Carl Yang
Position: General Alignment Has Hit a Ceiling; Edge Alignment Must Be Taken Seriously
Feb 23, 2026Abstract:Large language models are being deployed in complex socio-technical systems, which exposes limits in current alignment practice. We take the position that the dominant paradigm of General Alignment, which compresses diverse human values into a single scalar reward, reaches a structural ceiling in settings with conflicting values, plural stakeholders, and irreducible uncertainty. These failures follow from the mathematics and incentives of scalarization and lead to \textbf{structural} value flattening, \textbf{normative} representation loss, and \textbf{cognitive} uncertainty blindness. We introduce Edge Alignment as a distinct approach in which systems preserve multi dimensional value structure, support plural and democratic representation, and incorporate epistemic mechanisms for interaction and clarification. To make this approach practical, we propose seven interdependent pillars organized into three phases. We identify key challenges in data collection, training objectives, and evaluation, outlining complementary technical and governance directions. Taken together, these measures reframe alignment as a lifecycle problem of dynamic normative governance rather than as a single instance optimization task.
Traceable Latent Variable Discovery Based on Multi-Agent Collaboration
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Revealing the underlying causal mechanisms in the real world is crucial for scientific and technological progress. Despite notable advances in recent decades, the lack of high-quality data and the reliance of traditional causal discovery algorithms (TCDA) on the assumption of no latent confounders, as well as their tendency to overlook the precise semantics of latent variables, have long been major obstacles to the broader application of causal discovery. To address this issue, we propose a novel causal modeling framework, TLVD, which integrates the metadata-based reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) with the data-driven modeling capabilities of TCDA for inferring latent variables and their semantics. Specifically, we first employ a data-driven approach to construct a causal graph that incorporates latent variables. Then, we employ multi-LLM collaboration for latent variable inference, modeling this process as a game with incomplete information and seeking its Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (BNE) to infer the possible specific latent variables. Finally, to validate the inferred latent variables across multiple real-world web-based data sources, we leverage LLMs for evidence exploration to ensure traceability. We comprehensively evaluate TLVD on three de-identified real patient datasets provided by a hospital and two benchmark datasets. Extensive experimental results confirm the effectiveness and reliability of TLVD, with average improvements of 32.67% in Acc, 62.21% in CAcc, and 26.72% in ECit across the five datasets.
Alternating Reinforcement Learning for Rubric-Based Reward Modeling in Non-Verifiable LLM Post-Training
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Standard reward models typically predict scalar scores that fail to capture the multifaceted nature of response quality in non-verifiable domains, such as creative writing or open-ended instruction following. To address this limitation, we propose Rubric-ARM, a framework that jointly optimizes a rubric generator and a judge using reinforcement learning from preference feedback. Unlike existing methods that rely on static rubrics or disjoint training pipelines, our approach treats rubric generation as a latent action learned to maximize judgment accuracy. We introduce an alternating optimization strategy to mitigate the non-stationarity of simultaneous updates, providing theoretical analysis that demonstrates how this schedule reduces gradient variance during training. Extensive experiments show that Rubric-ARM achieves state-of-the-art performance among baselines on multiple benchmarks and significantly improves downstream policy alignment in both offline and online reinforcement learning settings.
Transferable Graph Condensation from the Causal Perspective
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:The increasing scale of graph datasets has significantly improved the performance of graph representation learning methods, but it has also introduced substantial training challenges. Graph dataset condensation techniques have emerged to compress large datasets into smaller yet information-rich datasets, while maintaining similar test performance. However, these methods strictly require downstream applications to match the original dataset and task, which often fails in cross-task and cross-domain scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose a novel causal-invariance-based and transferable graph dataset condensation method, named \textbf{TGCC}, providing effective and transferable condensed datasets. Specifically, to preserve domain-invariant knowledge, we first extract domain causal-invariant features from the spatial domain of the graph using causal interventions. Then, to fully capture the structural and feature information of the original graph, we perform enhanced condensation operations. Finally, through spectral-domain enhanced contrastive learning, we inject the causal-invariant features into the condensed graph, ensuring that the compressed graph retains the causal information of the original graph. Experimental results on five public datasets and our novel \textbf{FinReport} dataset demonstrate that TGCC achieves up to a 13.41\% improvement in cross-task and cross-domain complex scenarios compared to existing methods, and achieves state-of-the-art performance on 5 out of 6 datasets in the single dataset and task scenario.
Imaging-anchored Multiomics in Cardiovascular Disease: Integrating Cardiac Imaging, Bulk, Single-cell, and Spatial Transcriptomics
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Cardiovascular disease arises from interactions between inherited risk, molecular programmes, and tissue-scale remodelling that are observed clinically through imaging. Health systems now routinely generate large volumes of cardiac MRI, CT and echocardiography together with bulk, single-cell and spatial transcriptomics, yet these data are still analysed in separate pipelines. This review examines joint representations that link cardiac imaging phenotypes to transcriptomic and spatially resolved molecular states. An imaging-anchored perspective is adopted in which echocardiography, cardiac MRI and CT define a spatial phenotype of the heart, and bulk, single-cell and spatial transcriptomics provide cell-type- and location-specific molecular context. The biological and technical characteristics of these modalities are first summarised, and representation-learning strategies for each are outlined. Multimodal fusion approaches are reviewed, with emphasis on handling missing data, limited sample size, and batch effects. Finally, integrative pipelines for radiogenomics, spatial molecular alignment, and image-based prediction of gene expression are discussed, together with common failure modes, practical considerations, and open challenges. Spatial multiomics of human myocardium and atherosclerotic plaque, single-cell and spatial foundation models, and multimodal medical foundation models are collectively bringing imaging-anchored multiomics closer to large-scale cardiovascular translation.
EpiQAL: Benchmarking Large Language Models in Epidemiological Question Answering for Enhanced Alignment and Reasoning
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Reliable epidemiological reasoning requires synthesizing study evidence to infer disease burden, transmission dynamics, and intervention effects at the population level. Existing medical question answering benchmarks primarily emphasize clinical knowledge or patient-level reasoning, yet few systematically evaluate evidence-grounded epidemiological inference. We present EpiQAL, the first diagnostic benchmark for epidemiological question answering across diverse diseases, comprising three subsets built from open-access literature. The subsets respectively evaluate text-grounded factual recall, multi-step inference linking document evidence with epidemiological principles, and conclusion reconstruction with the Discussion section withheld. Construction combines expert-designed taxonomy guidance, multi-model verification, and retrieval-based difficulty control. Experiments on ten open models reveal that current LLMs show limited performance on epidemiological reasoning, with multi-step inference posing the greatest challenge. Model rankings shift across subsets, and scale alone does not predict success. Chain-of-Thought prompting benefits multi-step inference but yields mixed results elsewhere. EpiQAL provides fine-grained diagnostic signals for evidence grounding, inferential reasoning, and conclusion reconstruction.
BioMedJImpact: A Comprehensive Dataset and LLM Pipeline for AI Engagement and Scientific Impact Analysis of Biomedical Journals
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Assessing journal impact is central to scholarly communication, yet existing open resources rarely capture how collaboration structures and artificial intelligence (AI) research jointly shape venue prestige in biomedicine. We present BioMedJImpact, a large-scale, biomedical-oriented dataset designed to advance journal-level analysis of scientific impact and AI engagement. Built from 1.74 million PubMed Central articles across 2,744 journals, BioMedJImpact integrates bibliometric indicators, collaboration features, and LLM-derived semantic indicators for AI engagement. Specifically, the AI engagement feature is extracted through a reproducible three-stage LLM pipeline that we propose. Using this dataset, we analyze how collaboration intensity and AI engagement jointly influence scientific impact across pre- and post-pandemic periods (2016-2019, 2020-2023). Two consistent trends emerge: journals with higher collaboration intensity, particularly those with larger and more diverse author teams, tend to achieve greater citation impact, and AI engagement has become an increasingly strong correlate of journal prestige, especially in quartile rankings. To further validate the three-stage LLM pipeline we proposed for deriving the AI engagement feature, we conduct human evaluation, confirming substantial agreement in AI relevance detection and consistent subfield classification. Together, these contributions demonstrate that BioMedJImpact serves as both a comprehensive dataset capturing the intersection of biomedicine and AI, and a validated methodological framework enabling scalable, content-aware scientometric analysis of scientific impact and innovation dynamics. Code is available at https://github.com/JonathanWry/BioMedJImpact.
Simulator and Experience Enhanced Diffusion Model for Comprehensive ECG Generation
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Electrocardiograms (ECGs) are the most widely used non-invasive tool for cardiac assessment, yet large, well-annotated ECG corpora are scarce due to cost, privacy, and workflow constraints. Generating ECGs can be beneficial for the mechanistic understanding of cardiac electrical activity, enable the construction of large, heterogeneous, and unbiased datasets, and facilitate privacy-preserving data sharing. Generating realistic ECG signals from clinical context is important yet underexplored. Recent work has leveraged diffusion models for text-to-ECG generation, but two challenges remain: (i) existing methods often overlook the physiological simulator knowledge of cardiac activity; and (ii) they ignore broader, experience-based clinical knowledge grounded in real-world practice. To address these gaps, we propose SE-Diff, a novel physiological simulator and experience enhanced diffusion model for comprehensive ECG generation. SE-Diff integrates a lightweight ordinary differential equation (ODE)-based ECG simulator into the diffusion process via a beat decoder and simulator-consistent constraints, injecting mechanistic priors that promote physiologically plausible waveforms. In parallel, we design an LLM-powered experience retrieval-augmented strategy to inject clinical knowledge, providing more guidance for ECG generation. Extensive experiments on real-world ECG datasets demonstrate that SE-Diff improves both signal fidelity and text-ECG semantic alignment over baselines, proving its superiority for text-to-ECG generation. We further show that the simulator-based and experience-based knowledge also benefit downstream ECG classification.
Peeling Context from Cause for Multimodal Molecular Property Prediction
Nov 10, 2025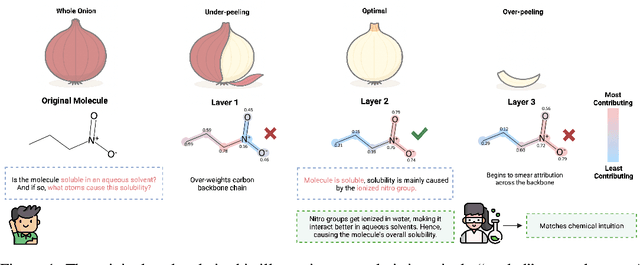
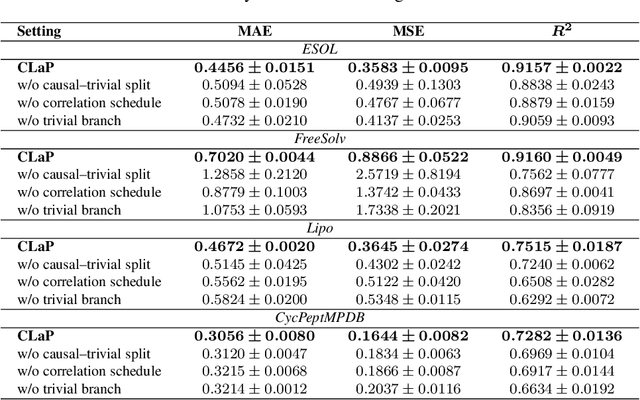
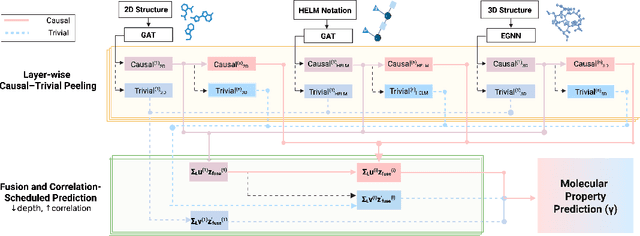
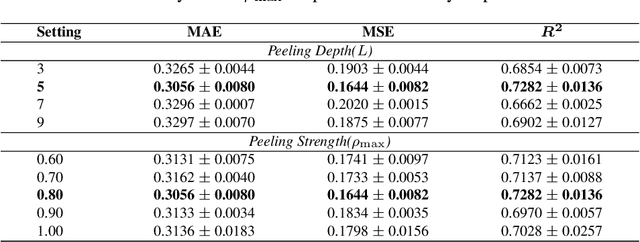
Abstract:Deep models are used for molecular property prediction, yet they are often difficult to interpret and may rely on spurious context rather than causal structure, which reduces reliability under distribution shift and harms predictive performance. We introduce CLaP (Causal Layerwise Peeling), a framework that separates causal signal from context in a layerwise manner and integrates diverse graph representations of molecules. At each layer, a causal block performs a soft split into causal and non-causal branches, fuses causal evidence across modalities, and progressively removes batch-coupled context to focus on label-relevant structure, thereby limiting shortcut signals and stabilizing layerwise refinement. Across four molecular benchmarks, CLaP consistently improves MAE, MSE, and $R^2$ over competitive baselines. The model also produces atom-level causal saliency maps that highlight substructures responsible for predictions, providing actionable guidance for targeted molecular edits. Case studies confirm the accuracy of these maps and their alignment with chemical intuition. By peeling context from cause at every layer, the model yields predictors that are both accurate and interpretable for molecular design.
Conditional Neural ODE for Longitudinal Parkinson's Disease Progression Forecasting
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Parkinson's disease (PD) shows heterogeneous, evolving brain-morphometry patterns. Modeling these longitudinal trajectories enables mechanistic insight, treatment development, and individualized 'digital-twin' forecasting. However, existing methods usually adopt recurrent neural networks and transformer architectures, which rely on discrete, regularly sampled data while struggling to handle irregular and sparse magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in PD cohorts. Moreover, these methods have difficulty capturing individual heterogeneity including variations in disease onset, progression rate, and symptom severity, which is a hallmark of PD. To address these challenges, we propose CNODE (Conditional Neural ODE), a novel framework for continuous, individualized PD progression forecasting. The core of CNODE is to model morphological brain changes as continuous temporal processes using a neural ODE model. In addition, we jointly learn patient-specific initial time and progress speed to align individual trajectories into a shared progression trajectory. We validate CNODE on the Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) dataset. Experimental results show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in forecasting longitudinal PD progression.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge