Yixuan Liao
Bi-directional Bias Attribution: Debiasing Large Language Models without Modifying Prompts
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities across a wide range of natural language processing tasks. However, their outputs often exhibit social biases, raising fairness concerns. Existing debiasing methods, such as fine-tuning on additional datasets or prompt engineering, face scalability issues or compromise user experience in multi-turn interactions. To address these challenges, we propose a framework for detecting stereotype-inducing words and attributing neuron-level bias in LLMs, without the need for fine-tuning or prompt modification. Our framework first identifies stereotype-inducing adjectives and nouns via comparative analysis across demographic groups. We then attribute biased behavior to specific neurons using two attribution strategies based on integrated gradients. Finally, we mitigate bias by directly intervening on their activations at the projection layer. Experiments on three widely used LLMs demonstrate that our method effectively reduces bias while preserving overall model performance. Code is available at the github link: https://github.com/XMUDeepLIT/Bi-directional-Bias-Attribution.
A Learning Rate Path Switching Training Paradigm for Version Updates of Large Language Models
Oct 05, 2024
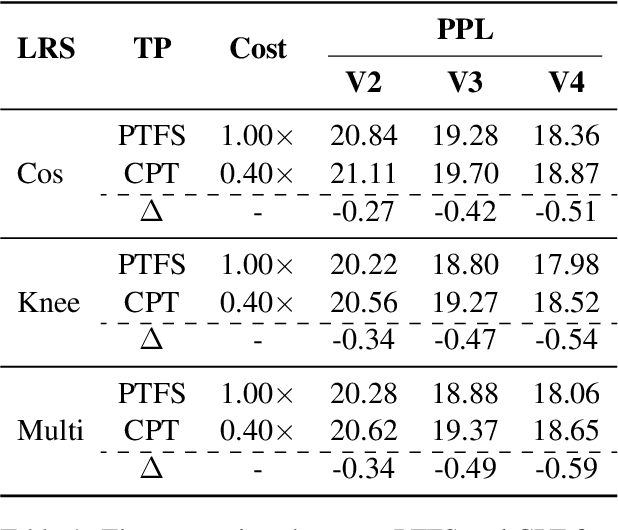


Abstract:Due to the continuous emergence of new data, version updates have become an indispensable requirement for Large Language Models (LLMs). The training paradigms for version updates of LLMs include pre-training from scratch (PTFS) and continual pre-training (CPT). Preliminary experiments demonstrate that PTFS achieves better pre-training performance, while CPT has lower training cost. Moreover, their performance and training cost gaps widen progressively with version updates. To investigate the underlying reasons for this phenomenon, we analyze the effect of learning rate adjustments during the two stages of CPT: preparing an initialization checkpoint and continual pre-training based on this checkpoint. We find that a large learning rate in the first stage and a complete learning rate decay process in the second stage are crucial for version updates of LLMs. Hence, we propose a learning rate path switching training paradigm. Our paradigm comprises one main path, where we pre-train a LLM with the maximal learning rate, and multiple branching paths, each of which corresponds to an update of the LLM with newly-added training data. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization of our paradigm. Particularly, when training four versions of LLMs, our paradigm reduces the total training cost to 58% compared to PTFS, while maintaining comparable pre-training performance.
DPL: Decoupled Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Models
Aug 19, 2023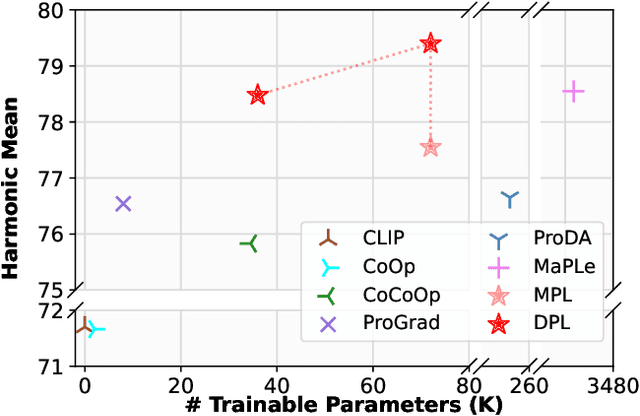
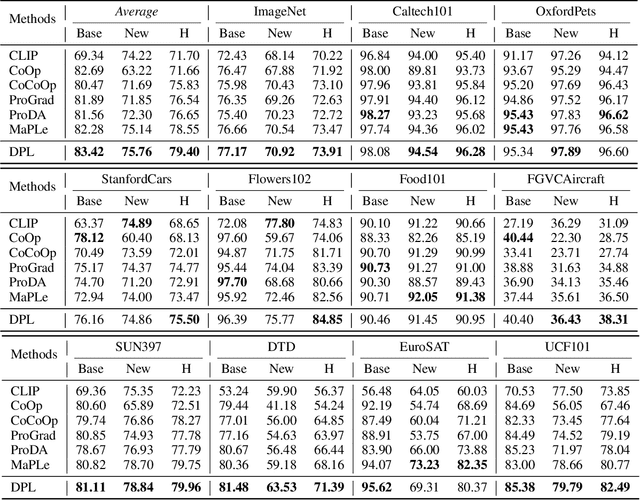
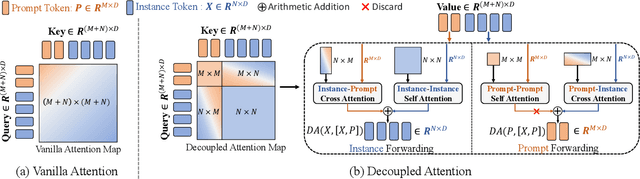
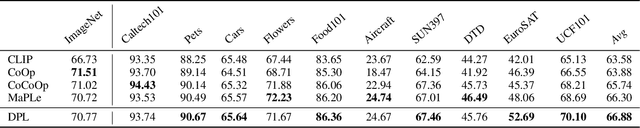
Abstract:Prompt learning has emerged as an efficient and effective approach for transferring foundational Vision-Language Models (e.g., CLIP) to downstream tasks. However, current methods tend to overfit to seen categories, thereby limiting their generalization ability for unseen classes. In this paper, we propose a new method, Decoupled Prompt Learning (DPL), which reformulates the attention in prompt learning to alleviate this problem. Specifically, we theoretically investigate the collaborative process between prompts and instances (i.e., image patches/text tokens) by reformulating the original self-attention into four separate sub-processes. Through detailed analysis, we observe that certain sub-processes can be strengthened to bolster robustness and generalizability by some approximation techniques. Furthermore, we introduce language-conditioned textual prompting based on decoupled attention to naturally preserve the generalization of text input. Our approach is flexible for both visual and textual modalities, making it easily extendable to multi-modal prompt learning. By combining the proposed techniques, our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on three representative benchmarks encompassing 15 image recognition datasets, while maintaining parameter-efficient. Moreover, our DPL does not rely on any auxiliary regularization task or extra training data, further demonstrating its remarkable generalization ability.
Progressive Visual Prompt Learning with Contrastive Feature Re-formation
Apr 17, 2023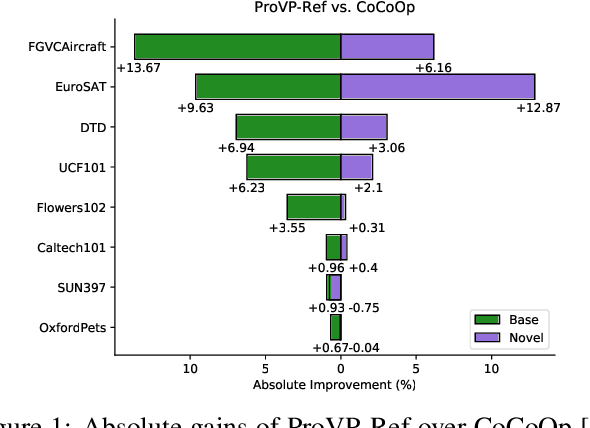
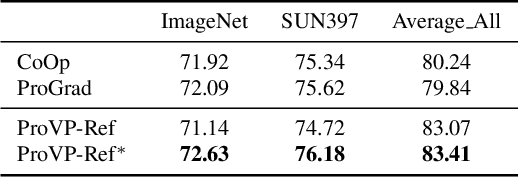
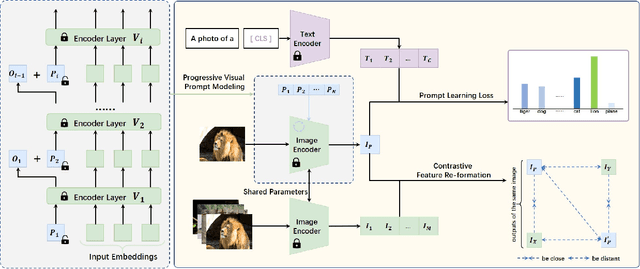
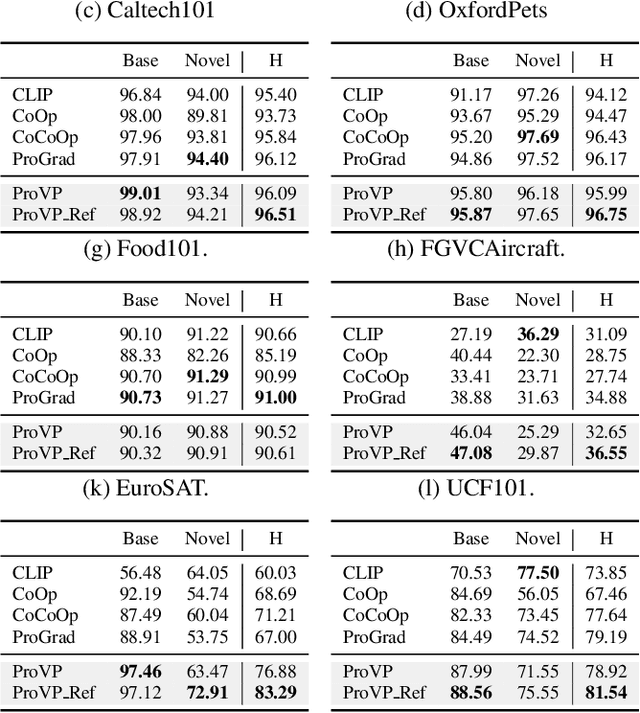
Abstract:Prompt learning has been designed as an alternative to fine-tuning for adapting Vision-language (V-L) models to the downstream tasks. Previous works mainly focus on text prompt while visual prompt works are limited for V-L models. The existing visual prompt methods endure either mediocre performance or unstable training process, indicating the difficulty of visual prompt learning. In this paper, we propose a new Progressive Visual Prompt (ProVP) structure to strengthen the interactions among prompts of different layers. More importantly, our ProVP could effectively propagate the image embeddings to deep layers and behave partially similar to an instance adaptive prompt method. To alleviate generalization deterioration, we further propose a new contrastive feature re-formation, which prevents the serious deviation of the prompted visual feature from the fixed CLIP visual feature distribution. Combining both, our method (ProVP-Ref) is evaluated on 11 image benchmark datasets and achieves 7/11 state-of-theart results on both few-shot and base-to-novel settings. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to demonstrate the superior performance of visual prompts in V-L models to previous prompt-based methods in downstream tasks. Meanwhile, it implies that our ProVP-Ref shows the best capability to adapt and to generalize.
CLUENER2020: Fine-grained Named Entity Recognition Dataset and Benchmark for Chinese
Jan 20, 2020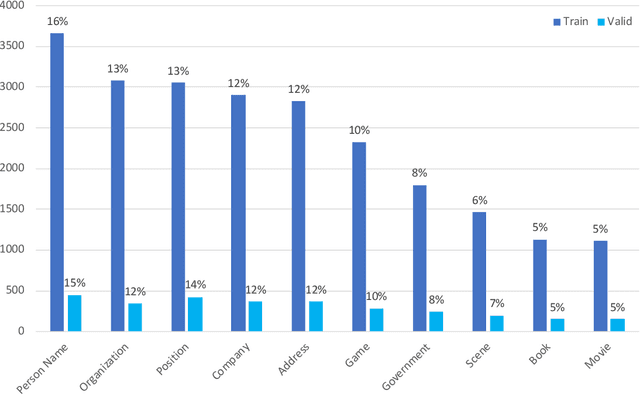

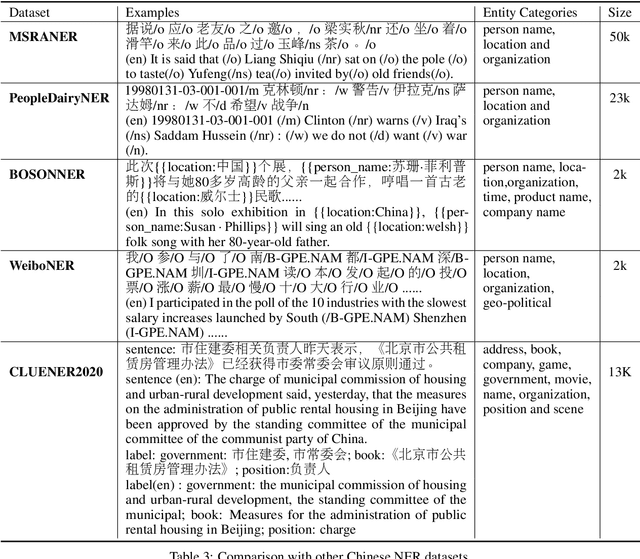
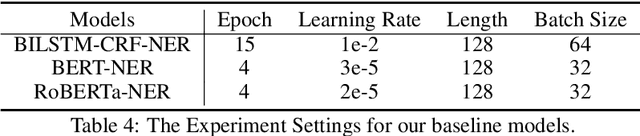
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the NER dataset from CLUE organization (CLUENER2020), a well-defined fine-grained dataset for named entity recognition in Chinese. CLUENER2020 contains 10 categories. Apart from common labels like person, organization, and location, it contains more diverse categories. It is more challenging than current other Chinese NER datasets and could better reflect real-world applications. For comparison, we implement several state-of-the-art baselines as sequence labeling tasks and report human performance, as well as its analysis. To facilitate future work on fine-grained NER for Chinese, we release our dataset, baselines, and leader-board.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge