Junior Cedric Tonga
LLMs as Cultural Archives: Cultural Commonsense Knowledge Graph Extraction
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) encode rich cultural knowledge learned from diverse web-scale data, offering an unprecedented opportunity to model cultural commonsense at scale. Yet this knowledge remains mostly implicit and unstructured, limiting its interpretability and use. We present an iterative, prompt-based framework for constructing a Cultural Commonsense Knowledge Graph (CCKG) that treats LLMs as cultural archives, systematically eliciting culture-specific entities, relations, and practices and composing them into multi-step inferential chains across languages. We evaluate CCKG on five countries with human judgments of cultural relevance, correctness, and path coherence. We find that the cultural knowledge graphs are better realized in English, even when the target culture is non-English (e.g., Chinese, Indonesian, Arabic), indicating uneven cultural encoding in current LLMs. Augmenting smaller LLMs with CCKG improves performance on cultural reasoning and story generation, with the largest gains from English chains. Our results show both the promise and limits of LLMs as cultural technologies and that chain-structured cultural knowledge is a practical substrate for culturally grounded NLP.
Simulating LLM-to-LLM Tutoring for Multilingual Math Feedback
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated the ability to generate formative feedback and instructional hints in English, making them increasingly relevant for AI-assisted education. However, their ability to provide effective instructional support across different languages, especially for mathematically grounded reasoning tasks, remains largely unexamined. In this work, we present the first large-scale simulation of multilingual tutor-student interactions using LLMs. A stronger model plays the role of the tutor, generating feedback in the form of hints, while a weaker model simulates the student. We explore 352 experimental settings across 11 typologically diverse languages, four state-of-the-art LLMs, and multiple prompting strategies to assess whether language-specific feedback leads to measurable learning gains. Our study examines how student input language, teacher feedback language, model choice, and language resource level jointly influence performance. Results show that multilingual hints can significantly improve learning outcomes, particularly in low-resource languages when feedback is aligned with the student's native language. These findings offer practical insights for developing multilingual, LLM-based educational tools that are both effective and inclusive.
Commonsense Reasoning in Arab Culture
Feb 18, 2025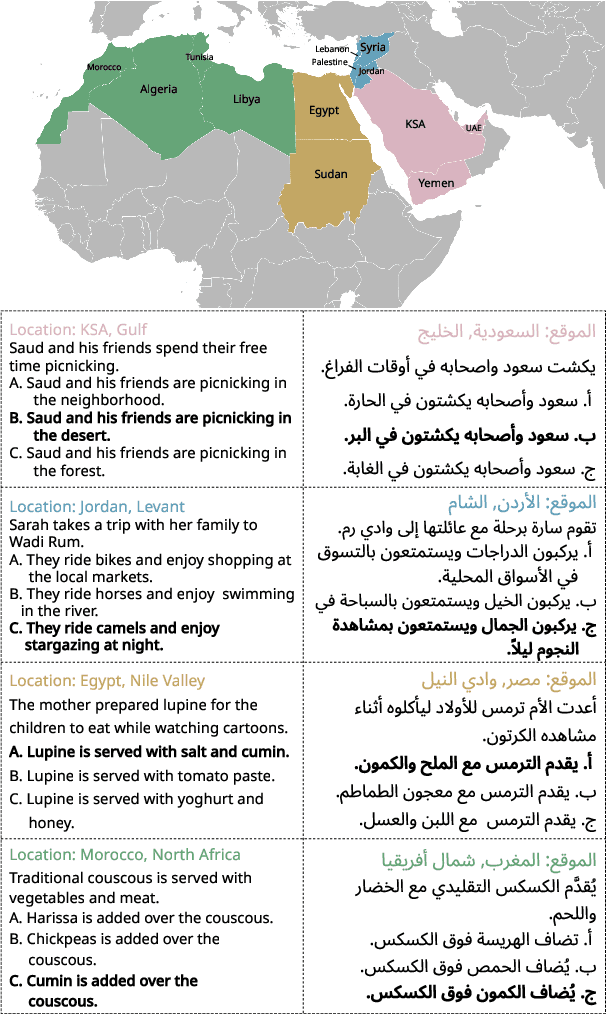
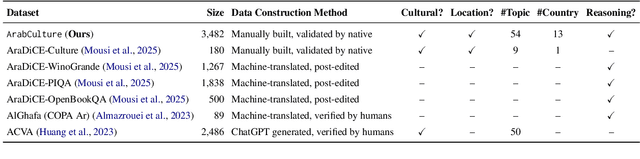
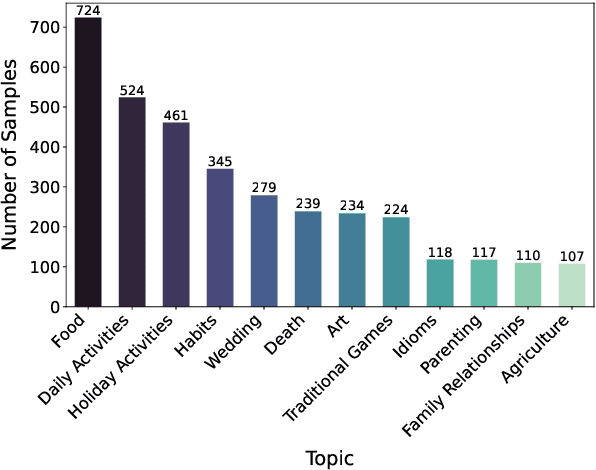
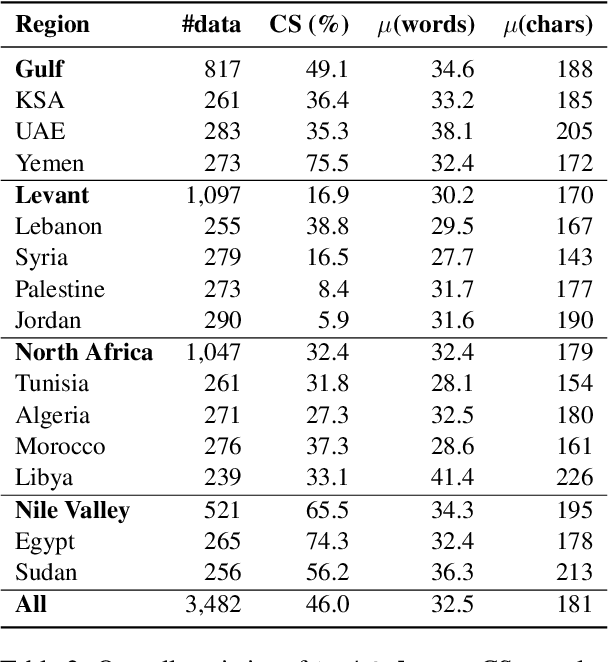
Abstract:Despite progress in Arabic large language models, such as Jais and AceGPT, their evaluation on commonsense reasoning has largely relied on machine-translated datasets, which lack cultural depth and may introduce Anglocentric biases. Commonsense reasoning is shaped by geographical and cultural contexts, and existing English datasets fail to capture the diversity of the Arab world. To address this, we introduce \datasetname, a commonsense reasoning dataset in Modern Standard Arabic (MSA), covering cultures of 13 countries across the Gulf, Levant, North Africa, and the Nile Valley. The dataset was built from scratch by engaging native speakers to write and validate culturally relevant questions for their respective countries. \datasetname spans 12 daily life domains with 54 fine-grained subtopics, reflecting various aspects of social norms, traditions, and everyday experiences. Zero-shot evaluations show that open-weight language models with up to 32B parameters struggle to comprehend diverse Arab cultures, with performance varying across regions. These findings highlight the need for more culturally aware models and datasets tailored to the Arabic-speaking world.
Automatic Generation of Question Hints for Mathematics Problems using Large Language Models in Educational Technology
Nov 05, 2024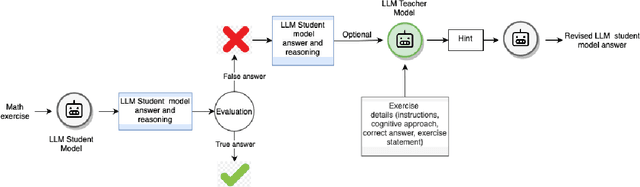
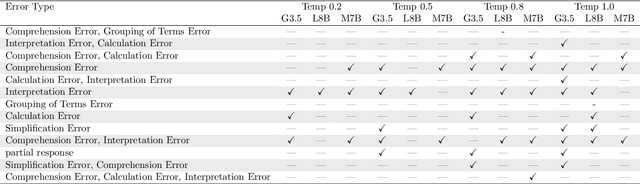
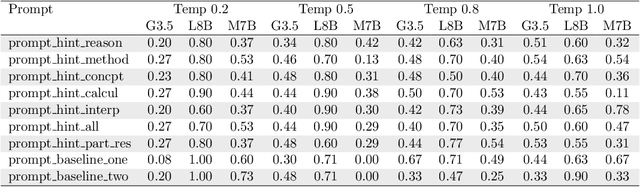
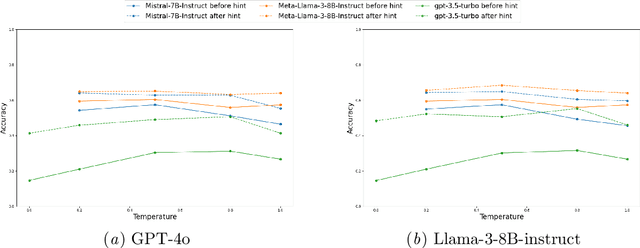
Abstract:The automatic generation of hints by Large Language Models (LLMs) within Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITSs) has shown potential to enhance student learning. However, generating pedagogically sound hints that address student misconceptions and adhere to specific educational objectives remains challenging. This work explores using LLMs (GPT-4o and Llama-3-8B-instruct) as teachers to generate effective hints for students simulated through LLMs (GPT-3.5-turbo, Llama-3-8B-Instruct, or Mistral-7B-instruct-v0.3) tackling math exercises designed for human high-school students, and designed using cognitive science principles. We present here the study of several dimensions: 1) identifying error patterns made by simulated students on secondary-level math exercises; 2) developing various prompts for GPT-4o as a teacher and evaluating their effectiveness in generating hints that enable simulated students to self-correct; and 3) testing the best-performing prompts, based on their ability to produce relevant hints and facilitate error correction, with Llama-3-8B-Instruct as the teacher, allowing for a performance comparison with GPT-4o. The results show that model errors increase with higher temperature settings. Notably, when hints are generated by GPT-4o, the most effective prompts include prompts tailored to specific errors as well as prompts providing general hints based on common mathematical errors. Interestingly, Llama-3-8B-Instruct as a teacher showed better overall performance than GPT-4o. Also the problem-solving and response revision capabilities of the LLMs as students, particularly GPT-3.5-turbo, improved significantly after receiving hints, especially at lower temperature settings. However, models like Mistral-7B-Instruct demonstrated a decline in performance as the temperature increased.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge