Feng Han
UniReason 1.0: A Unified Reasoning Framework for World Knowledge Aligned Image Generation and Editing
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Unified multimodal models often struggle with complex synthesis tasks that demand deep reasoning, and typically treat text-to-image generation and image editing as isolated capabilities rather than interconnected reasoning steps. To address this, we propose UniReason, a unified framework that harmonizes these two tasks through a dual reasoning paradigm. We formulate generation as world knowledge-enhanced planning to inject implicit constraints, and leverage editing capabilities for fine-grained visual refinement to further correct visual errors via self-reflection. This approach unifies generation and editing within a shared representation, mirroring the human cognitive process of planning followed by refinement. We support this framework by systematically constructing a large-scale reasoning-centric dataset (~300k samples) covering five major knowledge domains (e.g., cultural commonsense, physics, etc.) for planning, alongside an agent-generated corpus for visual self-correction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniReason achieves advanced performance on reasoning-intensive benchmarks such as WISE, KrisBench and UniREditBench, while maintaining superior general synthesis capabilities.
Unified Personalized Reward Model for Vision Generation
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in multimodal reward models (RMs) have significantly propelled the development of visual generation. Existing frameworks typically adopt Bradley-Terry-style preference modeling or leverage generative VLMs as judges, and subsequently optimize visual generation models via reinforcement learning. However, current RMs suffer from inherent limitations: they often follow a one-size-fits-all paradigm that assumes a monolithic preference distribution or relies on fixed evaluation rubrics. As a result, they are insensitive to content-specific visual cues, leading to systematic misalignment with subjective and context-dependent human preferences. To this end, inspired by human assessment, we propose UnifiedReward-Flex, a unified personalized reward model for vision generation that couples reward modeling with flexible and context-adaptive reasoning. Specifically, given a prompt and the generated visual content, it first interprets the semantic intent and grounds on visual evidence, then dynamically constructs a hierarchical assessment by instantiating fine-grained criteria under both predefined and self-generated high-level dimensions. Our training pipeline follows a two-stage process: (1) we first distill structured, high-quality reasoning traces from advanced closed-source VLMs to bootstrap SFT, equipping the model with flexible and context-adaptive reasoning behaviors; (2) we then perform direct preference optimization (DPO) on carefully curated preference pairs to further strengthen reasoning fidelity and discriminative alignment. To validate the effectiveness, we integrate UnifiedReward-Flex into the GRPO framework for image and video synthesis, and extensive results demonstrate its superiority.
VideoThinker: Building Agentic VideoLLMs with LLM-Guided Tool Reasoning
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Long-form video understanding remains a fundamental challenge for current Video Large Language Models. Most existing models rely on static reasoning over uniformly sampled frames, which weakens temporal localization and leads to substantial information loss in long videos. Agentic tools such as temporal retrieval, spatial zoom, and temporal zoom offer a natural way to overcome these limitations by enabling adaptive exploration of key moments. However, constructing agentic video understanding data requires models that already possess strong long-form video comprehension, creating a circular dependency. We address this challenge with VideoThinker, an agentic Video Large Language Model trained entirely on synthetic tool interaction trajectories. Our key idea is to convert videos into rich captions and employ a powerful agentic language model to generate multi-step tool use sequences in caption space. These trajectories are subsequently grounded back to video by replacing captions with the corresponding frames, yielding a large-scale interleaved video and tool reasoning dataset without requiring any long-form understanding from the underlying model. Training on this synthetic agentic dataset equips VideoThinker with dynamic reasoning capabilities, adaptive temporal exploration, and multi-step tool use. Remarkably, VideoThinker significantly outperforms both caption-only language model agents and strong video model baselines across long-video benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of tool augmented synthetic data and adaptive retrieval and zoom reasoning for long-form video understanding.
Kling-Omni Technical Report
Dec 18, 2025



Abstract:We present Kling-Omni, a generalist generative framework designed to synthesize high-fidelity videos directly from multimodal visual language inputs. Adopting an end-to-end perspective, Kling-Omni bridges the functional separation among diverse video generation, editing, and intelligent reasoning tasks, integrating them into a holistic system. Unlike disjointed pipeline approaches, Kling-Omni supports a diverse range of user inputs, including text instructions, reference images, and video contexts, processing them into a unified multimodal representation to deliver cinematic-quality and highly-intelligent video content creation. To support these capabilities, we constructed a comprehensive data system that serves as the foundation for multimodal video creation. The framework is further empowered by efficient large-scale pre-training strategies and infrastructure optimizations for inference. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that Kling-Omni demonstrates exceptional capabilities in in-context generation, reasoning-based editing, and multimodal instruction following. Moving beyond a content creation tool, we believe Kling-Omni is a pivotal advancement toward multimodal world simulators capable of perceiving, reasoning, generating and interacting with the dynamic and complex worlds.
GrOCE:Graph-Guided Online Concept Erasure for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Concept erasure aims to remove harmful, inappropriate, or copyrighted content from text-to-image diffusion models while preserving non-target semantics. However, existing methods either rely on costly fine-tuning or apply coarse semantic separation, often degrading unrelated concepts and lacking adaptability to evolving concept sets. To alleviate this issue, we propose Graph-Guided Online Concept Erasure (GrOCE), a training-free framework that performs precise and adaptive concept removal through graph-based semantic reasoning. GrOCE models concepts and their interrelations as a dynamic semantic graph, enabling principled reasoning over dependencies and fine-grained isolation of undesired content. It comprises three components: (1) Dynamic Topological Graph Construction for incremental graph building, (2) Adaptive Cluster Identification for multi-hop traversal with similarity-decay scoring, and (3) Selective Edge Severing for targeted edge removal while preserving global semantics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GrOCE achieves state-of-the-art performance on Concept Similarity (CS) and Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) metrics, offering efficient, accurate, and stable concept erasure without retraining.
Dual-LoRA and Quality-Enhanced Pseudo Replay for Multimodal Continual Food Learning
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Food analysis has become increasingly critical for health-related tasks such as personalized nutrition and chronic disease prevention. However, existing large multimodal models (LMMs) in food analysis suffer from catastrophic forgetting when learning new tasks, requiring costly retraining from scratch. To address this, we propose a novel continual learning framework for multimodal food learning, integrating a Dual-LoRA architecture with Quality-Enhanced Pseudo Replay. We introduce two complementary low-rank adapters for each task: a specialized LoRA that learns task-specific knowledge with orthogonal constraints to previous tasks' subspaces, and a cooperative LoRA that consolidates shared knowledge across tasks via pseudo replay. To improve the reliability of replay data, our Quality-Enhanced Pseudo Replay strategy leverages self-consistency and semantic similarity to reduce hallucinations in generated samples. Experiments on the comprehensive Uni-Food dataset show superior performance in mitigating forgetting, representing the first effective continual learning approach for complex food tasks.
Gemini Embedding: Generalizable Embeddings from Gemini
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:In this report, we introduce Gemini Embedding, a state-of-the-art embedding model leveraging the power of Gemini, Google's most capable large language model. Capitalizing on Gemini's inherent multilingual and code understanding capabilities, Gemini Embedding produces highly generalizable embeddings for text spanning numerous languages and textual modalities. The representations generated by Gemini Embedding can be precomputed and applied to a variety of downstream tasks including classification, similarity, clustering, ranking, and retrieval. Evaluated on the Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark (MMTEB), which includes over one hundred tasks across 250+ languages, Gemini Embedding substantially outperforms prior state-of-the-art models, demonstrating considerable improvements in embedding quality. Achieving state-of-the-art performance across MMTEB's multilingual, English, and code benchmarks, our unified model demonstrates strong capabilities across a broad selection of tasks and surpasses specialized domain-specific models.
DuMo: Dual Encoder Modulation Network for Precise Concept Erasure
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:The exceptional generative capability of text-to-image models has raised substantial safety concerns regarding the generation of Not-Safe-For-Work (NSFW) content and potential copyright infringement. To address these concerns, previous methods safeguard the models by eliminating inappropriate concepts. Nonetheless, these models alter the parameters of the backbone network and exert considerable influences on the structural (low-frequency) components of the image, which undermines the model's ability to retain non-target concepts. In this work, we propose our Dual encoder Modulation network (DuMo), which achieves precise erasure of inappropriate target concepts with minimum impairment to non-target concepts. In contrast to previous methods, DuMo employs the Eraser with PRior Knowledge (EPR) module which modifies the skip connection features of the U-NET and primarily achieves concept erasure on details (high-frequency) components of the image. To minimize the damage to non-target concepts during erasure, the parameters of the backbone U-NET are frozen and the prior knowledge from the original skip connection features is introduced to the erasure process. Meanwhile, the phenomenon is observed that distinct erasing preferences for the image structure and details are demonstrated by the EPR at different timesteps and layers. Therefore, we adopt a novel Time-Layer MOdulation process (TLMO) that adjusts the erasure scale of EPR module's outputs across different layers and timesteps, automatically balancing the erasure effects and model's generative ability. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on Explicit Content Erasure, Cartoon Concept Removal and Artistic Style Erasure, clearly outperforming alternative methods. Code is available at https://github.com/Maplebb/DuMo
Explaining Model Overfitting in CNNs via GMM Clustering
Dec 12, 2024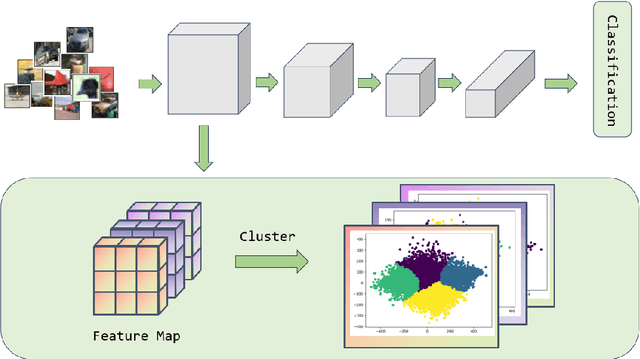
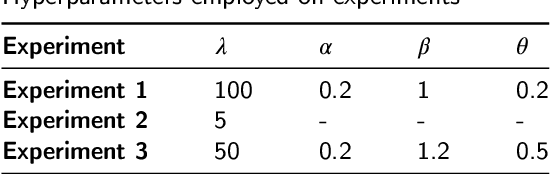
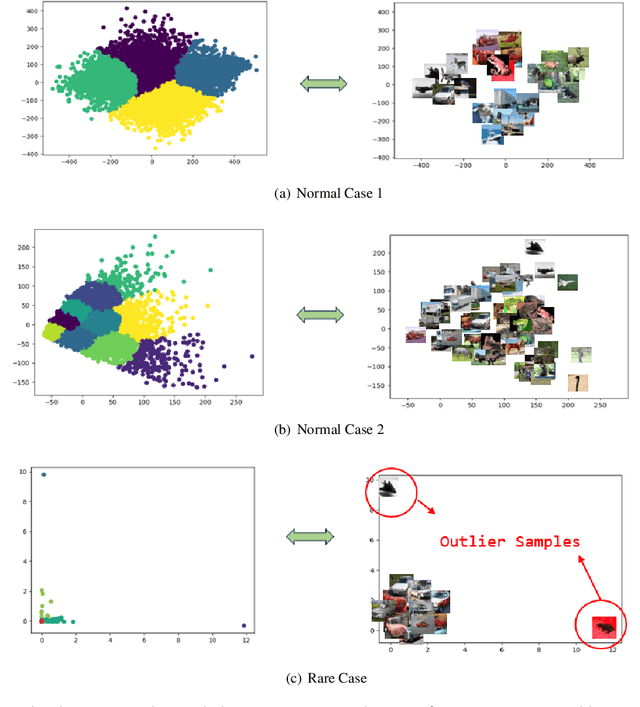

Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have demonstrated remarkable prowess in the field of computer vision. However, their opaque decision-making processes pose significant challenges for practical applications. In this study, we provide quantitative metrics for assessing CNN filters by clustering the feature maps corresponding to individual filters in the model via Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM). By analyzing the clustering results, we screen out some anomaly filters associated with outlier samples. We further analyze the relationship between the anomaly filters and model overfitting, proposing three hypotheses. This method is universally applicable across diverse CNN architectures without modifications, as evidenced by its successful application to models like AlexNet and LeNet-5. We present three meticulously designed experiments demonstrating our hypotheses from the perspectives of model behavior, dataset characteristics, and filter impacts. Through this work, we offer a novel perspective for evaluating the CNN performance and gain new insights into the operational behavior of model overfitting.
Hyperspectral Image Cross-Domain Object Detection Method based on Spectral-Spatial Feature Alignment
Nov 25, 2024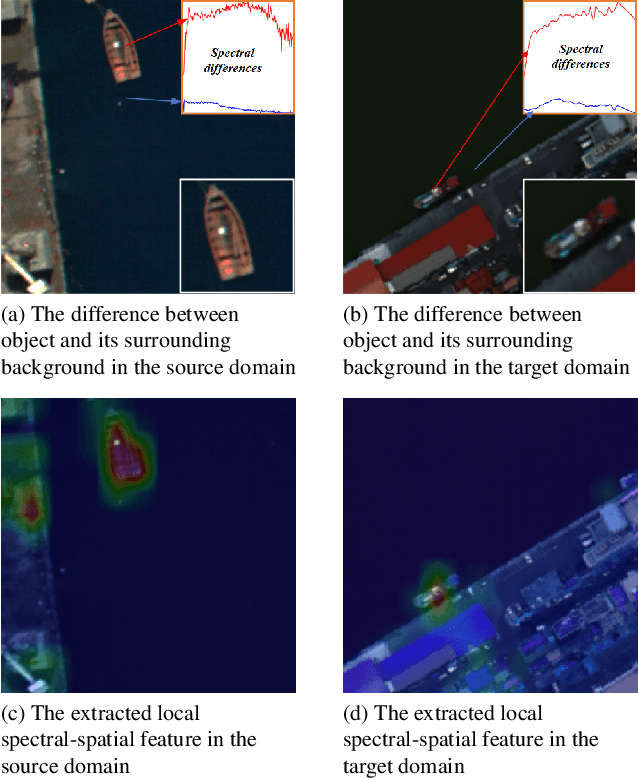
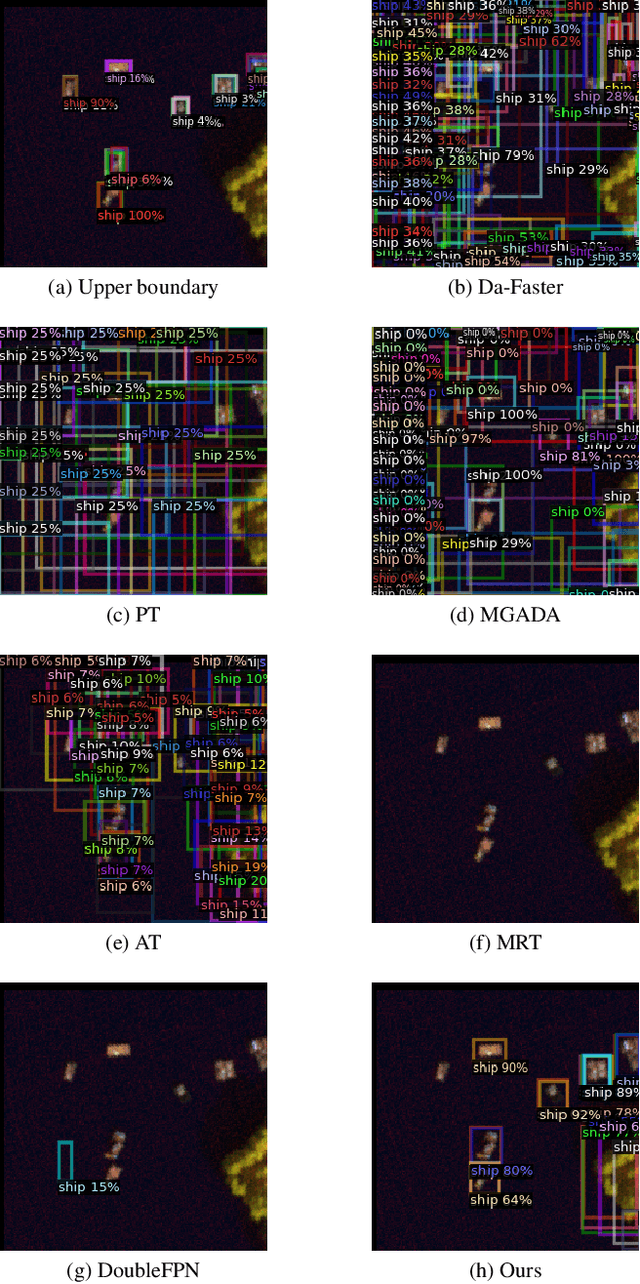
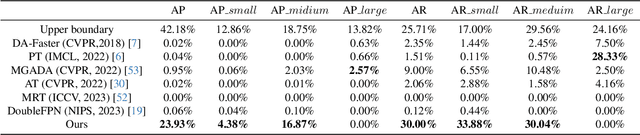

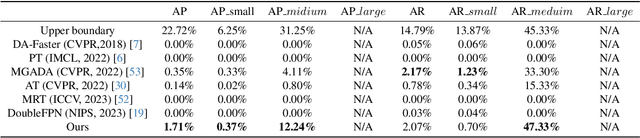
Abstract:With consecutive bands in a wide range of wavelengths, hyperspectral images (HSI) have provided a unique tool for object detection task. However, existing HSI object detection methods have not been fully utilized in real applications, which is mainly resulted by the difference of spatial and spectral resolution between the unlabeled target domain and a labeled source domain, i.e. the domain shift of HSI. In this work, we aim to explore the unsupervised cross-domain object detection of HSI. Our key observation is that the local spatial-spectral characteristics remain invariant across different domains. For solving the problem of domain-shift, we propose a HSI cross-domain object detection method based on spectral-spatial feature alignment, which is the first attempt in the object detection community to the best of our knowledge. Firstly, we develop a spectral-spatial alignment module to extract domain-invariant local spatial-spectral features. Secondly, the spectral autocorrelation module has been designed to solve the domain shift in the spectral domain specifically, which can effectively align HSIs with different spectral resolutions. Besides, we have collected and annotated an HSI dataset for the cross-domain object detection. Our experimental results have proved the effectiveness of HSI cross-domain object detection, which has firstly demonstrated a significant and promising step towards HSI cross-domain object detection in the object detection community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge