Zhihao Wang
SAFE-QAQ: End-to-End Slow-Thinking Audio-Text Fraud Detection via Reinforcement Learning
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Existing fraud detection methods predominantly rely on transcribed text, suffering from ASR errors and missing crucial acoustic cues like vocal tone and environmental context. This limits their effectiveness against complex deceptive strategies. To address these challenges, we first propose \textbf{SAFE-QAQ}, an end-to-end comprehensive framework for audio-based slow-thinking fraud detection. First, the SAFE-QAQ framework eliminates the impact of transcription errors on detection performance. Secondly, we propose rule-based slow-thinking reward mechanisms that systematically guide the system to identify fraud-indicative patterns by accurately capturing fine-grained audio details, through hierarchical reasoning processes. Besides, our framework introduces a dynamic risk assessment framework during live calls, enabling early detection and prevention of fraud. Experiments on the TeleAntiFraud-Bench demonstrate that SAFE-QAQ achieves dramatic improvements over existing methods in multiple key dimensions, including accuracy, inference efficiency, and real-time processing capabilities. Currently deployed and analyzing over 70,000 calls daily, SAFE-QAQ effectively automates complex fraud detection, reducing human workload and financial losses. Code: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SAFE-QAQ.
Dichotomous Diffusion Policy Optimization
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Diffusion-based policies have gained growing popularity in solving a wide range of decision-making tasks due to their superior expressiveness and controllable generation during inference. However, effectively training large diffusion policies using reinforcement learning (RL) remains challenging. Existing methods either suffer from unstable training due to directly maximizing value objectives, or face computational issues due to relying on crude Gaussian likelihood approximation, which requires a large amount of sufficiently small denoising steps. In this work, we propose DIPOLE (Dichotomous diffusion Policy improvement), a novel RL algorithm designed for stable and controllable diffusion policy optimization. We begin by revisiting the KL-regularized objective in RL, which offers a desirable weighted regression objective for diffusion policy extraction, but often struggles to balance greediness and stability. We then formulate a greedified policy regularization scheme, which naturally enables decomposing the optimal policy into a pair of stably learned dichotomous policies: one aims at reward maximization, and the other focuses on reward minimization. Under such a design, optimized actions can be generated by linearly combining the scores of dichotomous policies during inference, thereby enabling flexible control over the level of greediness.Evaluations in offline and offline-to-online RL settings on ExORL and OGBench demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. We also use DIPOLE to train a large vision-language-action (VLA) model for end-to-end autonomous driving (AD) and evaluate it on the large-scale real-world AD benchmark NAVSIM, highlighting its potential for complex real-world applications.
MVAR: MultiVariate AutoRegressive Air Pollutants Forecasting Model
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Air pollutants pose a significant threat to the environment and human health, thus forecasting accurate pollutant concentrations is essential for pollution warnings and policy-making. Existing studies predominantly focus on single-pollutant forecasting, neglecting the interactions among different pollutants and their diverse spatial responses. To address the practical needs of forecasting multivariate air pollutants, we propose MultiVariate AutoRegressive air pollutants forecasting model (MVAR), which reduces the dependency on long-time-window inputs and boosts the data utilization efficiency. We also design the Multivariate Autoregressive Training Paradigm, enabling MVAR to achieve 120-hour long-term sequential forecasting. Additionally, MVAR develops Meteorological Coupled Spatial Transformer block, enabling the flexible coupling of AI-based meteorological forecasts while learning the interactions among pollutants and their diverse spatial responses. As for the lack of standardized datasets in air pollutants forecasting, we construct a comprehensive dataset covering 6 major pollutants across 75 cities in North China from 2018 to 2023, including ERA5 reanalysis data and FuXi-2.0 forecast data. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms state-of-the-art methods and validate the effectiveness of the proposed architecture.
Rainbow Artifacts from Electromagnetic Signal Injection Attacks on Image Sensors
Jul 10, 2025
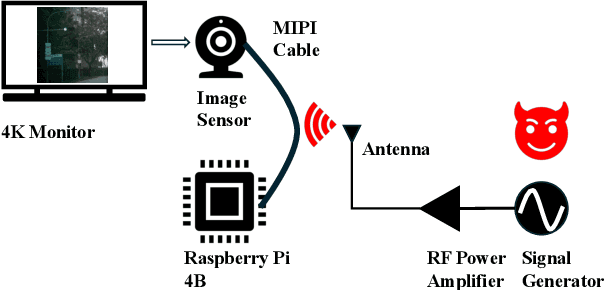


Abstract:Image sensors are integral to a wide range of safety- and security-critical systems, including surveillance infrastructure, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation. These systems rely on the integrity of visual data to make decisions. In this work, we investigate a novel class of electromagnetic signal injection attacks that target the analog domain of image sensors, allowing adversaries to manipulate raw visual inputs without triggering conventional digital integrity checks. We uncover a previously undocumented attack phenomenon on CMOS image sensors: rainbow-like color artifacts induced in images captured by image sensors through carefully tuned electromagnetic interference. We further evaluate the impact of these attacks on state-of-the-art object detection models, showing that the injected artifacts propagate through the image signal processing pipeline and lead to significant mispredictions. Our findings highlight a critical and underexplored vulnerability in the visual perception stack, highlighting the need for more robust defenses against physical-layer attacks in such systems.
A Novel ViDAR Device With Visual Inertial Encoder Odometry and Reinforcement Learning-Based Active SLAM Method
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:In the field of multi-sensor fusion for simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), monocular cameras and IMUs are widely used to build simple and effective visual-inertial systems. However, limited research has explored the integration of motor-encoder devices to enhance SLAM performance. By incorporating such devices, it is possible to significantly improve active capability and field of view (FOV) with minimal additional cost and structural complexity. This paper proposes a novel visual-inertial-encoder tightly coupled odometry (VIEO) based on a ViDAR (Video Detection and Ranging) device. A ViDAR calibration method is introduced to ensure accurate initialization for VIEO. In addition, a platform motion decoupled active SLAM method based on deep reinforcement learning (DRL) is proposed. Experimental data demonstrate that the proposed ViDAR and the VIEO algorithm significantly increase cross-frame co-visibility relationships compared to its corresponding visual-inertial odometry (VIO) algorithm, improving state estimation accuracy. Additionally, the DRL-based active SLAM algorithm, with the ability to decouple from platform motion, can increase the diversity weight of the feature points and further enhance the VIEO algorithm's performance. The proposed methodology sheds fresh insights into both the updated platform design and decoupled approach of active SLAM systems in complex environments.
* 12 pages, 13 figures
An Empirical Study of Federated Prompt Learning for Vision Language Model
May 29, 2025Abstract:The Vision Language Model (VLM) excels in aligning vision and language representations, and prompt learning has emerged as a key technique for adapting such models to downstream tasks. However, the application of prompt learning with VLM in federated learning (\fl{}) scenarios remains underexplored. This paper systematically investigates the behavioral differences between language prompt learning (LPT) and vision prompt learning (VPT) under data heterogeneity challenges, including label skew and domain shift. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate the impact of various \fl{} and prompt configurations, such as client scale, aggregation strategies, and prompt length, to assess the robustness of Federated Prompt Learning (FPL). Furthermore, we explore strategies for enhancing prompt learning in complex scenarios where label skew and domain shift coexist, including leveraging both prompt types when computational resources allow. Our findings offer practical insights into optimizing prompt learning in federated settings, contributing to the broader deployment of VLMs in privacy-preserving environments.
Stereographic Multi-Try Metropolis Algorithms for Heavy-tailed Sampling
May 18, 2025Abstract:Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods for sampling from heavy-tailed distributions present unique challenges, particularly in high dimensions. Multi-proposal MCMC algorithms have recently gained attention for their potential to improve performance, especially through parallel implementation on modern hardware. This paper introduces a novel family of gradient-free MCMC algorithms that combine the multi-try Metropolis (MTM) with stereographic MCMC framework, specifically designed for efficient sampling from heavy-tailed targets. The proposed stereographic multi-try Metropolis (SMTM) algorithm not only outperforms traditional Euclidean MTM and existing stereographic random-walk Metropolis methods, but also avoids the pathological convergence behavior often observed in MTM and demonstrates strong robustness to tuning. These properties are supported by scaling analysis and extensive simulation studies.
Efficient Robotic Policy Learning via Latent Space Backward Planning
May 11, 2025Abstract:Current robotic planning methods often rely on predicting multi-frame images with full pixel details. While this fine-grained approach can serve as a generic world model, it introduces two significant challenges for downstream policy learning: substantial computational costs that hinder real-time deployment, and accumulated inaccuracies that can mislead action extraction. Planning with coarse-grained subgoals partially alleviates efficiency issues. However, their forward planning schemes can still result in off-task predictions due to accumulation errors, leading to misalignment with long-term goals. This raises a critical question: Can robotic planning be both efficient and accurate enough for real-time control in long-horizon, multi-stage tasks? To address this, we propose a Latent Space Backward Planning scheme (LBP), which begins by grounding the task into final latent goals, followed by recursively predicting intermediate subgoals closer to the current state. The grounded final goal enables backward subgoal planning to always remain aware of task completion, facilitating on-task prediction along the entire planning horizon. The subgoal-conditioned policy incorporates a learnable token to summarize the subgoal sequences and determines how each subgoal guides action extraction. Through extensive simulation and real-robot long-horizon experiments, we show that LBP outperforms existing fine-grained and forward planning methods, achieving SOTA performance. Project Page: https://lbp-authors.github.io
A Multi-Agent Framework with Automated Decision Rule Optimization for Cross-Domain Misinformation Detection
Mar 30, 2025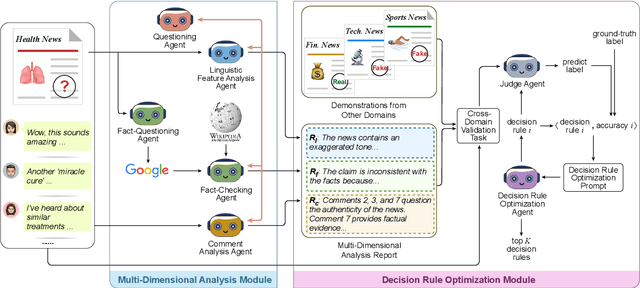
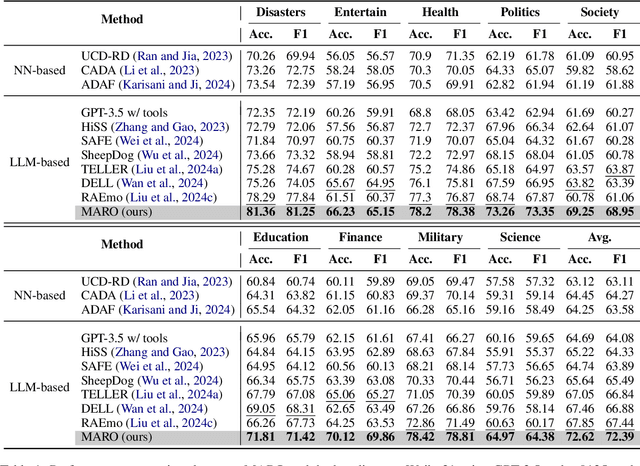
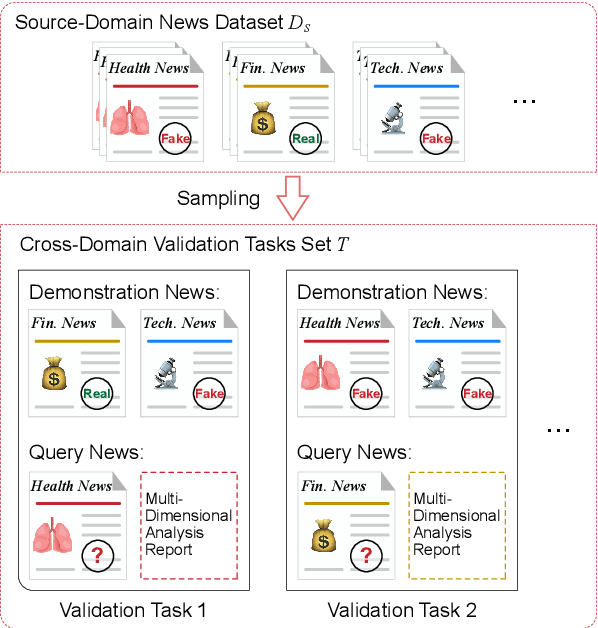
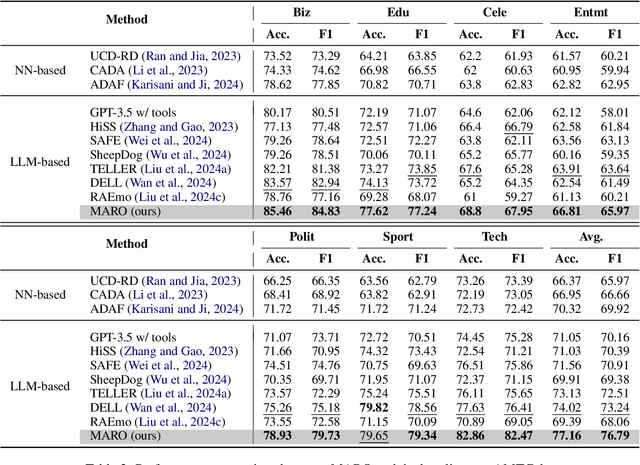
Abstract:Misinformation spans various domains, but detection methods trained on specific domains often perform poorly when applied to others. With the rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs), researchers have begun to utilize LLMs for cross-domain misinformation detection. However, existing LLM-based methods often fail to adequately analyze news in the target domain, limiting their detection capabilities. More importantly, these methods typically rely on manually designed decision rules, which are limited by domain knowledge and expert experience, thus limiting the generalizability of decision rules to different domains. To address these issues, we propose a MultiAgent Framework for cross-domain misinformation detection with Automated Decision Rule Optimization (MARO). Under this framework, we first employs multiple expert agents to analyze target-domain news. Subsequently, we introduce a question-reflection mechanism that guides expert agents to facilitate higherquality analysis. Furthermore, we propose a decision rule optimization approach based on carefully-designed cross-domain validation tasks to iteratively enhance the effectiveness of decision rules in different domains. Experimental results and in-depth analysis on commonlyused datasets demonstrate that MARO achieves significant improvements over existing methods.
Universal Actions for Enhanced Embodied Foundation Models
Jan 17, 2025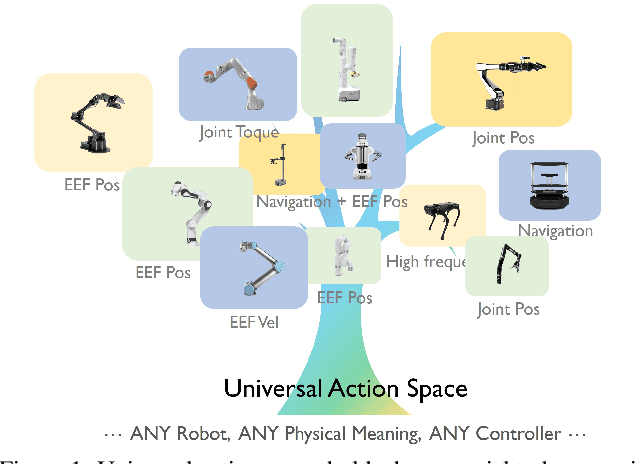

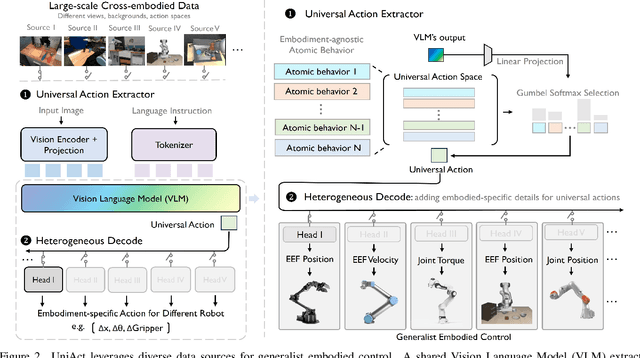
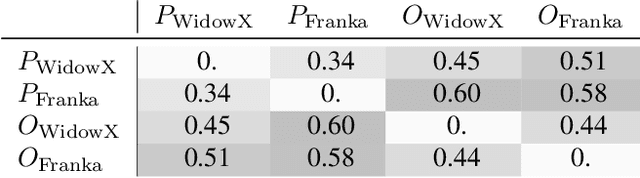
Abstract:Training on diverse, internet-scale data is a key factor in the success of recent large foundation models. Yet, using the same recipe for building embodied agents has faced noticeable difficulties. Despite the availability of many crowd-sourced embodied datasets, their action spaces often exhibit significant heterogeneity due to distinct physical embodiment and control interfaces for different robots, causing substantial challenges in developing embodied foundation models using cross-domain data. In this paper, we introduce UniAct, a new embodied foundation modeling framework operating in a tokenized Universal Action Space. Our learned universal actions capture the generic atomic behaviors across diverse robots by exploiting their shared structural features, and enable enhanced cross-domain data utilization and cross-embodiment generalizations by eliminating the notorious heterogeneity. The universal actions can be efficiently translated back to heterogeneous actionable commands by simply adding embodiment-specific details, from which fast adaptation to new robots becomes simple and straightforward. Our 0.5B instantiation of UniAct outperforms 14X larger SOTA embodied foundation models in extensive evaluations on various real-world and simulation robots, showcasing exceptional cross-embodiment control and adaptation capability, highlighting the crucial benefit of adopting universal actions. Project page: https://github.com/2toinf/UniAct
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge