Pouya Pezeshkpour
Shammie
From Task Solving to Robust Real-World Adaptation in LLM Agents
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language models are increasingly deployed as specialized agents that plan, call tools, and take actions over extended horizons. Yet many existing evaluations assume a "clean interface" where dynamics are specified and stable, tools and sensors are reliable, and success is captured by a single explicit objective-often overestimating real-world readiness. In practice, agents face underspecified rules, unreliable signals, shifting environments, and implicit, multi-stakeholder goals. The challenge is therefore not just solving tasks, but adapting while solving: deciding what to trust, what is wanted, when to verify, and when to fall back or escalate. We stress-test deployment-relevant robustness under four operational circumstances: partial observability, dynamic environments, noisy signals, and dynamic agent state. We benchmark agentic LLMs in a grid-based game with a simple goal but long-horizon execution. Episodes violate clean-interface assumptions yet remain solvable, forcing agents to infer rules, pay for information, adapt to environmental and internal shifts, and act cautiously under noise. Across five state-of-the-art LLM agents, we find large gaps between nominal task-solving and deployment-like robustness. Performance generally degrades as grid size and horizon increase, but rankings are unstable: weaker models can beat stronger ones when strategy matches the uncertainty regime. Despite no explicit instruction, agents trade off completion, efficiency, and penalty avoidance, suggesting partial objective inference. Ablations and feature analyses reveal model-specific sensitivities and failure drivers, motivating work on verification, safe action selection, and objective inference under partial observability, noise, and non-stationarity.
From Proof to Program: Characterizing Tool-Induced Reasoning Hallucinations in Large Language Models
Nov 14, 2025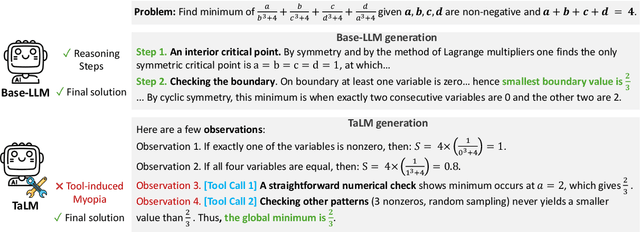
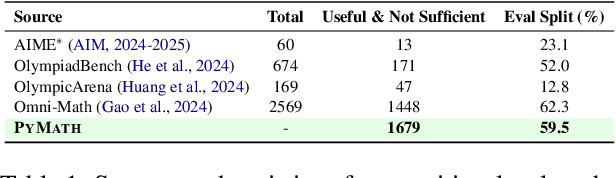
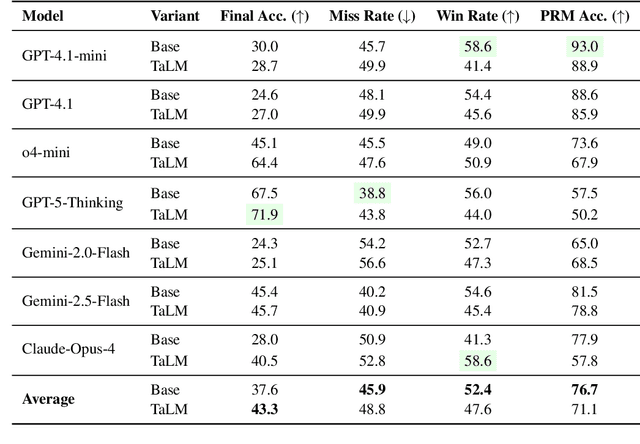
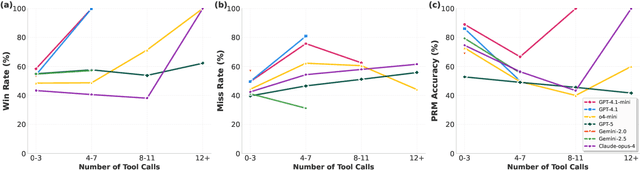
Abstract:Tool-augmented Language Models (TaLMs) can invoke external tools to solve problems beyond their parametric capacity. However, it remains unclear whether these tool-enabled gains reflect trustworthy reasoning. Focusing on the Code Interpreter tool, we show that even when tools are selected and executed correctly, TaLMs treat tool outputs as substitutes for reasoning, producing solutions that appear correct but lack coherent justification. We term this failure mode Tool-Induced Myopia (TIM), and study it using PYMATH, a benchmark of 1,679 competition-level mathematical problems for which Python code is helpful but not sufficient. We further develop a multi-dimensional evaluation suite to quantify reasoning degradation in TaLMs relative to their non-tool counterparts. Our findings reveal that while TaLMs achieve up to a 19.3 percentage point gain in final-answer accuracy, their reasoning behavior consistently deteriorates (e.g., non-tool LLMs win up to 41.5% more often in pairwise comparisons of the reasoning process). This degradation intensifies with tool use; the more frequently a model invokes tools, the less coherent its reasoning becomes. Moreover, tool use shifts errors from arithmetic mistakes toward global reasoning failures (logic, assumption, creativity); with TIM present in ~55% of high-risk cases. Finally, we propose a preference-optimization-based framework that realigns TaLMs to use tools as assistive evidence, improving both final-answer accuracy and reasoning depth under tool use. Codes and data are available at: https://github.com/megagonlabs/TIM.
Towards Reliable Benchmarking: A Contamination Free, Controllable Evaluation Framework for Multi-step LLM Function Calling
Sep 30, 2025
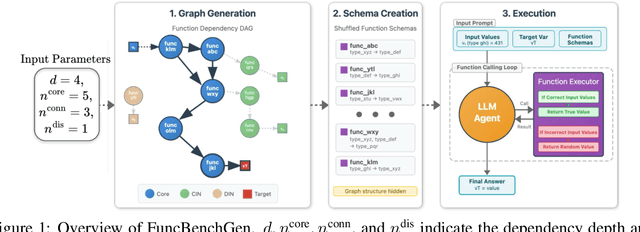
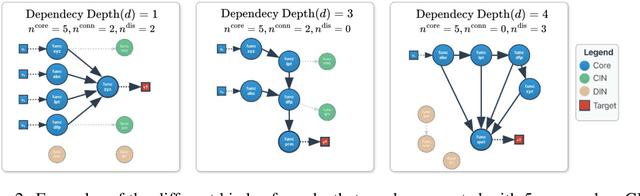

Abstract:As language models gain access to external tools via structured function calls, they become increasingly more capable of solving complex, multi-step tasks. However, existing benchmarks for tool-augmented language models (TaLMs) provide insufficient control over factors such as the number of functions accessible, task complexity, and input size, and remain vulnerable to data contamination. We present FuncBenchGen, a unified, contamination-free framework that evaluates TaLMs by generating synthetic multi-step tool-use tasks. The key idea is to cast tool use as traversal over a hidden function-dependency DAG where nodes are function calls and an edge between nodes represents one function consuming the output of another. Given a set of external function schemas, initial variable values, and a target variable, models must compose the correct call sequence to compute the target variable. FuncBenchGen allows users to precisely control task difficulty (e.g., graph size, dependency depth, and distractor functions) while avoiding data leakage. We apply our FuncBenchGen framework to evaluate seven LLMs on tool use tasks of varying difficulty. Reasoning-optimized models consistently outperform general-purpose models with GPT-5 significantly outperforming other models. Performance declines sharply as dependency depth increases. Furthermore, connected irrelevant functions prove especially difficult to handle. We find that strong models often make syntactically valid function calls but propagate incorrect or stale argument values across steps, revealing brittle state tracking by LLMs in multi-turn tool use. Motivated by this observation, we introduce a simple mitigation strategy that explicitly restates prior variable values to the agent at each step. Surprisingly, this lightweight change yields substantial gains across models. e.g., yielding a success rate improvement from 62.5% to 81.3% for GPT-5.
Mixed Signals: Decoding VLMs' Reasoning and Underlying Bias in Vision-Language Conflict
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance by effectively integrating visual and textual information to solve complex tasks. However, it is not clear how these models reason over the visual and textual data together, nor how the flow of information between modalities is structured. In this paper, we examine how VLMs reason by analyzing their biases when confronted with scenarios that present conflicting image and text cues, a common occurrence in real-world applications. To uncover the extent and nature of these biases, we build upon existing benchmarks to create five datasets containing mismatched image-text pairs, covering topics in mathematics, science, and visual descriptions. Our analysis shows that VLMs favor text in simpler queries but shift toward images as query complexity increases. This bias correlates with model scale, with the difference between the percentage of image- and text-preferred responses ranging from +56.8% (image favored) to -74.4% (text favored), depending on the task and model. In addition, we explore three mitigation strategies: simple prompt modifications, modifications that explicitly instruct models on how to handle conflicting information (akin to chain-of-thought prompting), and a task decomposition strategy that analyzes each modality separately before combining their results. Our findings indicate that the effectiveness of these strategies in identifying and mitigating bias varies significantly and is closely linked to the model's overall performance on the task and the specific modality in question.
Insight-RAG: Enhancing LLMs with Insight-Driven Augmentation
Mar 31, 2025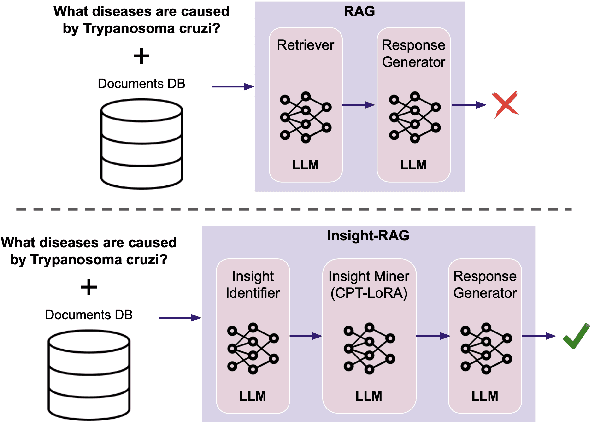


Abstract:Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) frameworks have shown significant promise in leveraging external knowledge to enhance the performance of large language models (LLMs). However, conventional RAG methods often retrieve documents based solely on surface-level relevance, leading to many issues: they may overlook deeply buried information within individual documents, miss relevant insights spanning multiple sources, and are not well-suited for tasks beyond traditional question answering. In this paper, we propose Insight-RAG, a novel framework designed to address these issues. In the initial stage of Insight-RAG, instead of using traditional retrieval methods, we employ an LLM to analyze the input query and task, extracting the underlying informational requirements. In the subsequent stage, a specialized LLM -- trained on the document database -- is queried to mine content that directly addresses these identified insights. Finally, by integrating the original query with the retrieved insights, similar to conventional RAG approaches, we employ a final LLM to generate a contextually enriched and accurate response. Using two scientific paper datasets, we created evaluation benchmarks targeting each of the mentioned issues and assessed Insight-RAG against traditional RAG pipeline. Our results demonstrate that the Insight-RAG pipeline successfully addresses these challenges, outperforming existing methods by a significant margin in most cases. These findings suggest that integrating insight-driven retrieval within the RAG framework not only enhances performance but also broadens the applicability of RAG to tasks beyond conventional question answering.
Evaluating Bias in LLMs for Job-Resume Matching: Gender, Race, and Education
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) offer the potential to automate hiring by matching job descriptions with candidate resumes, streamlining recruitment processes, and reducing operational costs. However, biases inherent in these models may lead to unfair hiring practices, reinforcing societal prejudices and undermining workplace diversity. This study examines the performance and fairness of LLMs in job-resume matching tasks within the English language and U.S. context. It evaluates how factors such as gender, race, and educational background influence model decisions, providing critical insights into the fairness and reliability of LLMs in HR applications. Our findings indicate that while recent models have reduced biases related to explicit attributes like gender and race, implicit biases concerning educational background remain significant. These results highlight the need for ongoing evaluation and the development of advanced bias mitigation strategies to ensure equitable hiring practices when using LLMs in industry settings.
Learning Beyond the Surface: How Far Can Continual Pre-Training with LoRA Enhance LLMs' Domain-Specific Insight Learning?
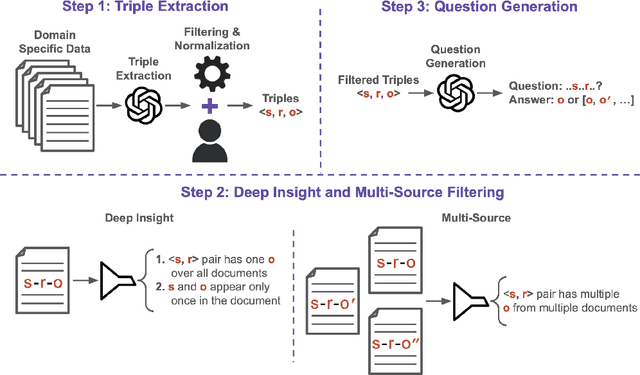
Jan 29, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on various tasks, yet their ability to extract and internalize deeper insights from domain-specific datasets remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate how continual pre-training can enhance LLMs' capacity for insight learning across three distinct forms: declarative, statistical, and probabilistic insights. Focusing on two critical domains: medicine and finance, we employ LoRA to train LLMs on two existing datasets. To evaluate each insight type, we create benchmarks to measure how well continual pre-training helps models go beyond surface-level knowledge. We also assess the impact of document modification on capturing insights. The results show that, while continual pre-training on original documents has a marginal effect, modifying documents to retain only essential information significantly enhances the insight-learning capabilities of LLMs.
LLMs Are Not Intelligent Thinkers: Introducing Mathematical Topic Tree Benchmark for Comprehensive Evaluation of LLMs
Jun 07, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive capabilities in mathematical reasoning. However, despite these achievements, current evaluations are mostly limited to specific mathematical topics, and it remains unclear whether LLMs are genuinely engaging in reasoning. To address these gaps, we present the Mathematical Topics Tree (MaTT) benchmark, a challenging and structured benchmark that offers 1,958 questions across a wide array of mathematical subjects, each paired with a detailed hierarchical chain of topics. Upon assessing different LLMs using the MaTT benchmark, we find that the most advanced model, GPT-4, achieved a mere 54\% accuracy in a multiple-choice scenario. Interestingly, even when employing Chain-of-Thought prompting, we observe mostly no notable improvement. Moreover, LLMs accuracy dramatically reduced by up to 24.2 percentage point when the questions were presented without providing choices. Further detailed analysis of the LLMs' performance across a range of topics showed significant discrepancy even for closely related subtopics within the same general mathematical area. In an effort to pinpoint the reasons behind LLMs performances, we conducted a manual evaluation of the completeness and correctness of the explanations generated by GPT-4 when choices were available. Surprisingly, we find that in only 53.3\% of the instances where the model provided a correct answer, the accompanying explanations were deemed complete and accurate, i.e., the model engaged in genuine reasoning.
A Blueprint Architecture of Compound AI Systems for Enterprise
Jun 02, 2024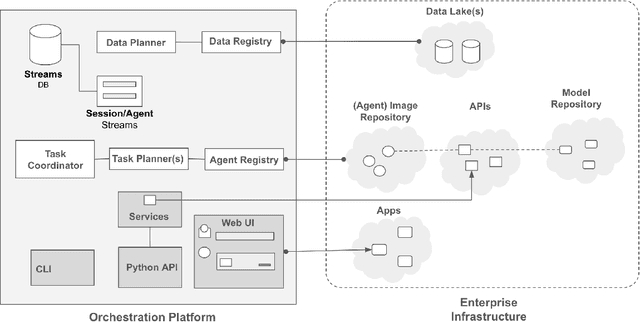
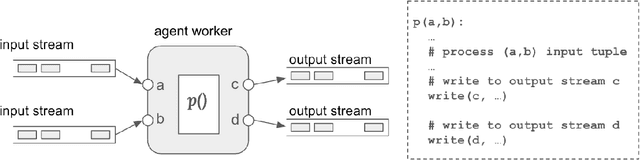
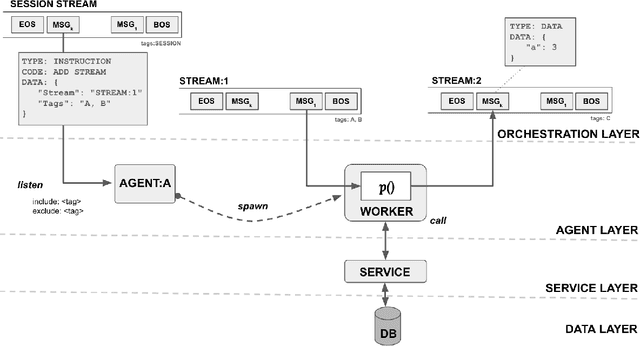
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have showcased remarkable capabilities surpassing conventional NLP challenges, creating opportunities for use in production use cases. Towards this goal, there is a notable shift to building compound AI systems, wherein LLMs are integrated into an expansive software infrastructure with many components like models, retrievers, databases and tools. In this paper, we introduce a blueprint architecture for compound AI systems to operate in enterprise settings cost-effectively and feasibly. Our proposed architecture aims for seamless integration with existing compute and data infrastructure, with ``stream'' serving as the key orchestration concept to coordinate data and instructions among agents and other components. Task and data planners, respectively, break down, map, and optimize tasks and data to available agents and data sources defined in respective registries, given production constraints such as accuracy and latency.
Multi-Conditional Ranking with Large Language Models
Mar 30, 2024



Abstract:Utilizing large language models (LLMs) to rank a set of items has become a common approach in recommendation and retrieval systems. Typically, these systems focus on ordering a substantial number of documents in a monotonic order based on a given query. However, real-world scenarios often present a different challenge: ranking a comparatively smaller set of items, but according to a variety of diverse and occasionally conflicting conditions. In this paper, we define and explore the task of multi-conditional ranking by introducing MCRank, a benchmark tailored for assessing multi-conditional ranking across various item types and conditions. Our analysis of LLMs using MCRank indicates a significant decrease in performance as the number and complexity of items and conditions grow. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel decomposed reasoning method, consisting of EXtracting and Sorting the conditions, and then Iterativly Ranking the items (EXSIR). Our extensive experiments show that this decomposed reasoning method enhances LLMs' performance significantly, achieving up to a 12% improvement over existing LLMs. We also provide a detailed analysis of LLMs performance across various condition categories, and examine the effectiveness of decomposition step. Furthermore, we compare our method with existing approaches such as Chain-of-Thought and an encoder-type ranking model, demonstrating the superiority of our approach and complexity of MCR task. We released our dataset and code.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge