Cong Yu
Fine-Tuning Large Language Models on Quantum Optimization Problems for Circuit Generation
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLM) have achieved remarkable outcomes in addressing complex problems, including math, coding, and analyzing large amounts of scientific reports. Yet few works have explored the potential of LLM in quantum computing. The most challenging problem is how to leverage LLMs to automatically generate quantum circuits at a large scale. In this paper, we address such a challenge by fine-tuning LLMs and injecting the domain-specific knowledge of quantum computing. In particular, we investigate the mechanisms to generate training data sets and construct the end-to-end pipeline to fine-tune pre-trained LLMs that produce parameterized quantum circuits for optimization problems. We have prepared 14,000 quantum circuits covering a substantial part of the quantum optimization landscape: 12 optimization problem instances and their optimized QAOA, VQE, and adaptive VQE circuits. The fine-tuned LLMs can construct syntactically correct parametrized quantum circuits in the most recent OpenQASM 3.0. We have evaluated the quality of the parameters by comparing them to the optimized expectation values and distributions. Our evaluation shows that the fine-tuned LLM outperforms state-of-the-art models and that the parameters are better than random. The LLM-generated parametrized circuits and initial parameters can be used as a starting point for further optimization, \emph{e.g.,} templates in quantum machine learning and the benchmark for compilers and hardware.
Are Large Language Models Really Robust to Word-Level Perturbations?
Sep 27, 2023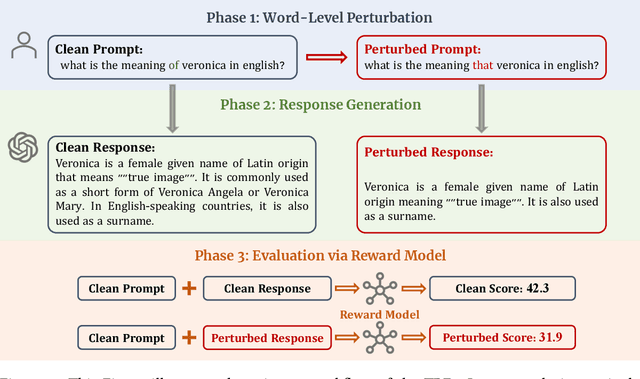
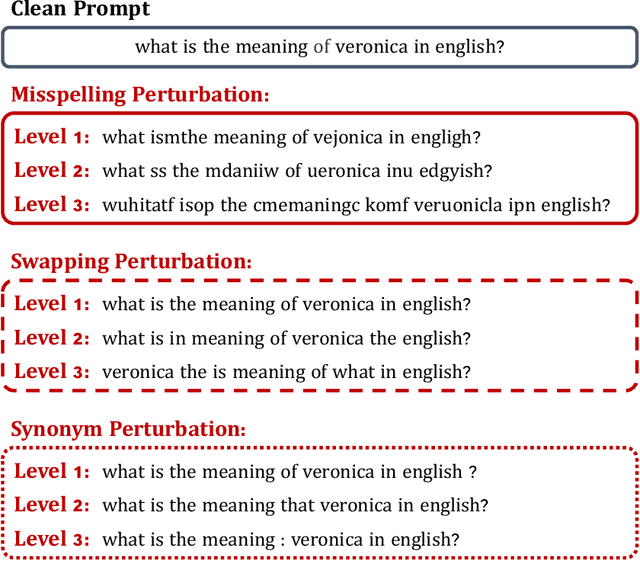
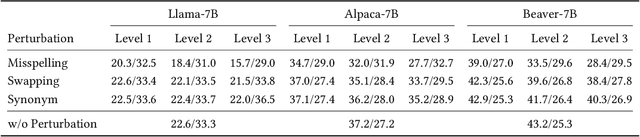
Abstract:The swift advancement in the scales and capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) positions them as promising tools for a variety of downstream tasks. In addition to the pursuit of better performance and the avoidance of violent feedback on a certain prompt, to ensure the responsibility of the LLM, much attention is drawn to the robustness of LLMs. However, existing evaluation methods mostly rely on traditional question answering datasets with predefined supervised labels, which do not align with the superior generation capabilities of contemporary LLMs. To address this issue, we propose a novel rational evaluation approach that leverages pre-trained reward models as diagnostic tools to evaluate the longer conversation generated from more challenging open questions by LLMs, which we refer to as the Reward Model for Reasonable Robustness Evaluation (TREvaL). Longer conversations manifest the comprehensive grasp of language models in terms of their proficiency in understanding questions, a capability not entirely encompassed by individual words or letters, which may exhibit oversimplification and inherent biases. Our extensive empirical experiments demonstrate that TREvaL provides an innovative method for evaluating the robustness of an LLM. Furthermore, our results demonstrate that LLMs frequently exhibit vulnerability to word-level perturbations that are commonplace in daily language usage. Notably, we are surprised to discover that robustness tends to decrease as fine-tuning (SFT and RLHF) is conducted. The code of TREval is available in https://github.com/Harry-mic/TREvaL.
Scaling Multimodal Pre-Training via Cross-Modality Gradient Harmonization
Nov 03, 2022



Abstract:Self-supervised pre-training recently demonstrates success on large-scale multimodal data, and state-of-the-art contrastive learning methods often enforce the feature consistency from cross-modality inputs, such as video/audio or video/text pairs. Despite its convenience to formulate and leverage in practice, such cross-modality alignment (CMA) is only a weak and noisy supervision, since two modalities can be semantically misaligned even they are temporally aligned. For example, even in the commonly adopted instructional videos, a speaker can sometimes refer to something that is not visually present in the current frame; and the semantic misalignment would only be more unpredictable for the raw videos from the internet. We conjecture that might cause conflicts and biases among modalities, and may hence prohibit CMA from scaling up to training with larger and more heterogeneous data. This paper first verifies our conjecture by observing that, even in the latest VATT pre-training using only instructional videos, there exist strong gradient conflicts between different CMA losses within the same video, audio, text triplet, indicating them as the noisy source of supervision. We then propose to harmonize such gradients, via two techniques: (i) cross-modality gradient realignment: modifying different CMA loss gradients for each sample triplet, so that their gradient directions are more aligned; and (ii) gradient-based curriculum learning: leveraging the gradient conflict information on an indicator of sample noisiness, to develop a curriculum learning strategy to prioritize training on less noisy sample triplets. Applying those techniques to pre-training VATT on the HowTo100M dataset, we consistently improve its performance on different downstream tasks. Moreover, we are able to scale VATT pre-training to more complicated non-narrative Youtube8M dataset to further improve the state-of-the-arts.
All Birds with One Stone: Multi-task Text Classification for Efficient Inference with One Forward Pass
May 22, 2022



Abstract:Multi-Task Learning (MTL) models have shown their robustness, effectiveness, and efficiency for transferring learned knowledge across tasks. In real industrial applications such as web content classification, multiple classification tasks are predicted from the same input text such as a web article. However, at the serving time, the existing multitask transformer models such as prompt or adaptor based approaches need to conduct N forward passes for N tasks with O(N) computation cost. To tackle this problem, we propose a scalable method that can achieve stronger performance with close to O(1) computation cost via only one forward pass. To illustrate real application usage, we release a multitask dataset on news topic and style classification. Our experiments show that our proposed method outperforms strong baselines on both the GLUE benchmark and our news dataset. Our code and dataset are publicly available at https://bit.ly/mtop-code.
Image Steganography based on Style Transfer
Mar 09, 2022


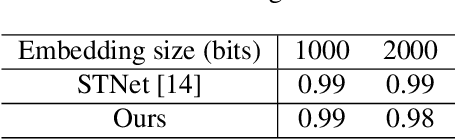
Abstract:Image steganography is the art and science of using images as cover for covert communications. With the development of neural networks, traditional image steganography is more likely to be detected by deep learning-based steganalysis. To improve upon this, we propose image steganography network based on style transfer, and the embedding of secret messages can be disguised as image stylization. We embed secret information while transforming the content image style. In latent space, the secret information is integrated into the latent representation of the cover image to generate the stego images, which are indistinguishable from normal stylized images. It is an end-to-end unsupervised model without pre-training. Extensive experiments on the benchmark dataset demonstrate the reliability, quality and security of stego images generated by our steganographic network.
RFMask: A Simple Baseline for Human Silhouette Segmentation with Radio Signals
Jan 25, 2022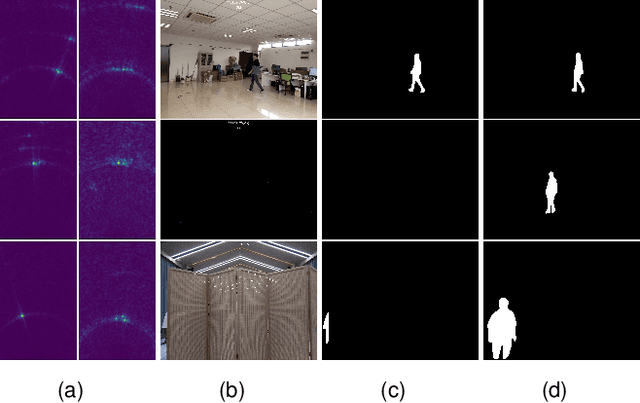
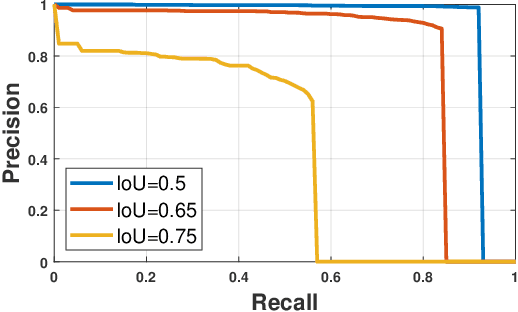
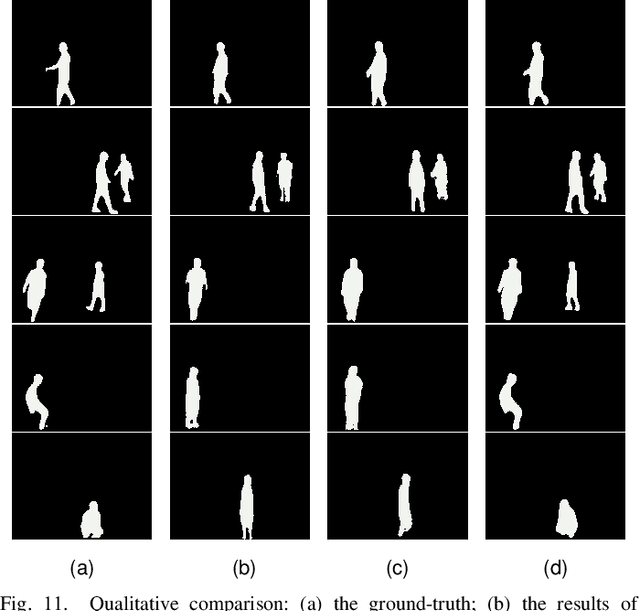

Abstract:Human silhouette segmentation, which is originally defined in computer vision, has achieved promising results for understanding human activities. However, the physical limitation makes existing systems based on optical cameras suffer from severe performance degradation under low illumination, smoke, and/or opaque obstruction conditions. To overcome such limitations, in this paper, we propose to utilize the radio signals, which can traverse obstacles and are unaffected by the lighting conditions to achieve silhouette segmentation. The proposed RFMask framework is composed of three modules. It first transforms RF signals captured by millimeter wave radar on two planes into spatial domain and suppress interference with the signal processing module. Then, it locates human reflections on RF frames and extract features from surrounding signals with human detection module. Finally, the extracted features from RF frames are aggregated with an attention based mask generation module. To verify our proposed framework, we collect a dataset containing 804,760 radio frames and 402,380 camera frames with human activities under various scenes. Experimental results show that the proposed framework can achieve impressive human silhouette segmentation even under the challenging scenarios(such as low light and occlusion scenarios) where traditional optical-camera-based methods fail. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first investigation towards segmenting human silhouette based on millimeter wave signals. We hope that our work can serve as a baseline and inspire further research that perform vision tasks with radio signals. The dataset and codes will be made in public.
RFGAN: RF-Based Human Synthesis
Dec 07, 2021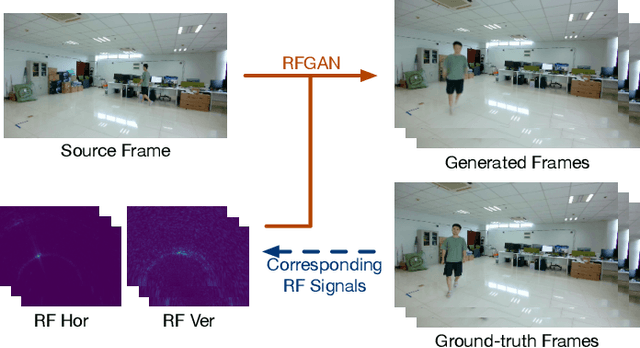


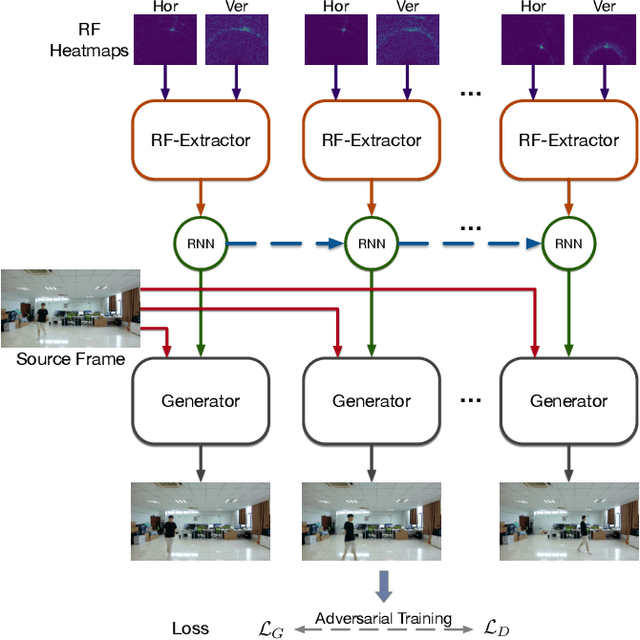
Abstract:This paper demonstrates human synthesis based on the Radio Frequency (RF) signals, which leverages the fact that RF signals can record human movements with the signal reflections off the human body. Different from existing RF sensing works that can only perceive humans roughly, this paper aims to generate fine-grained optical human images by introducing a novel cross-modal RFGAN model. Specifically, we first build a radio system equipped with horizontal and vertical antenna arrays to transceive RF signals. Since the reflected RF signals are processed as obscure signal projection heatmaps on the horizontal and vertical planes, we design a RF-Extractor with RNN in RFGAN for RF heatmap encoding and combining to obtain the human activity information. Then we inject the information extracted by the RF-Extractor and RNN as the condition into GAN using the proposed RF-based adaptive normalizations. Finally, we train the whole model in an end-to-end manner. To evaluate our proposed model, we create two cross-modal datasets (RF-Walk & RF-Activity) that contain thousands of optical human activity frames and corresponding RF signals. Experimental results show that the RFGAN can generate target human activity frames using RF signals. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to generate optical images based on RF signals.
ReasonBERT: Pre-trained to Reason with Distant Supervision
Sep 10, 2021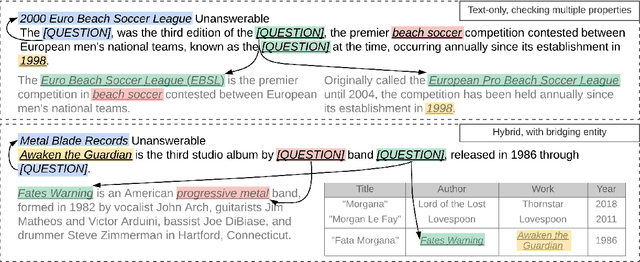

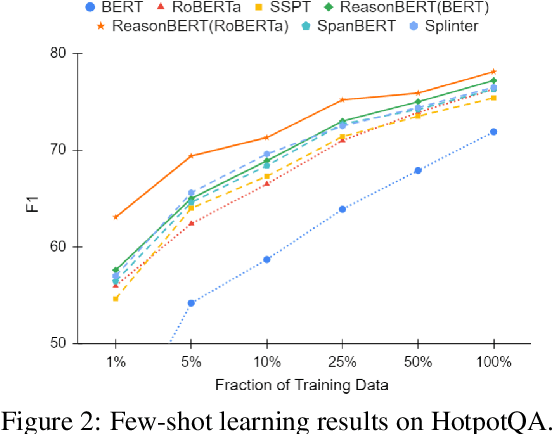
Abstract:We present ReasonBert, a pre-training method that augments language models with the ability to reason over long-range relations and multiple, possibly hybrid contexts. Unlike existing pre-training methods that only harvest learning signals from local contexts of naturally occurring texts, we propose a generalized notion of distant supervision to automatically connect multiple pieces of text and tables to create pre-training examples that require long-range reasoning. Different types of reasoning are simulated, including intersecting multiple pieces of evidence, bridging from one piece of evidence to another, and detecting unanswerable cases. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation on a variety of extractive question answering datasets ranging from single-hop to multi-hop and from text-only to table-only to hybrid that require various reasoning capabilities and show that ReasonBert achieves remarkable improvement over an array of strong baselines. Few-shot experiments further demonstrate that our pre-training method substantially improves sample efficiency.
Charformer: Fast Character Transformers via Gradient-based Subword Tokenization
Jul 02, 2021



Abstract:State-of-the-art models in natural language processing rely on separate rigid subword tokenization algorithms, which limit their generalization ability and adaptation to new settings. In this paper, we propose a new model inductive bias that learns a subword tokenization end-to-end as part of the model. To this end, we introduce a soft gradient-based subword tokenization module (GBST) that automatically learns latent subword representations from characters in a data-driven fashion. Concretely, GBST enumerates candidate subword blocks and learns to score them in a position-wise fashion using a block scoring network. We additionally introduce Charformer, a deep Transformer model that integrates GBST and operates on the byte level. Via extensive experiments on English GLUE, multilingual, and noisy text datasets, we show that Charformer outperforms a series of competitive byte-level baselines while generally performing on par and sometimes outperforming subword-based models. Additionally, Charformer is fast, improving the speed of both vanilla byte-level and subword-level Transformers by 28%-100% while maintaining competitive quality. We believe this work paves the way for highly performant token-free models that are trained completely end-to-end.
NewsEmbed: Modeling News through Pre-trained Document Representations
Jun 05, 2021



Abstract:Effectively modeling text-rich fresh content such as news articles at document-level is a challenging problem. To ensure a content-based model generalize well to a broad range of applications, it is critical to have a training dataset that is large beyond the scale of human labels while achieving desired quality. In this work, we address those two challenges by proposing a novel approach to mine semantically-relevant fresh documents, and their topic labels, with little human supervision. Meanwhile, we design a multitask model called NewsEmbed that alternatively trains a contrastive learning with a multi-label classification to derive a universal document encoder. We show that the proposed approach can provide billions of high quality organic training examples and can be naturally extended to multilingual setting where texts in different languages are encoded in the same semantic space. We experimentally demonstrate NewsEmbed's competitive performance across multiple natural language understanding tasks, both supervised and unsupervised.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge