Matthew Stone
University of Pennsylvania
Dialogue with Robots: Proposals for Broadening Participation and Research in the SLIVAR Community
Apr 01, 2024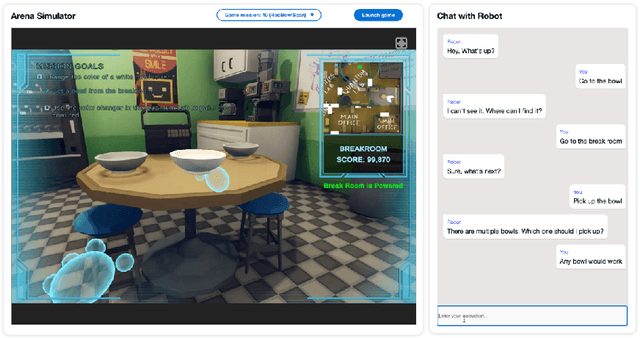
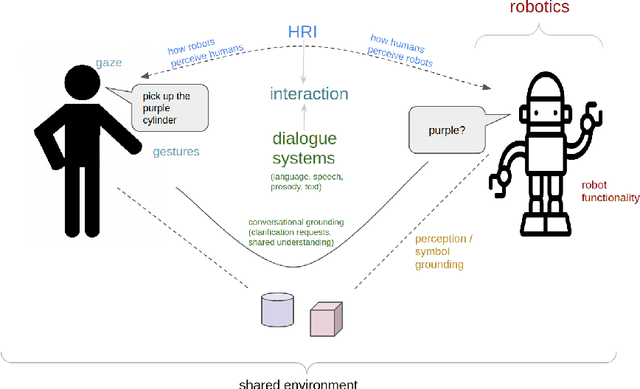
Abstract:The ability to interact with machines using natural human language is becoming not just commonplace, but expected. The next step is not just text interfaces, but speech interfaces and not just with computers, but with all machines including robots. In this paper, we chronicle the recent history of this growing field of spoken dialogue with robots and offer the community three proposals, the first focused on education, the second on benchmarks, and the third on the modeling of language when it comes to spoken interaction with robots. The three proposals should act as white papers for any researcher to take and build upon.
Socially Cognizant Robotics for a Technology Enhanced Society
Oct 27, 2023



Abstract:Emerging applications of robotics, and concerns about their impact, require the research community to put human-centric objectives front-and-center. To meet this challenge, we advocate an interdisciplinary approach, socially cognizant robotics, which synthesizes technical and social science methods. We argue that this approach follows from the need to empower stakeholder participation (from synchronous human feedback to asynchronous societal assessment) in shaping AI-driven robot behavior at all levels, and leads to a range of novel research perspectives and problems both for improving robots' interactions with individuals and impacts on society. Drawing on these arguments, we develop best practices for socially cognizant robot design that balance traditional technology-based metrics (e.g. efficiency, precision and accuracy) with critically important, albeit challenging to measure, human and society-based metrics.
Investigating Reinforcement Learning for Communication Strategies in a Task-Initiative Setting
Aug 03, 2023Abstract:Many conversational domains require the system to present nuanced information to users. Such systems must follow up what they say to address clarification questions and repair misunderstandings. In this work, we explore this interactive strategy in a referential communication task. Using simulation, we analyze the communication trade-offs between initial presentation and subsequent followup as a function of user clarification strategy, and compare the performance of several baseline strategies to policies derived by reinforcement learning. We find surprising advantages to coherence-based representations of dialogue strategy, which bring minimal data requirements, explainable choices, and strong audit capabilities, but incur little loss in predicted outcomes across a wide range of user models.
Zero-shot Cross-Linguistic Learning of Event Semantics
Jul 05, 2022
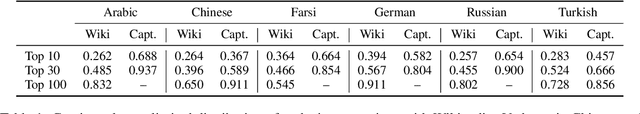
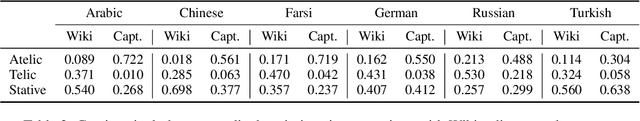
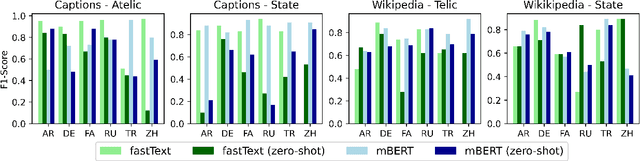
Abstract:Typologically diverse languages offer systems of lexical and grammatical aspect that allow speakers to focus on facets of event structure in ways that comport with the specific communicative setting and discourse constraints they face. In this paper, we look specifically at captions of images across Arabic, Chinese, Farsi, German, Russian, and Turkish and describe a computational model for predicting lexical aspects. Despite the heterogeneity of these languages, and the salient invocation of distinctive linguistic resources across their caption corpora, speakers of these languages show surprising similarities in the ways they frame image content. We leverage this observation for zero-shot cross-lingual learning and show that lexical aspects can be predicted for a given language despite not having observed any annotated data for this language at all.
Cross-Modal Coherence for Text-to-Image Retrieval
Sep 22, 2021

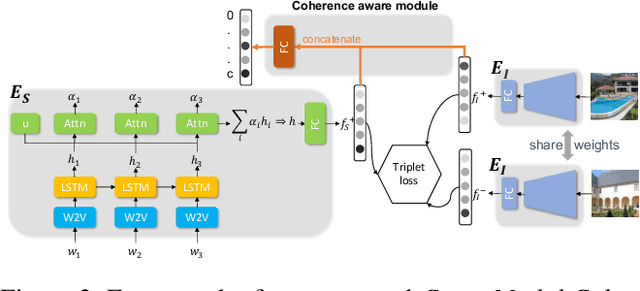
Abstract:Common image-text joint understanding techniques presume that images and the associated text can universally be characterized by a single implicit model. However, co-occurring images and text can be related in qualitatively different ways, and explicitly modeling it could improve the performance of current joint understanding models. In this paper, we train a Cross-Modal Coherence Modelfor text-to-image retrieval task. Our analysis shows that models trained with image--text coherence relations can retrieve images originally paired with target text more often than coherence-agnostic models. We also show via human evaluation that images retrieved by the proposed coherence-aware model are preferred over a coherence-agnostic baseline by a huge margin. Our findings provide insights into the ways that different modalities communicate and the role of coherence relations in capturing commonsense inferences in text and imagery.
COSMic: A Coherence-Aware Generation Metric for Image Descriptions
Sep 11, 2021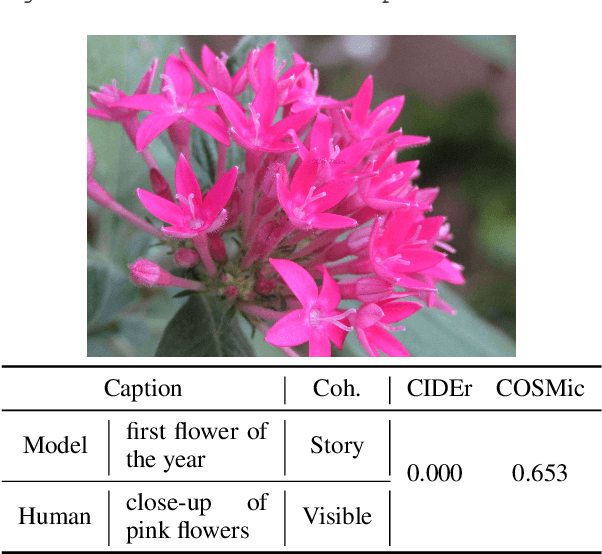
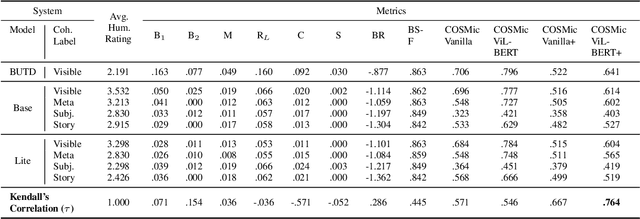

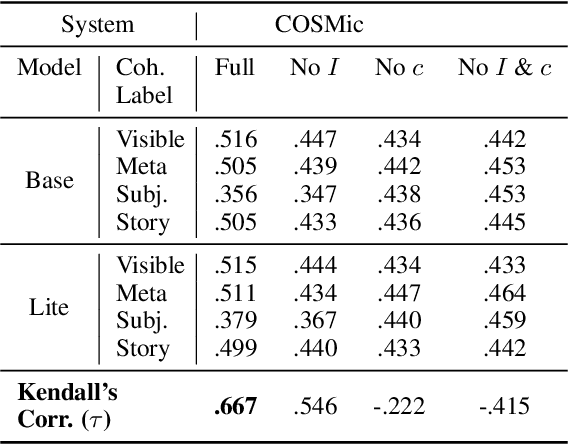
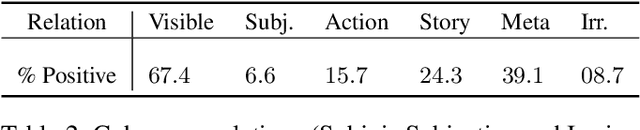
Abstract:Developers of text generation models rely on automated evaluation metrics as a stand-in for slow and expensive manual evaluations. However, image captioning metrics have struggled to give accurate learned estimates of the semantic and pragmatic success of output text. We address this weakness by introducing the first discourse-aware learned generation metric for evaluating image descriptions. Our approach is inspired by computational theories of discourse for capturing information goals using coherence. We present a dataset of image$\unicode{x2013}$description pairs annotated with coherence relations. We then train a coherence-aware metric on a subset of the Conceptual Captions dataset and measure its effectiveness$\unicode{x2014}$its ability to predict human ratings of output captions$\unicode{x2014}$on a test set composed of out-of-domain images. We demonstrate a higher Kendall Correlation Coefficient for our proposed metric with the human judgments for the results of a number of state-of-the-art coherence-aware caption generation models when compared to several other metrics including recently proposed learned metrics such as BLEURT and BERTScore.
Aspectuality Across Genre: A Distributional Semantics Approach
Oct 31, 2020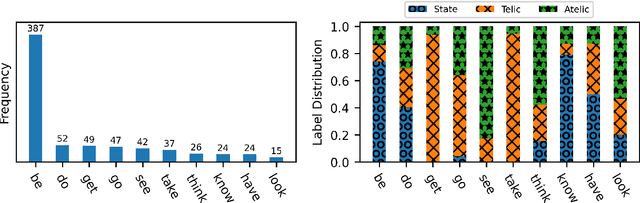
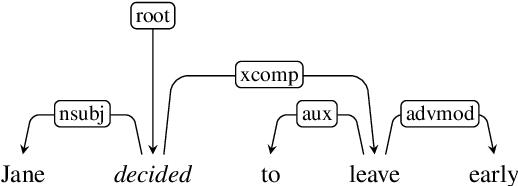
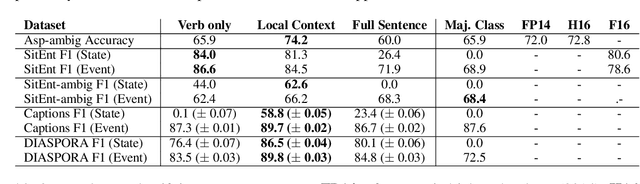
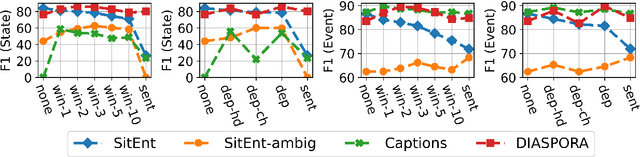
Abstract:The interpretation of the lexical aspect of verbs in English plays a crucial role for recognizing textual entailment and learning discourse-level inferences. We show that two elementary dimensions of aspectual class, states vs. events, and telic vs. atelic events, can be modelled effectively with distributional semantics. We find that a verb's local context is most indicative of its aspectual class, and demonstrate that closed class words tend to be stronger discriminating contexts than content words. Our approach outperforms previous work on three datasets. Lastly, we contribute a dataset of human--human conversations annotated with lexical aspect and present experiments that show the correlation of telicity with genre and discourse goals.
Discourse Coherence, Reference Grounding and Goal Oriented Dialogue
Jul 08, 2020
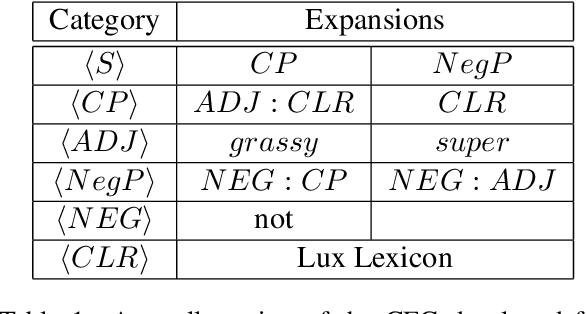
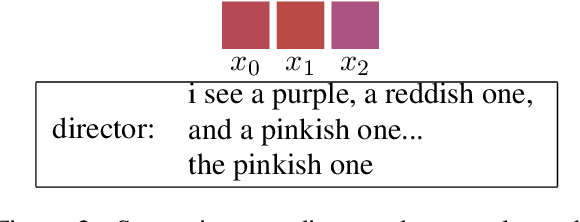
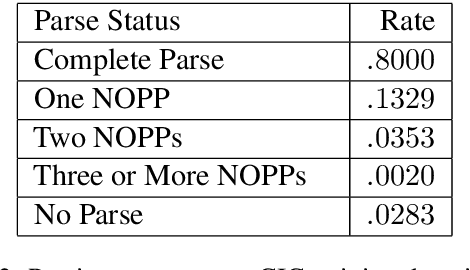
Abstract:Prior approaches to realizing mixed-initiative human--computer referential communication have adopted information-state or collaborative problem-solving approaches. In this paper, we argue for a new approach, inspired by coherence-based models of discourse such as SDRT \cite{asher-lascarides:2003a}, in which utterances attach to an evolving discourse structure and the associated knowledge graph of speaker commitments serves as an interface to real-world reasoning and conversational strategy. As first steps towards implementing the approach, we describe a simple dialogue system in a referential communication domain that accumulates constraints across discourse, interprets them using a learned probabilistic model, and plans clarification using reinforcement learning.
Clue: Cross-modal Coherence Modeling for Caption Generation
May 02, 2020
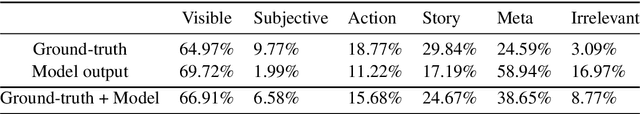

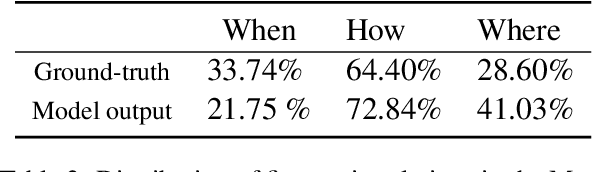
Abstract:We use coherence relations inspired by computational models of discourse to study the information needs and goals of image captioning. Using an annotation protocol specifically devised for capturing image--caption coherence relations, we annotate 10,000 instances from publicly-available image--caption pairs. We introduce a new task for learning inferences in imagery and text, coherence relation prediction, and show that these coherence annotations can be exploited to learn relation classifiers as an intermediary step, and also train coherence-aware, controllable image captioning models. The results show a dramatic improvement in the consistency and quality of the generated captions with respect to information needs specified via coherence relations.
That and There: Judging the Intent of Pointing Actions with Robotic Arms
Dec 13, 2019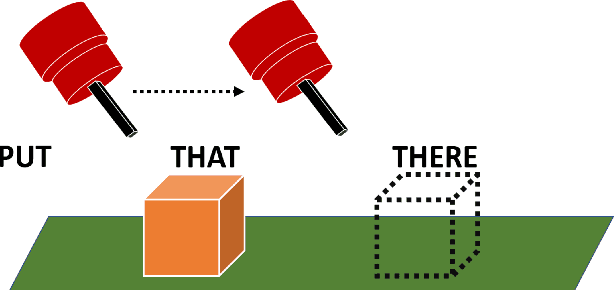
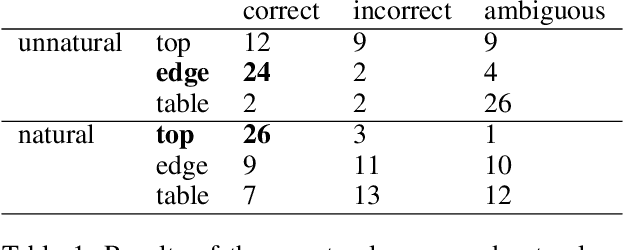
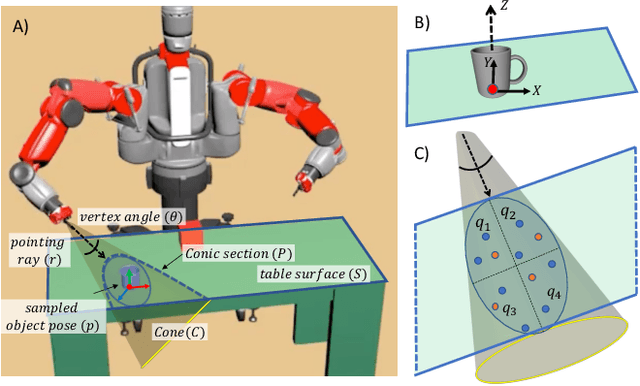
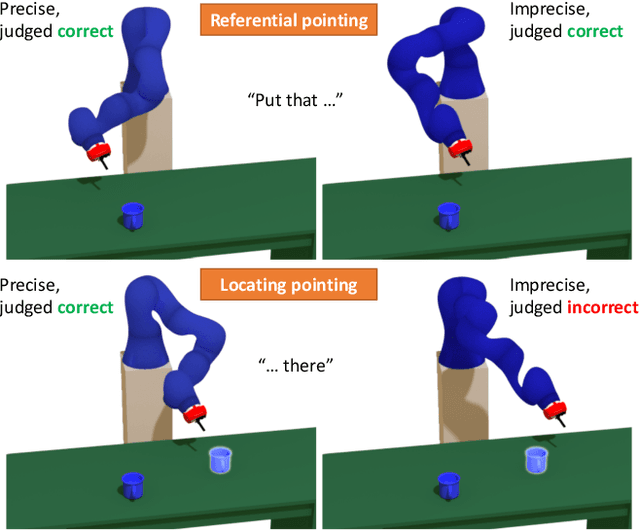
Abstract:Collaborative robotics requires effective communication between a robot and a human partner. This work proposes a set of interpretive principles for how a robotic arm can use pointing actions to communicate task information to people by extending existing models from the related literature. These principles are evaluated through studies where English-speaking human subjects view animations of simulated robots instructing pick-and-place tasks. The evaluation distinguishes two classes of pointing actions that arise in pick-and-place tasks: referential pointing (identifying objects) and locating pointing (identifying locations). The study indicates that human subjects show greater flexibility in interpreting the intent of referential pointing compared to locating pointing, which needs to be more deliberate. The results also demonstrate the effects of variation in the environment and task context on the interpretation of pointing. Our corpus, experiments and design principles advance models of context, common sense reasoning and communication in embodied communication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge