Shahab Raji
Zero-shot Cross-Linguistic Learning of Event Semantics
Jul 05, 2022
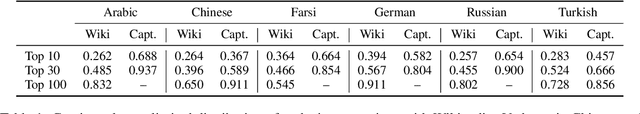
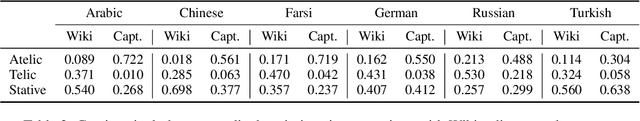
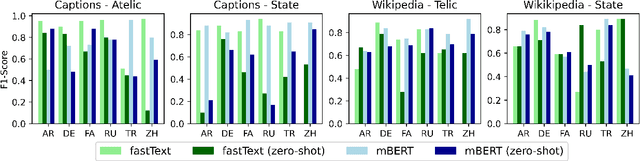
Abstract:Typologically diverse languages offer systems of lexical and grammatical aspect that allow speakers to focus on facets of event structure in ways that comport with the specific communicative setting and discourse constraints they face. In this paper, we look specifically at captions of images across Arabic, Chinese, Farsi, German, Russian, and Turkish and describe a computational model for predicting lexical aspects. Despite the heterogeneity of these languages, and the salient invocation of distinctive linguistic resources across their caption corpora, speakers of these languages show surprising similarities in the ways they frame image content. We leverage this observation for zero-shot cross-lingual learning and show that lexical aspects can be predicted for a given language despite not having observed any annotated data for this language at all.
NL-Augmenter: A Framework for Task-Sensitive Natural Language Augmentation
Dec 06, 2021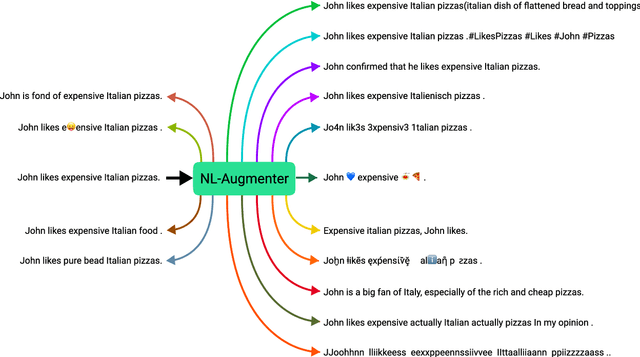
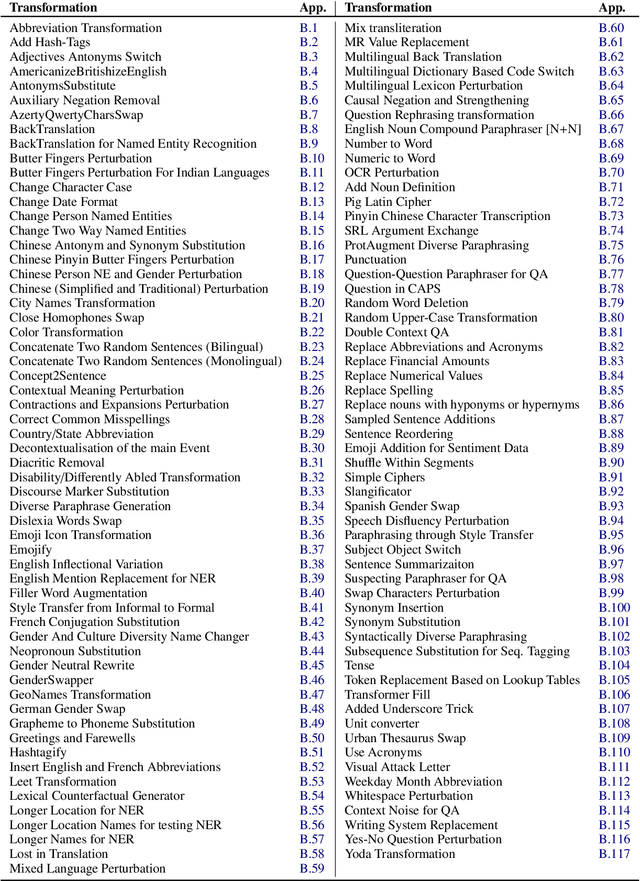
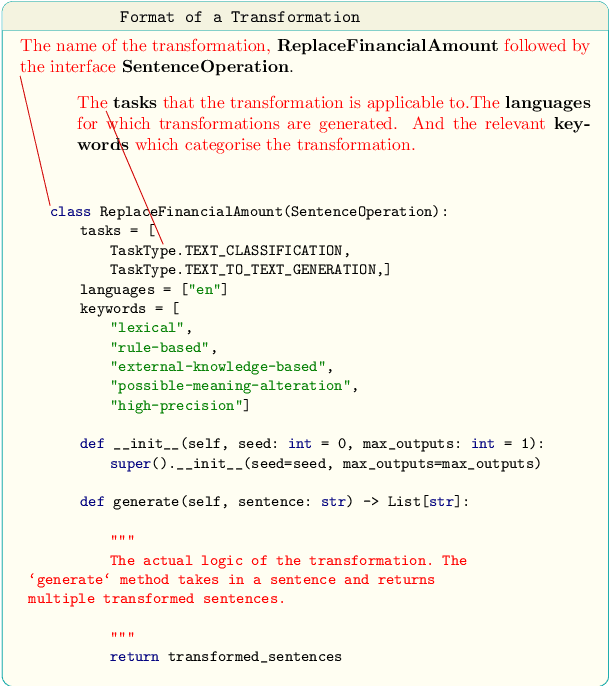
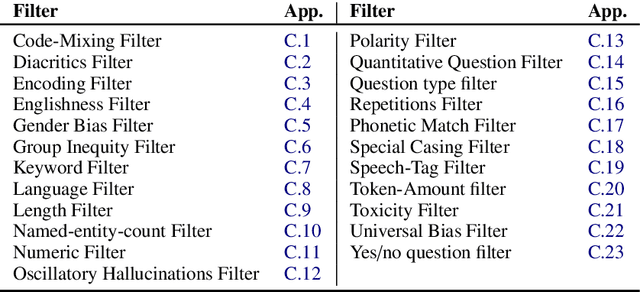
Abstract:Data augmentation is an important component in the robustness evaluation of models in natural language processing (NLP) and in enhancing the diversity of the data they are trained on. In this paper, we present NL-Augmenter, a new participatory Python-based natural language augmentation framework which supports the creation of both transformations (modifications to the data) and filters (data splits according to specific features). We describe the framework and an initial set of 117 transformations and 23 filters for a variety of natural language tasks. We demonstrate the efficacy of NL-Augmenter by using several of its transformations to analyze the robustness of popular natural language models. The infrastructure, datacards and robustness analysis results are available publicly on the NL-Augmenter repository (\url{https://github.com/GEM-benchmark/NL-Augmenter}).
Guilt by Association: Emotion Intensities in Lexical Representations
Apr 18, 2021

Abstract:What do word vector representations reveal about the emotions associated with words? In this study, we consider the task of estimating word-level emotion intensity scores for specific emotions, exploring unsupervised, supervised, and finally a self-supervised method of extracting emotional associations from word vector representations. Overall, we find that word vectors carry substantial potential for inducing fine-grained emotion intensity scores, showing a far higher correlation with human ground truth ratings than achieved by state-of-the-art emotion lexicons.
ParsiNLU: A Suite of Language Understanding Challenges for Persian
Dec 11, 2020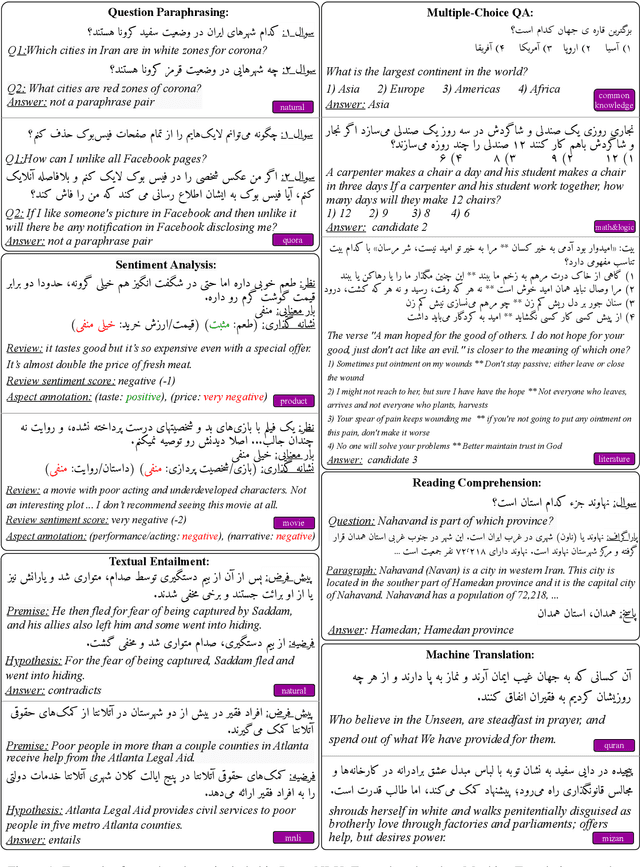
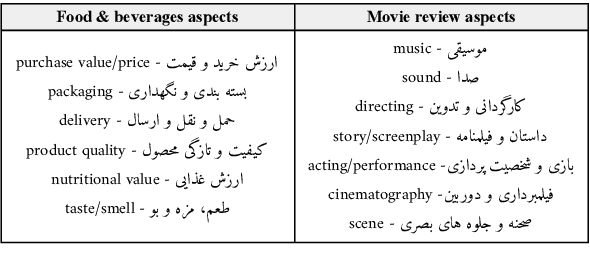
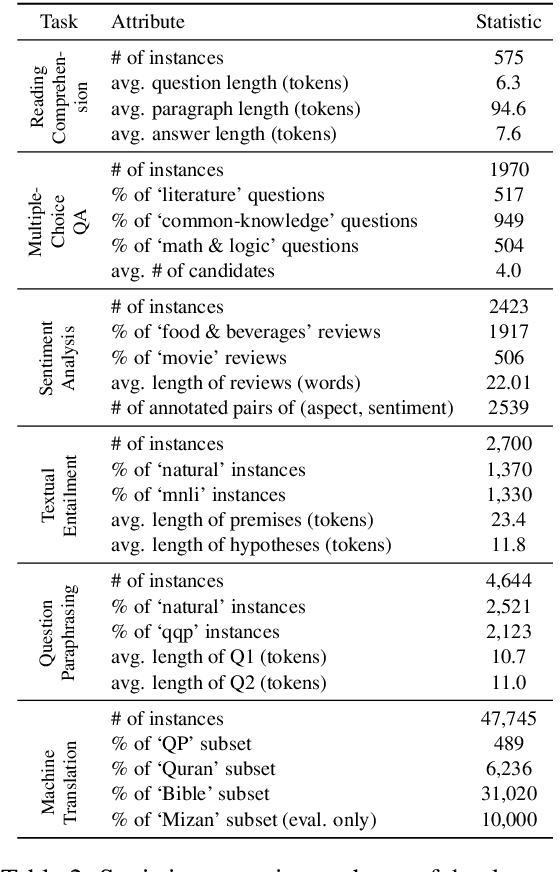
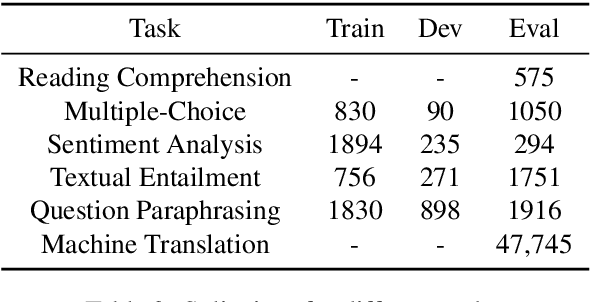
Abstract:Despite the progress made in recent years in addressing natural language understanding (NLU) challenges, the majority of this progress remains to be concentrated on resource-rich languages like English. This work focuses on Persian language, one of the widely spoken languages in the world, and yet there are few NLU datasets available for this rich language. The availability of high-quality evaluation datasets is a necessity for reliable assessment of the progress on different NLU tasks and domains. We introduce ParsiNLU, the first benchmark in Persian language that includes a range of high-level tasks -- Reading Comprehension, Textual Entailment, etc. These datasets are collected in a multitude of ways, often involving manual annotations by native speakers. This results in over 14.5$k$ new instances across 6 distinct NLU tasks. Besides, we present the first results on state-of-the-art monolingual and multi-lingual pre-trained language-models on this benchmark and compare them with human performance, which provides valuable insights into our ability to tackle natural language understanding challenges in Persian. We hope ParsiNLU fosters further research and advances in Persian language understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge