Jingang Yi
Optimal Planning for Multi-Robot Simultaneous Area and Line Coverage Using Hierarchical Cyclic Merging Regulation
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:The double coverage problem focuses on determining efficient, collision-free routes for multiple robots to simultaneously cover linear features (e.g., surface cracks or road routes) and survey areas (e.g., parking lots or local regions) in known environments. In these problems, each robot carries two functional roles: service (linear feature footprint coverage) and exploration (complete area coverage). Service has a smaller operational footprint but incurs higher costs (e.g., time) compared to exploration. We present optimal planning algorithms for the double coverage problems using hierarchical cyclic merging regulation (HCMR). To reduce the complexity for optimal planning solutions, we analyze the manifold attachment process during graph traversal from a Morse theory perspective. We show that solutions satisfying minimum path length and collision-free constraints must belong to a Morse-bounded collection. To identify this collection, we introduce the HCMR algorithm. In HCMR, cyclic merging search regulates traversal behavior, while edge sequence back propagation converts these regulations into graph edge traversal sequences. Incorporating balanced partitioning, the optimal sequence is selected to generate routes for each robot. We prove the optimality of the HCMR algorithm under a fixed sweep direction. The multi-robot simulation results demonstrate that the HCMR algorithm significantly improves planned path length by at least 10.0%, reduces task time by at least 16.9% in average, and ensures conflict-free operation compared to other state-of-the-art planning methods.
Assistive Control of Knee Exoskeletons for Human Walking on Granular Terrains
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:Human walkers traverse diverse environments and demonstrate different gait locomotion and energy cost on granular terrains compared to solid ground. We present a stiffness-based model predictive control approach of knee exoskeleton assistance on sand. The gait and locomotion comparison is first discussed for human walkers on sand and solid ground. A machine learning-based estimation scheme is then presented to predict the ground reaction forces (GRFs) for human walkers on different terrains in real time. Built on the estimated GRFs and human joint torques, a knee exoskeleton controller is designed to provide assistive torque through a model predictive stiffness control scheme. We conduct indoor and outdoor experiments to validate the modeling and control design and their performance. The experiments demonstrate the major muscle activation and metabolic reductions by respectively 15% and 3.7% under the assistive exoskeleton control of human walking on sand.
Exoskeleton-Assisted Balance and Task Evaluation During Quiet Stance and Kneeling in Construction
Aug 14, 2024Abstract:Construction workers exert intense physical effort and experience serious safety and health risks in hazardous working environments. Quiet stance and kneeling are among the most common postures performed by construction workers during their daily work. This paper analyzes lower-limb joint influence on neural balance control strategies using the frequency behavior of the intersection point of ground reaction forces. To evaluate the impact of elevation and wearable knee exoskeletons on postural balance and welding task performance, we design and integrate virtual- and mixed-reality (VR/MR) to simulate elevated environments and welding tasks. A linear quadratic regulator-controlled triple- and double-link inverted pendulum model is used for balance strategy quantification in quiet stance and kneeling, respectively. Extensive multi-subject experiments are conducted to evaluate the usability of occupational exoskeletons in destabilizing construction environments. The quantified balance strategies capture the significance of knee joint during balance control of quiet stance and kneeling gaits. Results show that center of pressure sway area reduced up to 62% in quiet stance and 39% in kneeling for subjects tested in high-elevation VR/MR worksites when provided knee exoskeleton assistance. The comprehensive balance and multitask evaluation methodology developed aims to reveal exoskeleton design considerations to mitigate the fall risk in construction.
Foot Shape-Dependent Resistive Force Model for Bipedal Walkers on Granular Terrains
Mar 06, 2024



Abstract:Legged robots have demonstrated high efficiency and effectiveness in unstructured and dynamic environments. However, it is still challenging for legged robots to achieve rapid and efficient locomotion on deformable, yielding substrates, such as granular terrains. We present an enhanced resistive force model for bipedal walkers on soft granular terrains by introducing effective intrusion depth correction. The enhanced force model captures fundamental kinetic results considering the robot foot shape, walking gait speed variation, and energy expense. The model is validated by extensive foot intrusion experiments with a bipedal robot. The results confirm the model accuracy on the given type of granular terrains. The model can be further integrated with the motion control of bipedal robotic walkers.
Biomechanical Comparison of Human Walking Locomotion on Solid Ground and Sand
Mar 06, 2024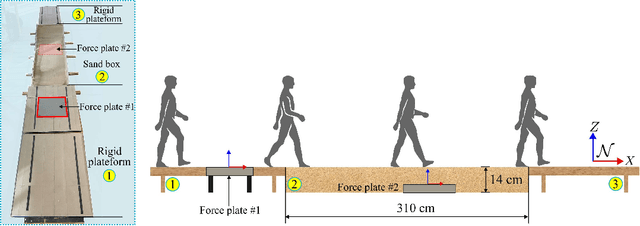
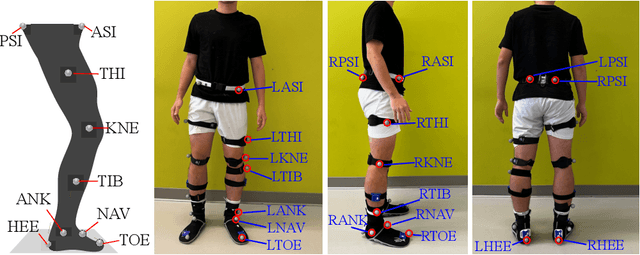
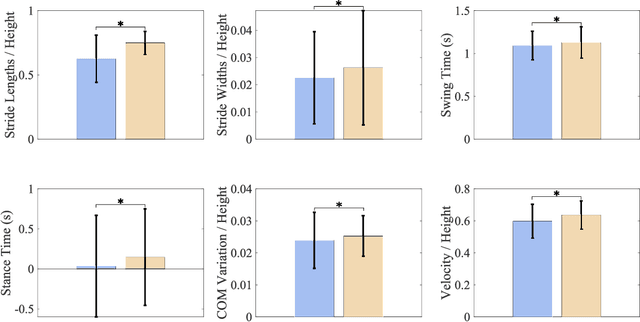
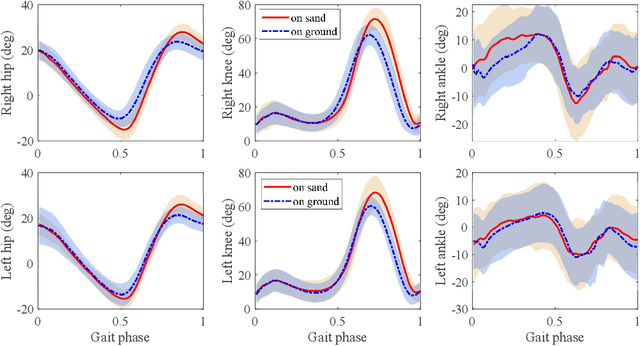
Abstract:Current studies on human locomotion focus mainly on solid ground walking conditions. In this paper, we present a biomechanic comparison of human walking locomotion on solid ground and sand. A novel dataset containing 3-dimensional motion and biomechanical data from 20 able-bodied adults for locomotion on solid ground and sand is collected. We present the data collection methods and report the sensor data along with the kinematic and kinetic profiles of joint biomechanics. A comprehensive analysis of human gait and joint stiffness profiles is presented. The kinematic and kinetic analysis reveals that human walking locomotion on sand shows different ground reaction forces and joint torque profiles, compared with those patterns from walking on solid ground. These gait differences reflect that humans adopt motion control strategies for yielding terrain conditions such as sand. The dataset also provides a source of locomotion data for researchers to study human activity recognition and assistive devices for walking on different terrains.
A Reduced-Order Resistive Force Model for Robotic Foot-Mud Interactions
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:Legged robots are well-suited for broad exploration tasks in complex environments with yielding terrain. Understanding robotic foot-terrain interactions is critical for safe locomotion and walking efficiency for legged robots. This paper presents a reduced-order resistive-force model for robotic-foot/mud interactions. We focus on vertical robot locomotion on mud and propose a visco-elasto-plastic analog to model the foot/mud interaction forces. Dynamic behaviors such as mud visco-elasticity, withdrawing cohesive suction, and yielding are explicitly discussed with the proposed model. Besides comparing with dry/wet granular materials, mud intrusion experiments are conducted to validate the force model. The dependency of the model parameter on water content and foot velocity is also studied to reveal in-depth model properties under various conditions. The proposed force model potentially provides an enabling tool for legged robot locomotion and control on muddy terrain.
Complete and Near-Optimal Robotic Crack Coverage and Filling in Civil Infrastructure
Mar 01, 2024Abstract:We present a simultaneous sensor-based inspection and footprint coverage (SIFC) planning and control design with applications to autonomous robotic crack mapping and filling. The main challenge of the SIFC problem lies in the coupling of complete sensing (for mapping) and robotic footprint (for filling) coverage tasks. Initially, we assume known target information (e.g., crack) and employ classic cell decomposition methods to achieve complete sensing coverage of the workspace and complete robotic footprint coverage using the least-cost route. Subsequently, we generalize the algorithm to handle unknown target information, allowing the robot to scan and incrementally construct the target graph online while conducting robotic footprint coverage. The online polynomial-time SIFC planning algorithm minimizes the total robot traveling distance, guarantees complete sensing coverage of the entire workspace, and achieves near-optimal robotic footprint coverage, as demonstrated through empirical experiments. For the demonstrated application, we design coordinated nozzle motion control with the planned robot trajectory to efficiently fill all cracks within the robot's footprint. Experimental results are presented to illustrate the algorithm's design, performance, and comparisons. The SIFC algorithm offers a high-efficiency motion planning solution for various robotic applications requiring simultaneous sensing and actuation coverage.
Gaussian Process-Based Learning Control of Underactuated Balance Robots with an External and Internal Convertible Modeling Structure
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:External and internal convertible (EIC) form-based motion control is one of the effective designs of simultaneously trajectory tracking and balance for underactuated balance robots. Under certain conditions, the EIC-based control design however leads to uncontrolled robot motion. We present a Gaussian process (GP)-based data-driven learning control for underactuated balance robots with the EIC modeling structure. Two GP-based learning controllers are presented by using the EIC structure property. The partial EIC (PEIC)-based control design partitions the robotic dynamics into a fully actuated subsystem and one reduced-order underactuated system. The null-space EIC (NEIC)-based control compensates for the uncontrolled motion in a subspace, while the other closed-loop dynamics are not affected. Under the PEIC- and NEIC-based, the tracking and balance tasks are guaranteed and convergence rate and bounded errors are achieved without causing any uncontrolled motion by the original EIC-based control. We validate the results and demonstrate the GP-based learning control design performance using two inverted pendulum platforms.
A Physics-informed Machine Learning-based Control Method for Nonlinear Dynamic Systems with Highly Noisy Measurements
Nov 12, 2023



Abstract:This study presents a physics-informed machine learning-based control method for nonlinear dynamic systems with highly noisy measurements. Existing data-driven control methods that use machine learning for system identification cannot effectively cope with highly noisy measurements, resulting in unstable control performance. To address this challenge, the present study extends current physics-informed machine learning capabilities for modeling nonlinear dynamics with control and integrates them into a model predictive control framework. To demonstrate the capability of the proposed method we test and validate with two noisy nonlinear dynamic systems: the chaotic Lorenz 3 system, and turning machine tool. Analysis of the results illustrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art benchmarks as measured by both modeling accuracy and control performance for nonlinear dynamic systems under high-noise conditions.
Socially Cognizant Robotics for a Technology Enhanced Society
Oct 27, 2023



Abstract:Emerging applications of robotics, and concerns about their impact, require the research community to put human-centric objectives front-and-center. To meet this challenge, we advocate an interdisciplinary approach, socially cognizant robotics, which synthesizes technical and social science methods. We argue that this approach follows from the need to empower stakeholder participation (from synchronous human feedback to asynchronous societal assessment) in shaping AI-driven robot behavior at all levels, and leads to a range of novel research perspectives and problems both for improving robots' interactions with individuals and impacts on society. Drawing on these arguments, we develop best practices for socially cognizant robot design that balance traditional technology-based metrics (e.g. efficiency, precision and accuracy) with critically important, albeit challenging to measure, human and society-based metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge