Explaining Model Overfitting in CNNs via GMM Clustering
Paper and Code
Dec 12, 2024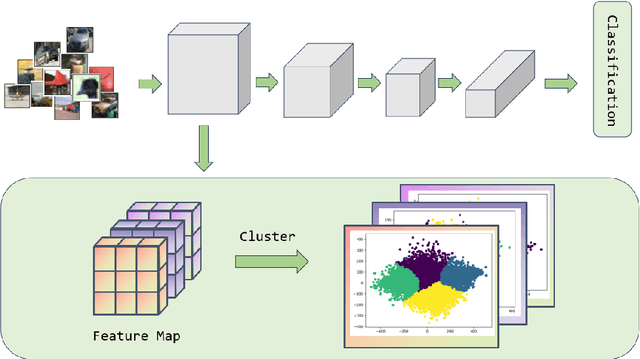
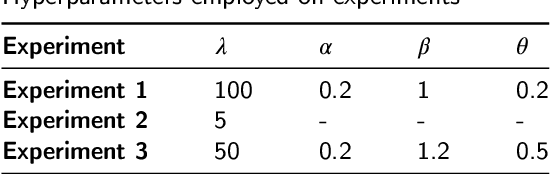
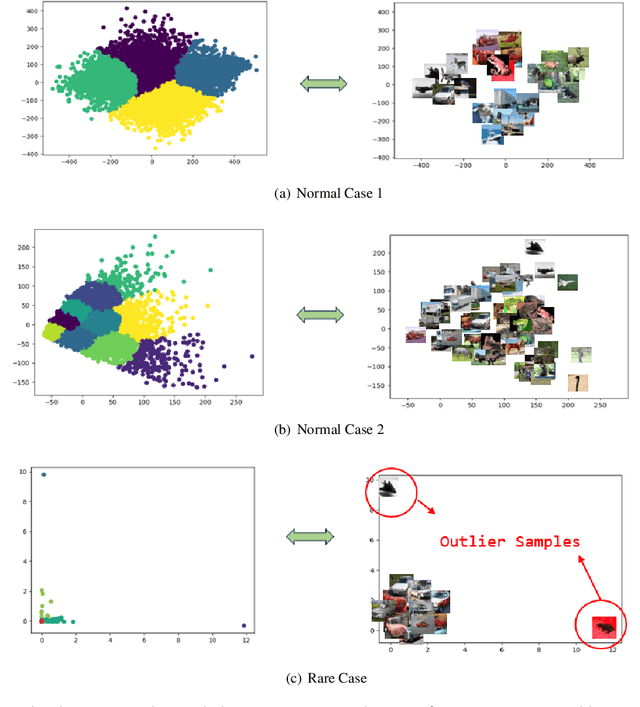

Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have demonstrated remarkable prowess in the field of computer vision. However, their opaque decision-making processes pose significant challenges for practical applications. In this study, we provide quantitative metrics for assessing CNN filters by clustering the feature maps corresponding to individual filters in the model via Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM). By analyzing the clustering results, we screen out some anomaly filters associated with outlier samples. We further analyze the relationship between the anomaly filters and model overfitting, proposing three hypotheses. This method is universally applicable across diverse CNN architectures without modifications, as evidenced by its successful application to models like AlexNet and LeNet-5. We present three meticulously designed experiments demonstrating our hypotheses from the perspectives of model behavior, dataset characteristics, and filter impacts. Through this work, we offer a novel perspective for evaluating the CNN performance and gain new insights into the operational behavior of model overfitting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge