Ekaterina Kochmar
Pedagogy-driven Evaluation of Generative AI-powered Intelligent Tutoring Systems
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:The interdisciplinary research domain of Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) has a long history of developing Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITSs) by integrating insights from technological advancements, educational theories, and cognitive psychology. The remarkable success of generative AI (GenAI) models has accelerated the development of large language model (LLM)-powered ITSs, which have potential to imitate human-like, pedagogically rich, and cognitively demanding tutoring. However, the progress and impact of these systems remain largely untraceable due to the absence of reliable, universally accepted, and pedagogy-driven evaluation frameworks and benchmarks. Most existing educational dialogue-based ITS evaluations rely on subjective protocols and non-standardized benchmarks, leading to inconsistencies and limited generalizability. In this work, we take a step back from mainstream ITS development and provide comprehensive state-of-the-art evaluation practices, highlighting associated challenges through real-world case studies from careful and caring AIED research. Finally, building on insights from previous interdisciplinary AIED research, we propose three practical, feasible, and theoretically grounded research directions, rooted in learning science principles and aimed at establishing fair, unified, and scalable evaluation methodologies for ITSs.
* AIED 2025 (BlueSky)
Opportunities and Challenges of LLMs in Education: An NLP Perspective
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Interest in the role of large language models (LLMs) in education is increasing, considering the new opportunities they offer for teaching, learning, and assessment. In this paper, we examine the impact of LLMs on educational NLP in the context of two main application scenarios: {\em assistance} and {\em assessment}, grounding them along the four dimensions -- reading, writing, speaking, and tutoring. We then present the new directions enabled by LLMs, and the key challenges to address. We envision that this holistic overview would be useful for NLP researchers and practitioners interested in exploring the role of LLMs in developing language-focused and NLP-enabled educational applications of the future.
Intent Matters: Enhancing AI Tutoring with Fine-Grained Pedagogical Intent Annotation
Jun 09, 2025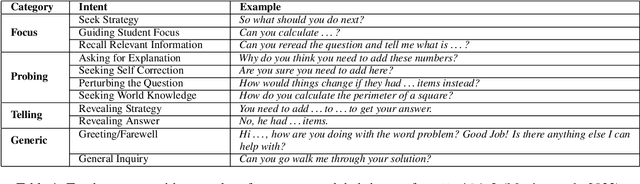

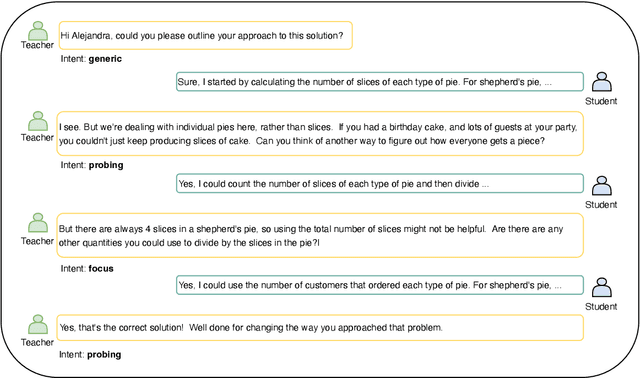
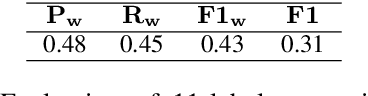
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) hold great promise for educational applications, particularly in intelligent tutoring systems. However, effective tutoring requires alignment with pedagogical strategies - something current LLMs lack without task-specific adaptation. In this work, we explore whether fine-grained annotation of teacher intents can improve the quality of LLM-generated tutoring responses. We focus on MathDial, a dialog dataset for math instruction, and apply an automated annotation framework to re-annotate a portion of the dataset using a detailed taxonomy of eleven pedagogical intents. We then fine-tune an LLM using these new annotations and compare its performance to models trained on the original four-category taxonomy. Both automatic and qualitative evaluations show that the fine-grained model produces more pedagogically aligned and effective responses. Our findings highlight the value of intent specificity for controlled text generation in educational settings, and we release our annotated data and code to facilitate further research.
Simulating LLM-to-LLM Tutoring for Multilingual Math Feedback
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated the ability to generate formative feedback and instructional hints in English, making them increasingly relevant for AI-assisted education. However, their ability to provide effective instructional support across different languages, especially for mathematically grounded reasoning tasks, remains largely unexamined. In this work, we present the first large-scale simulation of multilingual tutor-student interactions using LLMs. A stronger model plays the role of the tutor, generating feedback in the form of hints, while a weaker model simulates the student. We explore 352 experimental settings across 11 typologically diverse languages, four state-of-the-art LLMs, and multiple prompting strategies to assess whether language-specific feedback leads to measurable learning gains. Our study examines how student input language, teacher feedback language, model choice, and language resource level jointly influence performance. Results show that multilingual hints can significantly improve learning outcomes, particularly in low-resource languages when feedback is aligned with the student's native language. These findings offer practical insights for developing multilingual, LLM-based educational tools that are both effective and inclusive.
A Fully Automated Pipeline for Conversational Discourse Annotation: Tree Scheme Generation and Labeling with Large Language Models
Apr 11, 2025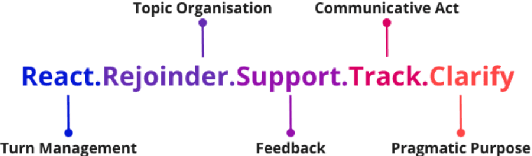
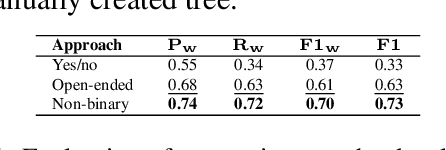
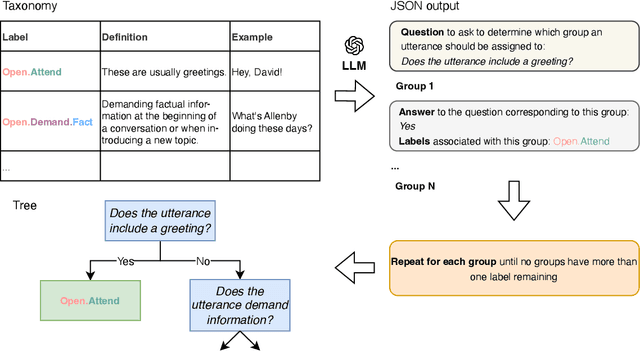
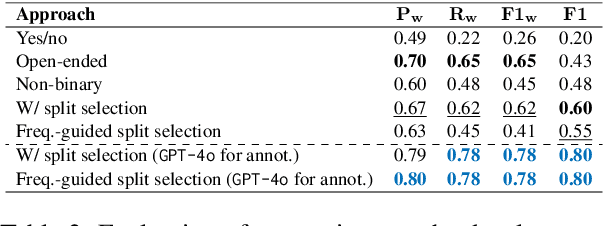
Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in automating discourse annotation for conversations. While manually designing tree annotation schemes significantly improves annotation quality for humans and models, their creation remains time-consuming and requires expert knowledge. We propose a fully automated pipeline that uses LLMs to construct such schemes and perform annotation. We evaluate our approach on speech functions (SFs) and the Switchboard-DAMSL (SWBD-DAMSL) taxonomies. Our experiments compare various design choices, and we show that frequency-guided decision trees, paired with an advanced LLM for annotation, can outperform previously manually designed trees and even match or surpass human annotators while significantly reducing the time required for annotation. We release all code and resultant schemes and annotations to facilitate future research on discourse annotation.
Llama-3.1-Sherkala-8B-Chat: An Open Large Language Model for Kazakh
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Llama-3.1-Sherkala-8B-Chat, or Sherkala-Chat (8B) for short, is a state-of-the-art instruction-tuned open generative large language model (LLM) designed for Kazakh. Sherkala-Chat (8B) aims to enhance the inclusivity of LLM advancements for Kazakh speakers. Adapted from the LLaMA-3.1-8B model, Sherkala-Chat (8B) is trained on 45.3B tokens across Kazakh, English, Russian, and Turkish. With 8 billion parameters, it demonstrates strong knowledge and reasoning abilities in Kazakh, significantly outperforming existing open Kazakh and multilingual models of similar scale while achieving competitive performance in English. We release Sherkala-Chat (8B) as an open-weight instruction-tuned model and provide a detailed overview of its training, fine-tuning, safety alignment, and evaluation, aiming to advance research and support diverse real-world applications.
KazMMLU: Evaluating Language Models on Kazakh, Russian, and Regional Knowledge of Kazakhstan
Feb 18, 2025



Abstract:Despite having a population of twenty million, Kazakhstan's culture and language remain underrepresented in the field of natural language processing. Although large language models (LLMs) continue to advance worldwide, progress in Kazakh language has been limited, as seen in the scarcity of dedicated models and benchmark evaluations. To address this gap, we introduce KazMMLU, the first MMLU-style dataset specifically designed for Kazakh language. KazMMLU comprises 23,000 questions that cover various educational levels, including STEM, humanities, and social sciences, sourced from authentic educational materials and manually validated by native speakers and educators. The dataset includes 10,969 Kazakh questions and 12,031 Russian questions, reflecting Kazakhstan's bilingual education system and rich local context. Our evaluation of several state-of-the-art multilingual models (Llama-3.1, Qwen-2.5, GPT-4, and DeepSeek V3) demonstrates substantial room for improvement, as even the best-performing models struggle to achieve competitive performance in Kazakh and Russian. These findings underscore significant performance gaps compared to high-resource languages. We hope that our dataset will enable further research and development of Kazakh-centric LLMs. Data and code will be made available upon acceptance.
What Makes Cryptic Crosswords Challenging for LLMs?
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Cryptic crosswords are puzzles that rely on general knowledge and the solver's ability to manipulate language on different levels, dealing with various types of wordplay. Previous research suggests that solving such puzzles is challenging even for modern NLP models, including Large Language Models (LLMs). However, there is little to no research on the reasons for their poor performance on this task. In this paper, we establish the benchmark results for three popular LLMs: Gemma2, LLaMA3 and ChatGPT, showing that their performance on this task is still significantly below that of humans. We also investigate why these models struggle to achieve superior performance. We release our code and introduced datasets at https://github.com/bodasadallah/decrypting-crosswords.
* COLING 2025
Unifying AI Tutor Evaluation: An Evaluation Taxonomy for Pedagogical Ability Assessment of LLM-Powered AI Tutors
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we investigate whether current state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) are effective as AI tutors and whether they demonstrate pedagogical abilities necessary for good AI tutoring in educational dialogues. Previous efforts towards evaluation have been limited to subjective protocols and benchmarks. To bridge this gap, we propose a unified evaluation taxonomy with eight pedagogical dimensions based on key learning sciences principles, which is designed to assess the pedagogical value of LLM-powered AI tutor responses grounded in student mistakes or confusion in the mathematical domain. We release MRBench -- a new evaluation benchmark containing 192 conversations and 1,596 responses from seven state-of-the-art LLM-based and human tutors, providing gold annotations for eight pedagogical dimensions. We assess reliability of the popular Prometheus2 LLM as an evaluator and analyze each tutor's pedagogical abilities, highlighting which LLMs are good tutors and which ones are more suitable as question-answering systems. We believe that the presented taxonomy, benchmark, and human-annotated labels will streamline the evaluation process and help track the progress in AI tutors' development.
LLMs in Education: Novel Perspectives, Challenges, and Opportunities
Sep 18, 2024Abstract:The role of large language models (LLMs) in education is an increasing area of interest today, considering the new opportunities they offer for teaching, learning, and assessment. This cutting-edge tutorial provides an overview of the educational applications of NLP and the impact that the recent advances in LLMs have had on this field. We will discuss the key challenges and opportunities presented by LLMs, grounding them in the context of four major educational applications: reading, writing, and speaking skills, and intelligent tutoring systems (ITS). This COLING 2025 tutorial is designed for researchers and practitioners interested in the educational applications of NLP and the role LLMs have to play in this area. It is the first of its kind to address this timely topic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge