge-driven Prompts), a novel framework that integrates dynamic Mixture-of-Experts (D-MoE) and knowledge-driven prompts for pan-tumor segmentation. Specifically, text and anatomical prompts provide domain-specific priors, guiding tumor representation learning, while D-MoE dynamically selects experts to balance generic and tumor-specific feature learning, improving segmentation accuracy across diverse tumor types. To enhance efficiency, we employ Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT), optimizing MAST-Pro with significantly reduced computational overhead. Experiments on multi-anatomical tumor datasets demonstrate that MAST-Pro outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving up to a 5.20% improvement in average DSC while reducing trainable parameters by 91.04%, without compromising accuracy.
Anatomically and Metabolically Informed Diffusion for Unified Denoising and Segmentation in Low-Count PET Imaging
Mar 17, 2025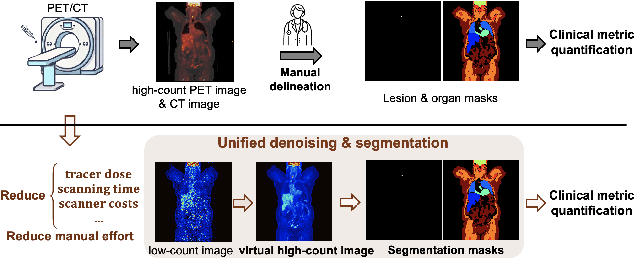
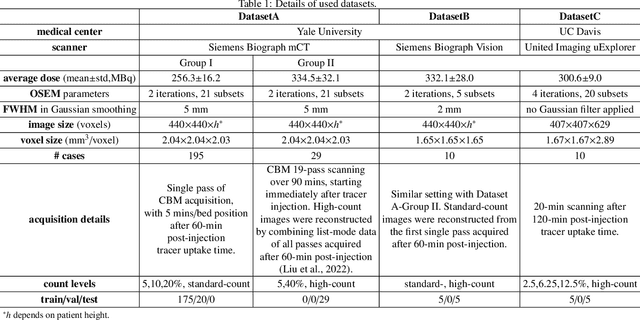
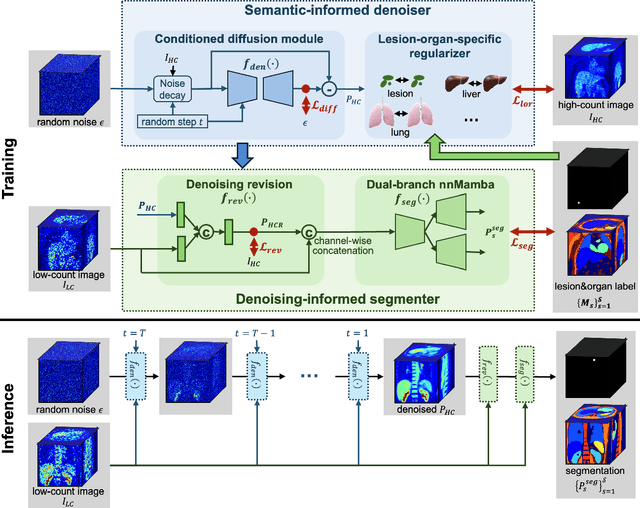
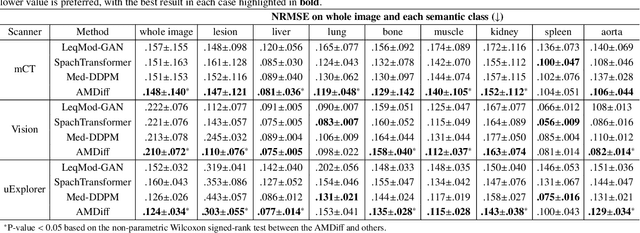
Abstract:Positron emission tomography (PET) image denoising, along with lesion and organ segmentation, are critical steps in PET-aided diagnosis. However, existing methods typically treat these tasks independently, overlooking inherent synergies between them as correlated steps in the analysis pipeline. In this work, we present the anatomically and metabolically informed diffusion (AMDiff) model, a unified framework for denoising and lesion/organ segmentation in low-count PET imaging. By integrating multi-task functionality and exploiting the mutual benefits of these tasks, AMDiff enables direct quantification of clinical metrics, such as total lesion glycolysis (TLG), from low-count inputs. The AMDiff model incorporates a semantic-informed denoiser based on diffusion strategy and a denoising-informed segmenter utilizing nnMamba architecture. The segmenter constrains denoised outputs via a lesion-organ-specific regularizer, while the denoiser enhances the segmenter by providing enriched image information through a denoising revision module. These components are connected via a warming-up mechanism to optimize multitask interactions. Experiments on multi-vendor, multi-center, and multi-noise-level datasets demonstrate the superior performance of AMDiff. For test cases below 20% of the clinical count levels from participating sites, AMDiff achieves TLG quantification biases of -26.98%, outperforming its ablated versions which yield biases of -35.85% (without the lesion-organ-specific regularizer) and -40.79% (without the denoising revision module).
Prediction of Frozen Region Growth in Kidney Cryoablation Intervention Using a 3D Flow-Matching Model
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:This study presents a 3D flow-matching model designed to predict the progression of the frozen region (iceball) during kidney cryoablation. Precise intraoperative guidance is critical in cryoablation to ensure complete tumor eradication while preserving adjacent healthy tissue. However, conventional methods, typically based on physics driven or diffusion based simulations, are computationally demanding and often struggle to represent complex anatomical structures accurately. To address these limitations, our approach leverages intraoperative CT imaging to inform the model. The proposed 3D flow matching model is trained to learn a continuous deformation field that maps early-stage CT scans to future predictions. This transformation not only estimates the volumetric expansion of the iceball but also generates corresponding segmentation masks, effectively capturing spatial and morphological changes over time. Quantitative analysis highlights the model robustness, demonstrating strong agreement between predictions and ground-truth segmentations. The model achieves an Intersection over Union (IoU) score of 0.61 and a Dice coefficient of 0.75. By integrating real time CT imaging with advanced deep learning techniques, this approach has the potential to enhance intraoperative guidance in kidney cryoablation, improving procedural outcomes and advancing the field of minimally invasive surgery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge