Bashar Alhafni
Opportunities and Challenges of LLMs in Education: An NLP Perspective
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Interest in the role of large language models (LLMs) in education is increasing, considering the new opportunities they offer for teaching, learning, and assessment. In this paper, we examine the impact of LLMs on educational NLP in the context of two main application scenarios: {\em assistance} and {\em assessment}, grounding them along the four dimensions -- reading, writing, speaking, and tutoring. We then present the new directions enabled by LLMs, and the key challenges to address. We envision that this holistic overview would be useful for NLP researchers and practitioners interested in exploring the role of LLMs in developing language-focused and NLP-enabled educational applications of the future.
BALSAM: A Platform for Benchmarking Arabic Large Language Models
Jul 30, 2025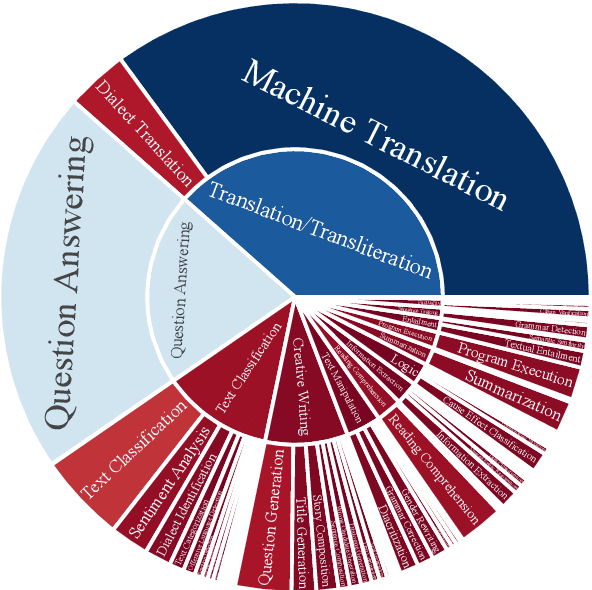



Abstract:The impressive advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) in English has not been matched across all languages. In particular, LLM performance in Arabic lags behind, due to data scarcity, linguistic diversity of Arabic and its dialects, morphological complexity, etc. Progress is further hindered by the quality of Arabic benchmarks, which typically rely on static, publicly available data, lack comprehensive task coverage, or do not provide dedicated platforms with blind test sets. This makes it challenging to measure actual progress and to mitigate data contamination. Here, we aim to bridge these gaps. In particular, we introduce BALSAM, a comprehensive, community-driven benchmark aimed at advancing Arabic LLM development and evaluation. It includes 78 NLP tasks from 14 broad categories, with 52K examples divided into 37K test and 15K development, and a centralized, transparent platform for blind evaluation. We envision BALSAM as a unifying platform that sets standards and promotes collaborative research to advance Arabic LLM capabilities.
ARWI: Arabic Write and Improve
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Although Arabic is spoken by over 400 million people, advanced Arabic writing assistance tools remain limited. To address this gap, we present ARWI, a new writing assistant that helps learners improve essay writing in Modern Standard Arabic. ARWI is the first publicly available Arabic writing assistant to include a prompt database for different proficiency levels, an Arabic text editor, state-of-the-art grammatical error detection and correction, and automated essay scoring aligned with the Common European Framework of Reference standards for language attainment. Moreover, ARWI can be used to gather a growing auto-annotated corpus, facilitating further research on Arabic grammar correction and essay scoring, as well as profiling patterns of errors made by native speakers and non-native learners. A preliminary user study shows that ARWI provides actionable feedback, helping learners identify grammatical gaps, assess language proficiency, and guide improvement.
Enhancing Text Editing for Grammatical Error Correction: Arabic as a Case Study
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:Text editing frames grammatical error correction (GEC) as a sequence tagging problem, where edit tags are assigned to input tokens, and applying these edits results in the corrected text. This approach has gained attention for its efficiency and interpretability. However, while extensively explored for English, text editing remains largely underexplored for morphologically rich languages like Arabic. In this paper, we introduce a text editing approach that derives edit tags directly from data, eliminating the need for language-specific edits. We demonstrate its effectiveness on Arabic, a diglossic and morphologically rich language, and investigate the impact of different edit representations on model performance. Our approach achieves SOTA results on two Arabic GEC benchmarks and performs on par with SOTA on two others. Additionally, our models are over six times faster than existing Arabic GEC systems, making our approach more practical for real-world applications. Finally, we explore ensemble models, demonstrating how combining different models leads to further performance improvements. We make our code, data, and pretrained models publicly available.
LLMs in Education: Novel Perspectives, Challenges, and Opportunities
Sep 18, 2024Abstract:The role of large language models (LLMs) in education is an increasing area of interest today, considering the new opportunities they offer for teaching, learning, and assessment. This cutting-edge tutorial provides an overview of the educational applications of NLP and the impact that the recent advances in LLMs have had on this field. We will discuss the key challenges and opportunities presented by LLMs, grounding them in the context of four major educational applications: reading, writing, and speaking skills, and intelligent tutoring systems (ITS). This COLING 2025 tutorial is designed for researchers and practitioners interested in the educational applications of NLP and the role LLMs have to play in this area. It is the first of its kind to address this timely topic.
Exploiting Dialect Identification in Automatic Dialectal Text Normalization
Jul 03, 2024



Abstract:Dialectal Arabic is the primary spoken language used by native Arabic speakers in daily communication. The rise of social media platforms has notably expanded its use as a written language. However, Arabic dialects do not have standard orthographies. This, combined with the inherent noise in user-generated content on social media, presents a major challenge to NLP applications dealing with Dialectal Arabic. In this paper, we explore and report on the task of CODAfication, which aims to normalize Dialectal Arabic into the Conventional Orthography for Dialectal Arabic (CODA). We work with a unique parallel corpus of multiple Arabic dialects focusing on five major city dialects. We benchmark newly developed pretrained sequence-to-sequence models on the task of CODAfication. We further show that using dialect identification information improves the performance across all dialects. We make our code, data, and pretrained models publicly available.
Strategies for Arabic Readability Modeling
Jul 03, 2024
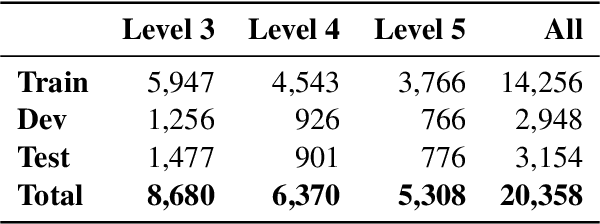


Abstract:Automatic readability assessment is relevant to building NLP applications for education, content analysis, and accessibility. However, Arabic readability assessment is a challenging task due to Arabic's morphological richness and limited readability resources. In this paper, we present a set of experimental results on Arabic readability assessment using a diverse range of approaches, from rule-based methods to Arabic pretrained language models. We report our results on a newly created corpus at different textual granularity levels (words and sentence fragments). Our results show that combining different techniques yields the best results, achieving an overall macro F1 score of 86.7 at the word level and 87.9 at the fragment level on a blind test set. We make our code, data, and pretrained models publicly available.
The SAMER Arabic Text Simplification Corpus
Apr 29, 2024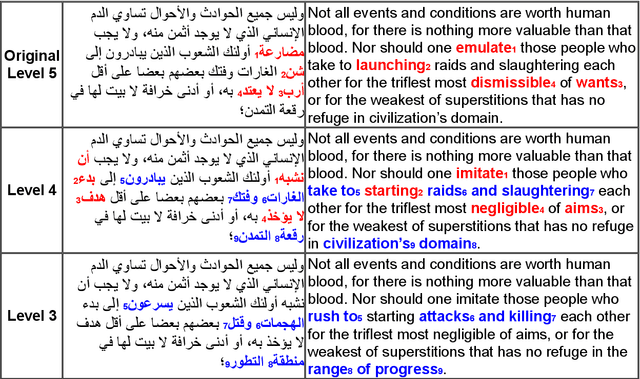
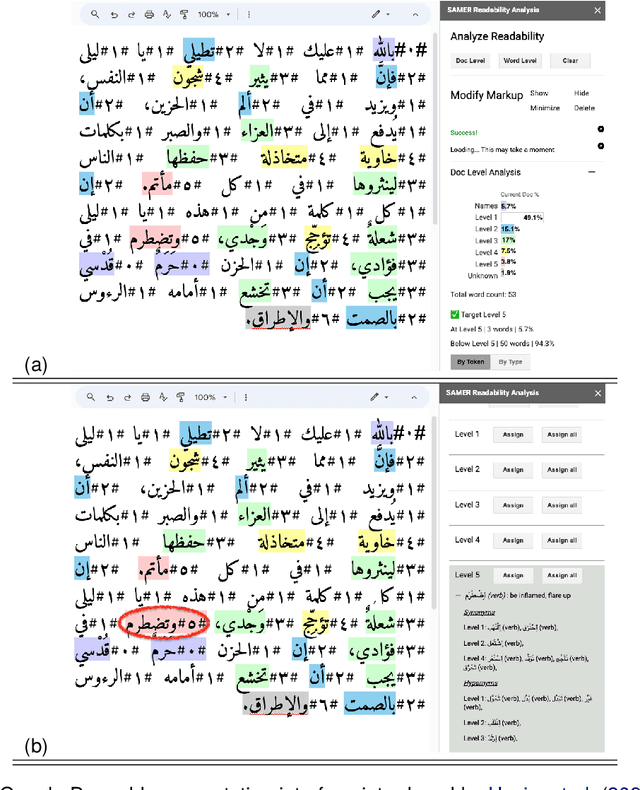
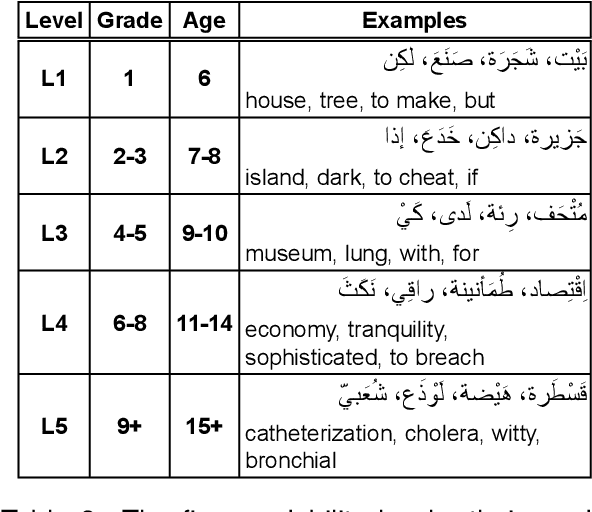
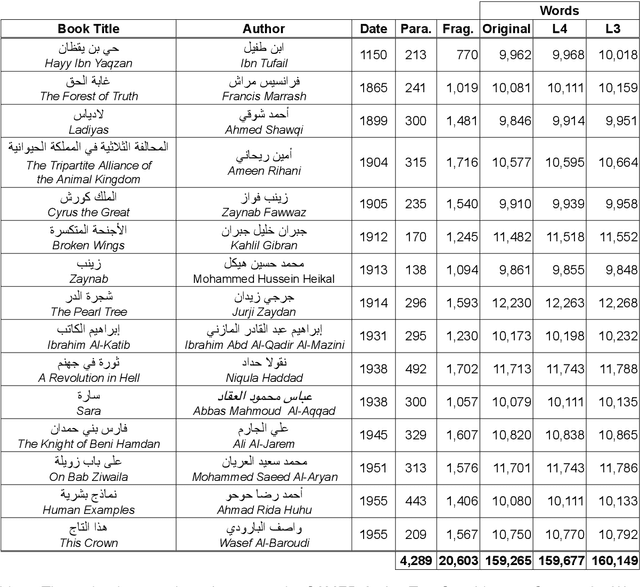
Abstract:We present the SAMER Corpus, the first manually annotated Arabic parallel corpus for text simplification targeting school-aged learners. Our corpus comprises texts of 159K words selected from 15 publicly available Arabic fiction novels most of which were published between 1865 and 1955. Our corpus includes readability level annotations at both the document and word levels, as well as two simplified parallel versions for each text targeting learners at two different readability levels. We describe the corpus selection process, and outline the guidelines we followed to create the annotations and ensure their quality. Our corpus is publicly available to support and encourage research on Arabic text simplification, Arabic automatic readability assessment, and the development of Arabic pedagogical language technologies.
mEdIT: Multilingual Text Editing via Instruction Tuning
Feb 26, 2024Abstract:We introduce mEdIT, a multi-lingual extension to CoEdIT -- the recent state-of-the-art text editing models for writing assistance. mEdIT models are trained by fine-tuning multi-lingual large, pre-trained language models (LLMs) via instruction tuning. They are designed to take instructions from the user specifying the attributes of the desired text in the form of natural language instructions, such as Grammatik korrigieren (German) or Parafrasee la oraci\'on (Spanish). We build mEdIT by curating data from multiple publicly available human-annotated text editing datasets for three text editing tasks (Grammatical Error Correction (GEC), Text Simplification, and Paraphrasing) across diverse languages belonging to six different language families. We detail the design and training of mEdIT models and demonstrate their strong performance on many multi-lingual text editing benchmarks against other multilingual LLMs. We also find that mEdIT generalizes effectively to new languages over multilingual baselines. We publicly release our data, code, and trained models at https://github.com/vipulraheja/medit.
Personalized Text Generation with Fine-Grained Linguistic Control
Feb 07, 2024



Abstract:As the text generation capabilities of large language models become increasingly prominent, recent studies have focused on controlling particular aspects of the generated text to make it more personalized. However, most research on controllable text generation focuses on controlling the content or modeling specific high-level/coarse-grained attributes that reflect authors' writing styles, such as formality, domain, or sentiment. In this paper, we focus on controlling fine-grained attributes spanning multiple linguistic dimensions, such as lexical and syntactic attributes. We introduce a novel benchmark to train generative models and evaluate their ability to generate personalized text based on multiple fine-grained linguistic attributes. We systematically investigate the performance of various large language models on our benchmark and draw insights from the factors that impact their performance. We make our code, data, and pretrained models publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge