Guancheng Wan
When Attention Betrays: Erasing Backdoor Attacks in Robotic Policies by Reconstructing Visual Tokens
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Downstream fine-tuning of vision-language-action (VLA) models enhances robotics, yet exposes the pipeline to backdoor risks. Attackers can pretrain VLAs on poisoned data to implant backdoors that remain stealthy but can trigger harmful behavior during inference. However, existing defenses either lack mechanistic insight into multimodal backdoors or impose prohibitive computational costs via full-model retraining. To this end, we uncover a deep-layer attention grabbing mechanism: backdoors redirect late-stage attention and form compact embedding clusters near the clean manifold. Leveraging this insight, we introduce Bera, a test-time backdoor erasure framework that detects tokens with anomalous attention via latent-space localization, masks suspicious regions using deep-layer cues, and reconstructs a trigger-free image to break the trigger-unsafe-action mapping while restoring correct behavior. Unlike prior defenses, Bera requires neither retraining of VLAs nor any changes to the training pipeline. Extensive experiments across multiple embodied platforms and tasks show that Bera effectively maintains nominal performance, significantly reduces attack success rates, and consistently restores benign behavior from backdoored outputs, thereby offering a robust and practical defense mechanism for securing robotic systems.
Divide, Conquer and Unite: Hierarchical Style-Recalibrated Prototype Alignment for Federated Medical Image Segmentation
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Federated learning enables multiple medical institutions to train a global model without sharing data, yet feature heterogeneity from diverse scanners or protocols remains a major challenge. Many existing works attempt to address this issue by leveraging model representations (e.g., mean feature vectors) to correct local training; however, they often face two key limitations: 1) Incomplete Contextual Representation Learning: Current approaches primarily focus on final-layer features, overlooking critical multi-level cues and thus diluting essential context for accurate segmentation. 2) Layerwise Style Bias Accumulation: Although utilizing representations can partially align global features, these methods neglect domain-specific biases within intermediate layers, allowing style discrepancies to build up and reduce model robustness. To address these challenges, we propose FedBCS to bridge feature representation gaps via domain-invariant contextual prototypes alignment. Specifically, we introduce a frequency-domain adaptive style recalibration into prototype construction that not only decouples content-style representations but also learns optimal style parameters, enabling more robust domain-invariant prototypes. Furthermore, we design a context-aware dual-level prototype alignment method that extracts domain-invariant prototypes from different layers of both encoder and decoder and fuses them with contextual information for finer-grained representation alignment. Extensive experiments on two public datasets demonstrate that our method exhibits remarkable performance.
Dynamic Generation of Multi-LLM Agents Communication Topologies with Graph Diffusion Models
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:The efficiency of multi-agent systems driven by large language models (LLMs) largely hinges on their communication topology. However, designing an optimal topology is a non-trivial challenge, as it requires balancing competing objectives such as task performance, communication cost, and robustness. Existing frameworks often rely on static or hand-crafted topologies, which inherently fail to adapt to diverse task requirements, leading to either excessive token consumption for simple problems or performance bottlenecks for complex ones. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel generative framework called \textit{Guided Topology Diffusion (GTD)}. Inspired by conditional discrete graph diffusion models, GTD formulates topology synthesis as an iterative construction process. At each step, the generation is steered by a lightweight proxy model that predicts multi-objective rewards (e.g., accuracy, utility, cost), enabling real-time, gradient-free optimization towards task-adaptive topologies. This iterative, guided synthesis process distinguishes GTD from single-step generative frameworks, enabling it to better navigate complex design trade-offs. We validated GTD across multiple benchmarks, and experiments show that this framework can generate highly task-adaptive, sparse, and efficient communication topologies, significantly outperforming existing methods in LLM agent collaboration.
S2FGL: Spatial Spectral Federated Graph Learning
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Federated Graph Learning (FGL) combines the privacy-preserving capabilities of federated learning (FL) with the strong graph modeling capability of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). Current research addresses subgraph-FL only from the structural perspective, neglecting the propagation of graph signals on spatial and spectral domains of the structure. From a spatial perspective, subgraph-FL introduces edge disconnections between clients, leading to disruptions in label signals and a degradation in the class knowledge of the global GNN. From a spectral perspective, spectral heterogeneity causes inconsistencies in signal frequencies across subgraphs, which makes local GNNs overfit the local signal propagation schemes. As a result, spectral client drifts occur, undermining global generalizability. To tackle the challenges, we propose a global knowledge repository to mitigate label signal disruption and a frequency alignment to address spectral client drifts. The combination of spatial and spectral strategies forms our framework S2FGL. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate the superiority of S2FGL. The code is available at https://github.com/Wonder7racer/S2FGL.git.
From Web Search towards Agentic Deep Research: Incentivizing Search with Reasoning Agents
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Information retrieval is a cornerstone of modern knowledge acquisition, enabling billions of queries each day across diverse domains. However, traditional keyword-based search engines are increasingly inadequate for handling complex, multi-step information needs. Our position is that Large Language Models (LLMs), endowed with reasoning and agentic capabilities, are ushering in a new paradigm termed Agentic Deep Research. These systems transcend conventional information search techniques by tightly integrating autonomous reasoning, iterative retrieval, and information synthesis into a dynamic feedback loop. We trace the evolution from static web search to interactive, agent-based systems that plan, explore, and learn. We also introduce a test-time scaling law to formalize the impact of computational depth on reasoning and search. Supported by benchmark results and the rise of open-source implementations, we demonstrate that Agentic Deep Research not only significantly outperforms existing approaches, but is also poised to become the dominant paradigm for future information seeking. All the related resources, including industry products, research papers, benchmark datasets, and open-source implementations, are collected for the community in https://github.com/DavidZWZ/Awesome-Deep-Research.
G-Memory: Tracing Hierarchical Memory for Multi-Agent Systems
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-powered multi-agent systems (MAS) have demonstrated cognitive and execution capabilities that far exceed those of single LLM agents, yet their capacity for self-evolution remains hampered by underdeveloped memory architectures. Upon close inspection, we are alarmed to discover that prevailing MAS memory mechanisms (1) are overly simplistic, completely disregarding the nuanced inter-agent collaboration trajectories, and (2) lack cross-trial and agent-specific customization, in stark contrast to the expressive memory developed for single agents. To bridge this gap, we introduce G-Memory, a hierarchical, agentic memory system for MAS inspired by organizational memory theory, which manages the lengthy MAS interaction via a three-tier graph hierarchy: insight, query, and interaction graphs. Upon receiving a new user query, G-Memory performs bi-directional memory traversal to retrieve both $\textit{high-level, generalizable insights}$ that enable the system to leverage cross-trial knowledge, and $\textit{fine-grained, condensed interaction trajectories}$ that compactly encode prior collaboration experiences. Upon task execution, the entire hierarchy evolves by assimilating new collaborative trajectories, nurturing the progressive evolution of agent teams. Extensive experiments across five benchmarks, three LLM backbones, and three popular MAS frameworks demonstrate that G-Memory improves success rates in embodied action and accuracy in knowledge QA by up to $20.89\%$ and $10.12\%$, respectively, without any modifications to the original frameworks. Our codes are available at https://github.com/bingreeky/GMemory.
An Empirical Study of Federated Prompt Learning for Vision Language Model
May 29, 2025Abstract:The Vision Language Model (VLM) excels in aligning vision and language representations, and prompt learning has emerged as a key technique for adapting such models to downstream tasks. However, the application of prompt learning with VLM in federated learning (\fl{}) scenarios remains underexplored. This paper systematically investigates the behavioral differences between language prompt learning (LPT) and vision prompt learning (VPT) under data heterogeneity challenges, including label skew and domain shift. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate the impact of various \fl{} and prompt configurations, such as client scale, aggregation strategies, and prompt length, to assess the robustness of Federated Prompt Learning (FPL). Furthermore, we explore strategies for enhancing prompt learning in complex scenarios where label skew and domain shift coexist, including leveraging both prompt types when computational resources allow. Our findings offer practical insights into optimizing prompt learning in federated settings, contributing to the broader deployment of VLMs in privacy-preserving environments.
FD-Bench: A Modular and Fair Benchmark for Data-driven Fluid Simulation
May 25, 2025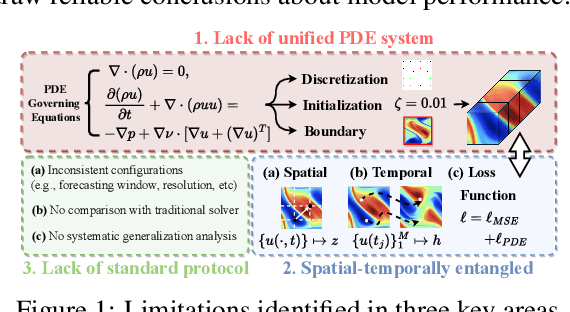
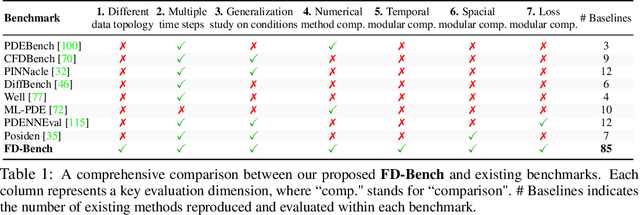
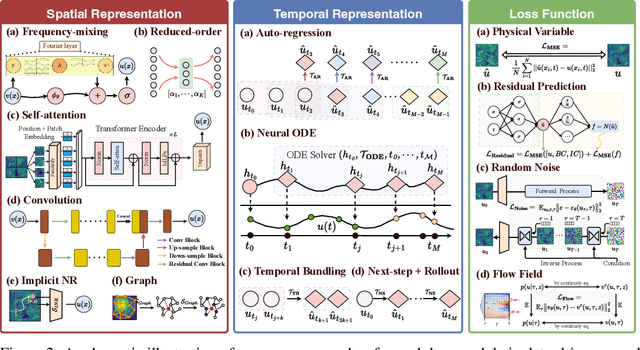
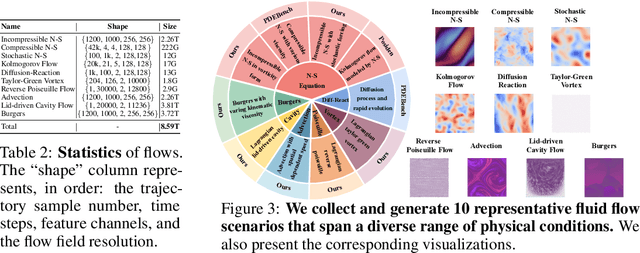
Abstract:Data-driven modeling of fluid dynamics has advanced rapidly with neural PDE solvers, yet a fair and strong benchmark remains fragmented due to the absence of unified PDE datasets and standardized evaluation protocols. Although architectural innovations are abundant, fair assessment is further impeded by the lack of clear disentanglement between spatial, temporal and loss modules. In this paper, we introduce FD-Bench, the first fair, modular, comprehensive and reproducible benchmark for data-driven fluid simulation. FD-Bench systematically evaluates 85 baseline models across 10 representative flow scenarios under a unified experimental setup. It provides four key contributions: (1) a modular design enabling fair comparisons across spatial, temporal, and loss function modules; (2) the first systematic framework for direct comparison with traditional numerical solvers; (3) fine-grained generalization analysis across resolutions, initial conditions, and temporal windows; and (4) a user-friendly, extensible codebase to support future research. Through rigorous empirical studies, FD-Bench establishes the most comprehensive leaderboard to date, resolving long-standing issues in reproducibility and comparability, and laying a foundation for robust evaluation of future data-driven fluid models. The code is open-sourced at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/FD-Bench-15BC.
ThanoRA: Task Heterogeneity-Aware Multi-Task Low-Rank Adaptation
May 24, 2025Abstract:Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) is widely adopted for downstream fine-tuning of foundation models due to its efficiency and zero additional inference cost. Many real-world applications require foundation models to specialize in multiple tasks simultaneously, motivating the need for efficient multi-task adaptation. While recent approaches integrate LoRA with mixture-of-experts (MoE) to address this, the use of routers prevents parameter mergeability, which increases inference overhead and hinders unified multi-task adaptation, thereby limiting deployment practicality. In this work, we propose ThanoRA, a Task Heterogeneity-Aware Multi-Task Low-Rank Adaptation framework that enables multi-task adaptation while preserving the inference efficiency of LoRA. ThanoRA jointly models task heterogeneity and mitigates subspace interference throughout training. Specifically, motivated by inherent differences in complexity and heterogeneity across tasks, ThanoRA constructs task-specific LoRA subspaces at initialization, enabling fine-grained knowledge injection aligned with task heterogeneity. Furthermore, to prevent task interference and subspace collapse during multi-task training, ThanoRA introduces a subspace-preserving regularization that maintains the independence of task-specific representations. With the synergy of both components, ThanoRA enables efficient and unified multi-task adaptation. Extensive experiments across multimodal and text-only benchmarks under varying multi-task mixtures demonstrate that ThanoRA consistently achieves robust and superior performance over strong baselines without introducing additional inference overhead. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/LiangJian24/ThanoRA.
CoT-Kinetics: A Theoretical Modeling Assessing LRM Reasoning Process
May 19, 2025Abstract:Recent Large Reasoning Models significantly improve the reasoning ability of Large Language Models by learning to reason, exhibiting the promising performance in solving complex tasks. LRMs solve tasks that require complex reasoning by explicitly generating reasoning trajectories together with answers. Nevertheless, judging the quality of such an output answer is not easy because only considering the correctness of the answer is not enough and the soundness of the reasoning trajectory part matters as well. Logically, if the soundness of the reasoning part is poor, even if the answer is correct, the confidence of the derived answer should be low. Existing methods did consider jointly assessing the overall output answer by taking into account the reasoning part, however, their capability is still not satisfactory as the causal relationship of the reasoning to the concluded answer cannot properly reflected. In this paper, inspired by classical mechanics, we present a novel approach towards establishing a CoT-Kinetics energy equation. Specifically, our CoT-Kinetics energy equation formulates the token state transformation process, which is regulated by LRM internal transformer layers, as like a particle kinetics dynamics governed in a mechanical field. Our CoT-Kinetics energy assigns a scalar score to evaluate specifically the soundness of the reasoning phase, telling how confident the derived answer could be given the evaluated reasoning. As such, the LRM's overall output quality can be accurately measured, rather than a coarse judgment (e.g., correct or incorrect) anymore.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge