Mingjie Tang
Large-Scale Terminal Agentic Trajectory Generation from Dockerized Environments
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Training agentic models for terminal-based tasks critically depends on high-quality terminal trajectories that capture realistic long-horizon interactions across diverse domains. However, constructing such data at scale remains challenging due to two key requirements: \textbf{\emph{Executability}}, since each instance requires a suitable and often distinct Docker environment; and \textbf{\emph{Verifiability}}, because heterogeneous task outputs preclude unified, standardized verification. To address these challenges, we propose \textbf{TerminalTraj}, a scalable pipeline that (i) filters high-quality repositories to construct Dockerized execution environments, (ii) generates Docker-aligned task instances, and (iii) synthesizes agent trajectories with executable validation code. Using TerminalTraj, we curate 32K Docker images and generate 50,733 verified terminal trajectories across eight domains. Models trained on this data with the Qwen2.5-Coder backbone achieve consistent performance improvements on TerminalBench (TB), with gains of up to 20\% on TB~1.0 and 10\% on TB~2.0 over their respective backbones. Notably, \textbf{TerminalTraj-32B} achieves strong performance among models with fewer than 100B parameters, reaching 35.30\% on TB~1.0 and 22.00\% on TB~2.0, and demonstrates improved test-time scaling behavior. All code and data are available at https://github.com/Wusiwei0410/TerminalTraj.
Close the Loop: Synthesizing Infinite Tool-Use Data via Multi-Agent Role-Playing
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Enabling Large Language Models (LLMs) to reliably invoke external tools remains a critical bottleneck for autonomous agents. Existing approaches suffer from three fundamental challenges: expensive human annotation for high-quality trajectories, poor generalization to unseen tools, and quality ceilings inherent in single-model synthesis that perpetuate biases and coverage gaps. We introduce InfTool, a fully autonomous framework that breaks these barriers through self-evolving multi-agent synthesis. Given only raw API specifications, InfTool orchestrates three collaborative agents (User Simulator, Tool-Calling Assistant, and MCP Server) to generate diverse, verified trajectories spanning single-turn calls to complex multi-step workflows. The framework establishes a closed loop: synthesized data trains the model via Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with gated rewards, the improved model generates higher-quality data targeting capability gaps, and this cycle iterates without human intervention. Experiments on the Berkeley Function-Calling Leaderboard (BFCL) demonstrate that InfTool transforms a base 32B model from 19.8% to 70.9% accuracy (+258%), surpassing models 10x larger and rivaling Claude-Opus, and entirely from synthetic data without human annotation.
AGRO-SQL: Agentic Group-Relative Optimization with High-Fidelity Data Synthesis
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:The advancement of Text-to-SQL systems is currently hindered by the scarcity of high-quality training data and the limited reasoning capabilities of models in complex scenarios. In this paper, we propose a holistic framework that addresses these issues through a dual-centric approach. From a Data-Centric perspective, we construct an iterative data factory that synthesizes RL-ready data characterized by high correctness and precise semantic-logic alignment, ensured by strict verification. From a Model-Centric perspective, we introduce a novel Agentic Reinforcement Learning framework. This framework employs a Diversity-Aware Cold Start stage to initialize a robust policy, followed by Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to refine the agent's reasoning via environmental feedback. Extensive experiments on BIRD and Spider benchmarks demonstrate that our synergistic approach achieves state-of-the-art performance among single-model methods.
Temporal-IRL: Modeling Port Congestion and Berth Scheduling with Inverse Reinforcement Learning
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Predicting port congestion is crucial for maintaining reliable global supply chains. Accurate forecasts enableimprovedshipment planning, reducedelaysand costs, and optimizeinventoryanddistributionstrategies, thereby ensuring timely deliveries and enhancing supply chain resilience. To achieve accurate predictions, analyzing vessel behavior and their stay times at specific port terminals is essential, focusing particularly on berth scheduling under various conditions. Crucially, the model must capture and learn the underlying priorities and patterns of berth scheduling. Berth scheduling and planning are influenced by a range of factors, including incoming vessel size, waiting times, and the status of vessels within the port terminal. By observing historical Automatic Identification System (AIS) positions of vessels, we reconstruct berth schedules, which are subsequently utilized to determine the reward function via Inverse Reinforcement Learning (IRL). For this purpose, we modeled a specific terminal at the Port of New York/New Jersey and developed Temporal-IRL. This Temporal-IRL model learns berth scheduling to predict vessel sequencing at the terminal and estimate vessel port stay, encompassing both waiting and berthing times, to forecast port congestion. Utilizing data from Maher Terminal spanning January 2015 to September 2023, we trained and tested the model, achieving demonstrably excellent results.
QUITE: A Query Rewrite System Beyond Rules with LLM Agents
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Query rewrite transforms SQL queries into semantically equivalent forms that run more efficiently. Existing approaches mainly rely on predefined rewrite rules, but they handle a limited subset of queries and can cause performance regressions. This limitation stems from three challenges of rule-based query rewrite: (1) it is hard to discover and verify new rules, (2) fixed rewrite rules do not generalize to new query patterns, and (3) some rewrite techniques cannot be expressed as fixed rules. Motivated by the fact that human experts exhibit significantly better rewrite ability but suffer from scalability, and Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated nearly human-level semantic and reasoning abilities, we propose a new approach of using LLMs to rewrite SQL queries beyond rules. Due to the hallucination problems in LLMs, directly applying LLMs often leads to nonequivalent and suboptimal queries. To address this issue, we propose QUITE (query rewrite), a training-free and feedback-aware system based on LLM agents that rewrites SQL queries into semantically equivalent forms with significantly better performance, covering a broader range of query patterns and rewrite strategies compared to rule-based methods. Firstly, we design a multi-agent framework controlled by a finite state machine (FSM) to equip LLMs with the ability to use external tools and enhance the rewrite process with real-time database feedback. Secondly, we develop a rewrite middleware to enhance the ability of LLMs to generate optimized query equivalents. Finally, we employ a novel hint injection technique to improve execution plans for rewritten queries. Extensive experiments show that QUITE reduces query execution time by up to 35.8% over state-of-the-art approaches and produces 24.1% more rewrites than prior methods, covering query cases that earlier systems did not handle.
CloneShield: A Framework for Universal Perturbation Against Zero-Shot Voice Cloning
May 25, 2025Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in text-to-speech (TTS) voice cloning have raised serious privacy concerns, allowing highly accurate vocal identity replication from just a few seconds of reference audio, while retaining the speaker's vocal authenticity. In this paper, we introduce CloneShield, a universal time-domain adversarial perturbation framework specifically designed to defend against zero-shot voice cloning. Our method provides protection that is robust across speakers and utterances, without requiring any prior knowledge of the synthesized text. We formulate perturbation generation as a multi-objective optimization problem, and propose Multi-Gradient Descent Algorithm (MGDA) to ensure the robust protection across diverse utterances. To preserve natural auditory perception for users, we decompose the adversarial perturbation via Mel-spectrogram representations and fine-tune it for each sample. This design ensures imperceptibility while maintaining strong degradation effects on zero-shot cloned outputs. Experiments on three state-of-the-art zero-shot TTS systems, five benchmark datasets and evaluations from 60 human listeners demonstrate that our method preserves near-original audio quality in protected inputs (PESQ = 3.90, SRS = 0.93) while substantially degrading both speaker similarity and speech quality in cloned samples (PESQ = 1.07, SRS = 0.08).
Concise Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Despite significant advancements in large language models (LLMs), a major drawback of reasoning models is their enormous token usage, which increases computational cost, resource requirements, and response time. In this work, we revisit the core principles of reinforcement learning (RL) and, through mathematical analysis, demonstrate that the tendency to generate lengthy responses arises inherently from RL-based optimization during training. This finding questions the prevailing assumption that longer responses inherently improve reasoning accuracy. Instead, we uncover a natural correlation between conciseness and accuracy that has been largely overlooked. Moreover, we show that introducing a secondary phase of RL post-training, using a small set of problems and limited resources, can significantly reduce a model's chain of thought while maintaining or even enhancing accuracy. Finally, we validate our conclusions through extensive experimental results.
DynMoLE: Boosting Mixture of LoRA Experts Fine-Tuning with a Hybrid Routing Mechanism
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Instruction-based fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) has achieved remarkable success in various natural language processing (NLP) tasks. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods, such as Mixture of LoRA Experts (MoLE), combine the efficiency of Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) with the versatility of Mixture of Experts (MoE) models, demonstrating significant potential for handling multiple downstream tasks. However, the existing routing mechanisms for MoLE often involve a trade-off between computational efficiency and predictive accuracy, and they fail to fully address the diverse expert selection demands across different transformer layers. In this work, we propose DynMoLE, a hybrid routing strategy that dynamically adjusts expert selection based on the Tsallis entropy of the router's probability distribution. This approach mitigates router uncertainty, enhances stability, and promotes more equitable expert participation, leading to faster convergence and improved model performance. Additionally, we introduce an auxiliary loss based on Tsallis entropy to further guide the model toward convergence with reduced uncertainty, thereby improving training stability and performance. Our extensive experiments on commonsense reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that DynMoLE achieves substantial performance improvements, outperforming LoRA by 9.6% and surpassing the state-of-the-art MoLE method, MoLA, by 2.3%. We also conduct a comprehensive ablation study to evaluate the contributions of DynMoLE's key components.
MixLoRA: Enhancing Large Language Models Fine-Tuning with LoRA based Mixture of Experts
Apr 22, 2024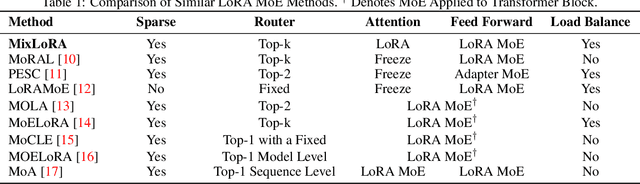
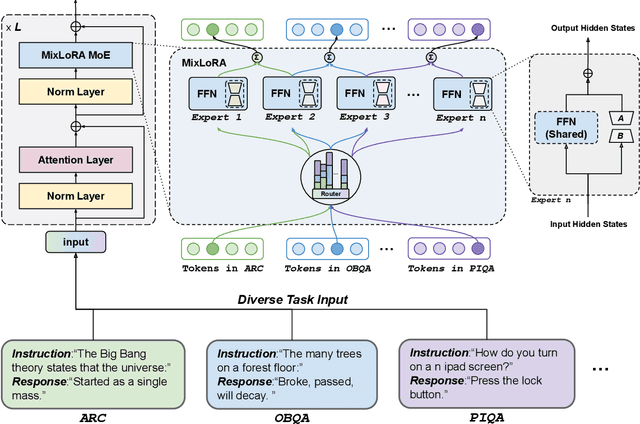

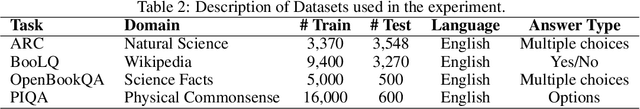
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have showcased exceptional performance across a wide array of Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. Fine-tuning techniques are commonly utilized to tailor pre-trained models to specific applications. While methods like LoRA have effectively tackled GPU memory constraints during fine-tuning, their applicability is often restricted to limited performance, especially on multi-task. On the other hand, Mix-of-Expert (MoE) models, such as Mixtral 8x7B, demonstrate remarkable performance across multiple NLP tasks while maintaining a reduced parameter count. However, the resource requirements of these MoEs still challenging, particularly for consumer-grade GPUs only have limited VRAM. To address these challenge, we propose MixLoRA, an innovative approach aimed at constructing a resource-efficient sparse MoE model based on LoRA. MixLoRA inserts multiple LoRA-based experts within the feed-forward network block of a frozen pre-trained dense model through fine-tuning, employing a commonly used top-k router. Unlike other LoRA based MoE methods, MixLoRA enhances model performance by utilizing independently configurable attention-layer LoRA adapters, supporting the use of LoRA and its variants for the construction of experts, and applying auxiliary load balance loss to address the imbalance problem of the router. In experiments, MixLoRA achieves commendable performance across all evaluation metrics in both single-task and multi-task learning scenarios. Implemented within the m-LoRA framework, MixLoRA enables parallel fine-tuning of multiple mixture-of-experts models on a single 24GB consumer-grade GPU without quantization, thereby reducing GPU memory consumption by 41\% and latency during the training process by 17\%.
BadPart: Unified Black-box Adversarial Patch Attacks against Pixel-wise Regression Tasks
Apr 01, 2024
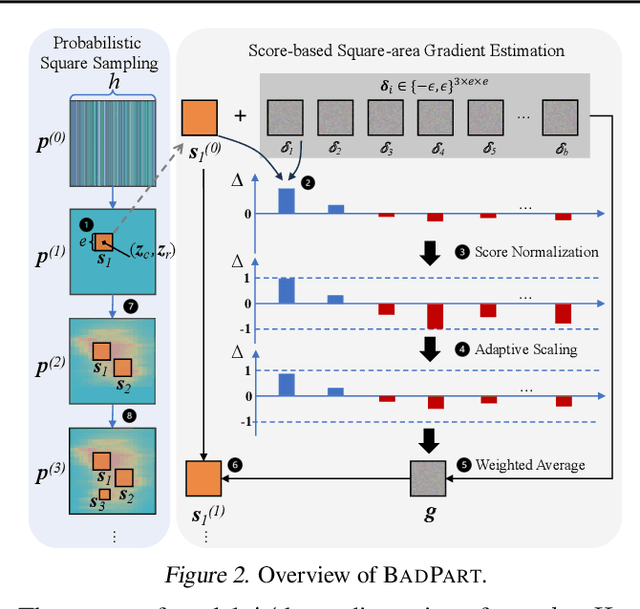
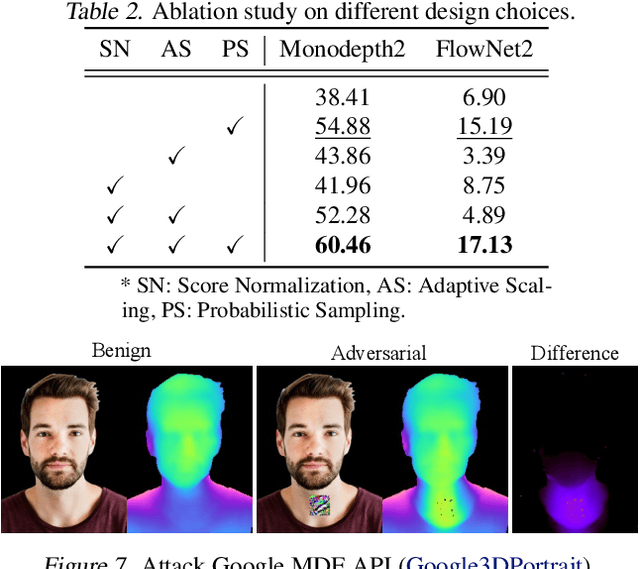
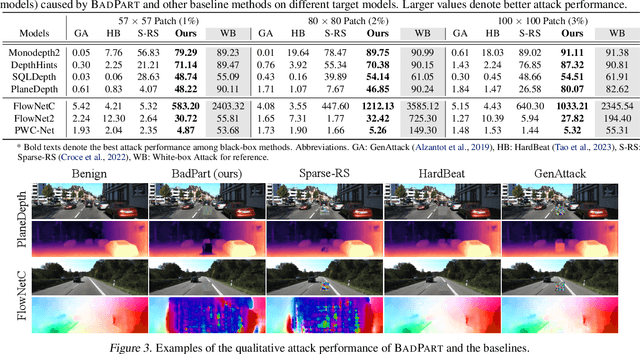
Abstract:Pixel-wise regression tasks (e.g., monocular depth estimation (MDE) and optical flow estimation (OFE)) have been widely involved in our daily life in applications like autonomous driving, augmented reality and video composition. Although certain applications are security-critical or bear societal significance, the adversarial robustness of such models are not sufficiently studied, especially in the black-box scenario. In this work, we introduce the first unified black-box adversarial patch attack framework against pixel-wise regression tasks, aiming to identify the vulnerabilities of these models under query-based black-box attacks. We propose a novel square-based adversarial patch optimization framework and employ probabilistic square sampling and score-based gradient estimation techniques to generate the patch effectively and efficiently, overcoming the scalability problem of previous black-box patch attacks. Our attack prototype, named BadPart, is evaluated on both MDE and OFE tasks, utilizing a total of 7 models. BadPart surpasses 3 baseline methods in terms of both attack performance and efficiency. We also apply BadPart on the Google online service for portrait depth estimation, causing 43.5% relative distance error with 50K queries. State-of-the-art (SOTA) countermeasures cannot defend our attack effectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge