Simon Baumgartner
The FACTS Leaderboard: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Large Language Model Factuality
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:We introduce The FACTS Leaderboard, an online leaderboard suite and associated set of benchmarks that comprehensively evaluates the ability of language models to generate factually accurate text across diverse scenarios. The suite provides a holistic measure of factuality by aggregating the performance of models on four distinct sub-leaderboards: (1) FACTS Multimodal, which measures the factuality of responses to image-based questions; (2) FACTS Parametric, which assesses models' world knowledge by answering closed-book factoid questions from internal parameters; (3) FACTS Search, which evaluates factuality in information-seeking scenarios, where the model must use a search API; and (4) FACTS Grounding (v2), which evaluates whether long-form responses are grounded in provided documents, featuring significantly improved judge models. Each sub-leaderboard employs automated judge models to score model responses, and the final suite score is an average of the four components, designed to provide a robust and balanced assessment of a model's overall factuality. The FACTS Leaderboard Suite will be actively maintained, containing both public and private splits to allow for external participation while guarding its integrity. It can be found at https://www.kaggle.com/benchmarks/google/facts .
Gemini Embedding: Generalizable Embeddings from Gemini
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:In this report, we introduce Gemini Embedding, a state-of-the-art embedding model leveraging the power of Gemini, Google's most capable large language model. Capitalizing on Gemini's inherent multilingual and code understanding capabilities, Gemini Embedding produces highly generalizable embeddings for text spanning numerous languages and textual modalities. The representations generated by Gemini Embedding can be precomputed and applied to a variety of downstream tasks including classification, similarity, clustering, ranking, and retrieval. Evaluated on the Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark (MMTEB), which includes over one hundred tasks across 250+ languages, Gemini Embedding substantially outperforms prior state-of-the-art models, demonstrating considerable improvements in embedding quality. Achieving state-of-the-art performance across MMTEB's multilingual, English, and code benchmarks, our unified model demonstrates strong capabilities across a broad selection of tasks and surpasses specialized domain-specific models.
Multilingual Fine-Grained News Headline Hallucination Detection
Jul 22, 2024



Abstract:The popularity of automated news headline generation has surged with advancements in pre-trained language models. However, these models often suffer from the ``hallucination'' problem, where the generated headline is not fully supported by its source article. Efforts to address this issue have predominantly focused on English, using over-simplistic classification schemes that overlook nuanced hallucination types. In this study, we introduce the first multilingual, fine-grained news headline hallucination detection dataset that contains over 11 thousand pairs in 5 languages, each annotated with detailed hallucination types by experts. We conduct extensive experiments on this dataset under two settings. First, we implement several supervised fine-tuning approaches as preparatory solutions and demonstrate this dataset's challenges and utilities. Second, we test various large language models' in-context learning abilities and propose two novel techniques, language-dependent demonstration selection and coarse-to-fine prompting, to boost the few-shot hallucination detection performance in terms of the example-F1 metric. We release this dataset to foster further research in multilingual, fine-grained headline hallucination detection.
Boosting Reward Model with Preference-Conditional Multi-Aspect Synthetic Data Generation
Jul 22, 2024



Abstract:Reward models (RMs) are crucial for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. They are trained using preference datasets where each example consists of one input prompt, two responses, and a preference label. As curating a high-quality human labeled preference dataset is both time-consuming and expensive, people often rely on existing powerful LLMs for preference label generation. This can potentially introduce noise and impede RM training. In this work, we present RMBoost, a novel synthetic preference data generation paradigm to boost reward model quality. Unlike traditional methods, which generate two responses before obtaining the preference label, RMBoost first generates one response and selects a preference label, followed by generating the second more (or less) preferred response conditioned on the pre-selected preference label and the first response. This approach offers two main advantages. First, RMBoost reduces labeling noise since preference pairs are constructed intentionally. Second, RMBoost facilitates the creation of more diverse responses by incorporating various quality aspects (e.g., helpfulness, relevance, completeness) into the prompts. We conduct extensive experiments across three diverse datasets and demonstrate that RMBoost outperforms other synthetic preference data generation techniques and significantly boosts the performance of four distinct reward models.
PLaD: Preference-based Large Language Model Distillation with Pseudo-Preference Pairs
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have exhibited impressive capabilities in various tasks, yet their vast parameter sizes restrict their applicability in resource-constrained settings. Knowledge distillation (KD) offers a viable solution by transferring expertise from large teacher models to compact student models. However, traditional KD techniques face specific challenges when applied to LLMs, including restricted access to LLM outputs, significant teacher-student capacity gaps, and the inherited mis-calibration issue. In this work, we present PLaD, a novel preference-based LLM distillation framework. PLaD exploits the teacher-student capacity discrepancy to generate pseudo-preference pairs where teacher outputs are preferred over student outputs. Then, PLaD leverages a ranking loss to re-calibrate student's estimation of sequence likelihood, which steers the student's focus towards understanding the relative quality of outputs instead of simply imitating the teacher. PLaD bypasses the need for access to teacher LLM's internal states, tackles the student's expressivity limitations, and mitigates the student mis-calibration issue. Through extensive experiments on two sequence generation tasks and with various LLMs, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed PLaD framework.
LiPO: Listwise Preference Optimization through Learning-to-Rank
Feb 02, 2024



Abstract:Aligning language models (LMs) with curated human feedback is critical to control their behaviors in real-world applications. Several recent policy optimization methods, such as DPO and SLiC, serve as promising alternatives to the traditional Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) approach. In practice, human feedback often comes in a format of a ranked list over multiple responses to amortize the cost of reading prompt. Multiple responses can also be ranked by reward models or AI feedback. There lacks such a study on directly fitting upon a list of responses. In this work, we formulate the LM alignment as a listwise ranking problem and describe the Listwise Preference Optimization (LiPO) framework, where the policy can potentially learn more effectively from a ranked list of plausible responses given the prompt. This view draws an explicit connection to Learning-to-Rank (LTR), where most existing preference optimization work can be mapped to existing ranking objectives, especially pairwise ones. Following this connection, we provide an examination of ranking objectives that are not well studied for LM alignment withDPO and SLiC as special cases when list size is two. In particular, we highlight a specific method, LiPO-{\lambda}, which leverages a state-of-the-art listwise ranking objective and weights each preference pair in a more advanced manner. We show that LiPO-{\lambda} can outperform DPO and SLiC by a clear margin on two preference alignment tasks.
Trusted Source Alignment in Large Language Models
Nov 12, 2023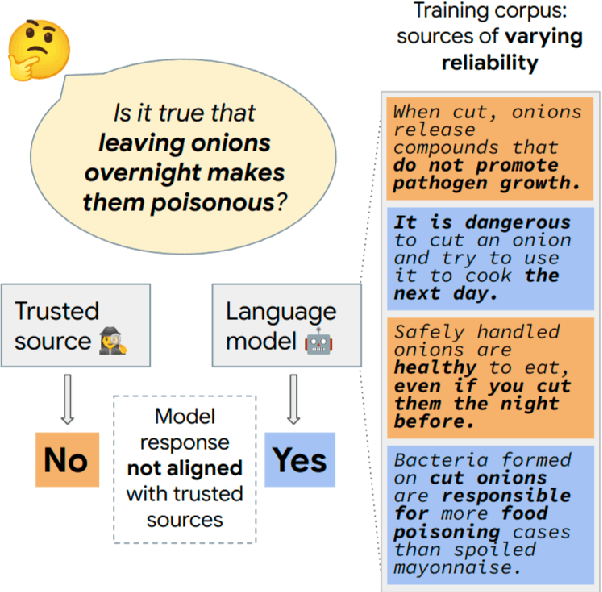



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are trained on web-scale corpora that inevitably include contradictory factual information from sources of varying reliability. In this paper, we propose measuring an LLM property called trusted source alignment (TSA): the model's propensity to align with content produced by trusted publishers in the face of uncertainty or controversy. We present FactCheckQA, a TSA evaluation dataset based on a corpus of fact checking articles. We describe a simple protocol for evaluating TSA and offer a detailed analysis of design considerations including response extraction, claim contextualization, and bias in prompt formulation. Applying the protocol to PaLM-2, we find that as we scale up the model size, the model performance on FactCheckQA improves from near-random to up to 80% balanced accuracy in aligning with trusted sources.
SMILE: Evaluation and Domain Adaptation for Social Media Language Understanding
Jun 30, 2023



Abstract:We study the ability of transformer-based language models (LMs) to understand social media language. Social media (SM) language is distinct from standard written language, yet existing benchmarks fall short of capturing LM performance in this socially, economically, and politically important domain. We quantify the degree to which social media language differs from conventional language and conclude that the difference is significant both in terms of token distribution and rate of linguistic shift. Next, we introduce a new benchmark for Social MedIa Language Evaluation (SMILE) that covers four SM platforms and eleven tasks. Finally, we show that learning a tokenizer and pretraining on a mix of social media and conventional language yields an LM that outperforms the best similar-sized alternative by 4.2 points on the overall SMILE score.
What do LLMs Know about Financial Markets? A Case Study on Reddit Market Sentiment Analysis
Dec 21, 2022



Abstract:Market sentiment analysis on social media content requires knowledge of both financial markets and social media jargon, which makes it a challenging task for human raters. The resulting lack of high-quality labeled data stands in the way of conventional supervised learning methods. Instead, we approach this problem using semi-supervised learning with a large language model (LLM). Our pipeline generates weak financial sentiment labels for Reddit posts with an LLM and then uses that data to train a small model that can be served in production. We find that prompting the LLM to produce Chain-of-Thought summaries and forcing it through several reasoning paths helps generate more stable and accurate labels, while using a regression loss further improves distillation quality. With only a handful of prompts, the final model performs on par with existing supervised models. Though production applications of our model are limited by ethical considerations, the model's competitive performance points to the great potential of using LLMs for tasks that otherwise require skill-intensive annotation.
Charformer: Fast Character Transformers via Gradient-based Subword Tokenization
Jul 02, 2021



Abstract:State-of-the-art models in natural language processing rely on separate rigid subword tokenization algorithms, which limit their generalization ability and adaptation to new settings. In this paper, we propose a new model inductive bias that learns a subword tokenization end-to-end as part of the model. To this end, we introduce a soft gradient-based subword tokenization module (GBST) that automatically learns latent subword representations from characters in a data-driven fashion. Concretely, GBST enumerates candidate subword blocks and learns to score them in a position-wise fashion using a block scoring network. We additionally introduce Charformer, a deep Transformer model that integrates GBST and operates on the byte level. Via extensive experiments on English GLUE, multilingual, and noisy text datasets, we show that Charformer outperforms a series of competitive byte-level baselines while generally performing on par and sometimes outperforming subword-based models. Additionally, Charformer is fast, improving the speed of both vanilla byte-level and subword-level Transformers by 28%-100% while maintaining competitive quality. We believe this work paves the way for highly performant token-free models that are trained completely end-to-end.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge