Nikita Bhutani
Efficient Context Selection for Long-Context QA: No Tuning, No Iteration, Just Adaptive-$k$
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and long-context language models (LCLMs) both address context limitations of LLMs in open-domain question answering (QA). However, optimal external context to retrieve remains an open problem: fixing the retrieval size risks either wasting tokens or omitting key evidence. Existing adaptive methods like Self-RAG and Self-Route rely on iterative LLM prompting and perform well on factoid QA, but struggle with aggregation QA, where the optimal context size is both unknown and variable. We present Adaptive-$k$ retrieval, a simple and effective single-pass method that adaptively selects the number of passages based on the distribution of the similarity scores between the query and the candidate passages. It does not require model fine-tuning, extra LLM inferences or changes to existing retriever-reader pipelines. On both factoid and aggregation QA benchmarks, Adaptive-$k$ matches or outperforms fixed-$k$ baselines while using up to 10x fewer tokens than full-context input, yet still retrieves 70% of relevant passages. It improves accuracy across five LCLMs and two embedding models, highlighting that dynamically adjusting context size leads to more efficient and accurate QA.
Orchestrating Agents and Data for Enterprise: A Blueprint Architecture for Compound AI
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have gained significant interest in industry due to their impressive capabilities across a wide range of tasks. However, the widespread adoption of LLMs presents several challenges, such as integration into existing applications and infrastructure, utilization of company proprietary data, models, and APIs, and meeting cost, quality, responsiveness, and other requirements. To address these challenges, there is a notable shift from monolithic models to compound AI systems, with the premise of more powerful, versatile, and reliable applications. However, progress thus far has been piecemeal, with proposals for agentic workflows, programming models, and extended LLM capabilities, without a clear vision of an overall architecture. In this paper, we propose a 'blueprint architecture' for compound AI systems for orchestrating agents and data for enterprise applications. In our proposed architecture the key orchestration concept is 'streams' to coordinate the flow of data and instructions among agents. Existing proprietary models and APIs in the enterprise are mapped to 'agents', defined in an 'agent registry' that serves agent metadata and learned representations for search and planning. Agents can utilize proprietary data through a 'data registry' that similarly registers enterprise data of various modalities. Tying it all together, data and task 'planners' break down, map, and optimize tasks and queries for given quality of service (QoS) requirements such as cost, accuracy, and latency. We illustrate an implementation of the architecture for a use-case in the HR domain and discuss opportunities and challenges for 'agentic AI' in the enterprise.
Evaluating Bias in LLMs for Job-Resume Matching: Gender, Race, and Education
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) offer the potential to automate hiring by matching job descriptions with candidate resumes, streamlining recruitment processes, and reducing operational costs. However, biases inherent in these models may lead to unfair hiring practices, reinforcing societal prejudices and undermining workplace diversity. This study examines the performance and fairness of LLMs in job-resume matching tasks within the English language and U.S. context. It evaluates how factors such as gender, race, and educational background influence model decisions, providing critical insights into the fairness and reliability of LLMs in HR applications. Our findings indicate that while recent models have reduced biases related to explicit attributes like gender and race, implicit biases concerning educational background remain significant. These results highlight the need for ongoing evaluation and the development of advanced bias mitigation strategies to ensure equitable hiring practices when using LLMs in industry settings.
Snippet-based Conversational Recommender System
Nov 09, 2024



Abstract:Conversational Recommender Systems (CRS) engage users in interactive dialogues to gather preferences and provide personalized recommendations. Traditionally, CRS rely on pre-defined attributes or expensive, domain-specific annotated datasets to guide conversations, which limits flexibility and adaptability across domains. In this work, we introduce SnipRec, a novel CRS that enhances dialogues and recommendations by extracting diverse expressions and preferences from user-generated content (UGC) like customer reviews. Using large language models, SnipRec maps user responses and UGC to concise snippets, which are used to generate clarification questions and retrieve relevant items. Our approach eliminates the need for domain-specific training, making it adaptable to new domains and effective without prior knowledge of user preferences. Extensive experiments on the Yelp dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of snippet-based representations against document and sentence-based representations. Additionally, SnipRec is able to improve Hits@10 by 0.25 over the course of five conversational turns, underscoring the efficiency of SnipRec in capturing user preferences through multi-turn conversations.
Natural Language Processing for Human Resources: A Survey
Oct 21, 2024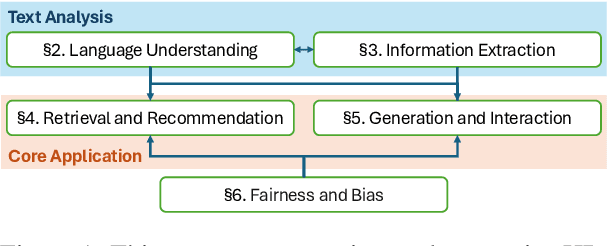
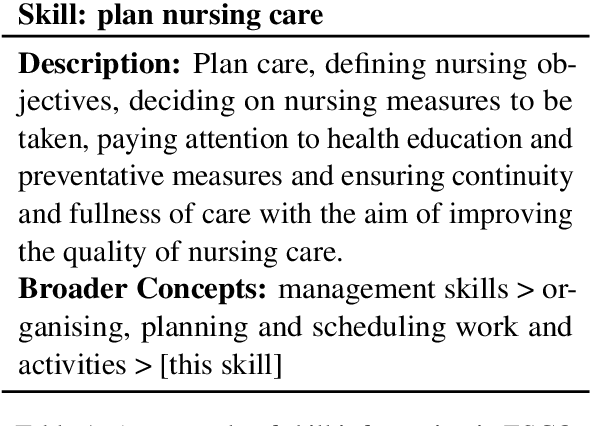

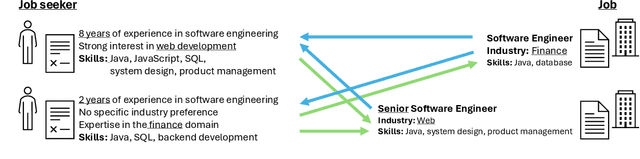
Abstract:The domain of human resources (HR) includes a broad spectrum of tasks related to natural language processing (NLP) techniques. Recent breakthroughs in NLP have generated significant interest in its industrial applications in this domain and potentially alleviate challenges such as the difficulty of resource acquisition and the complexity of problems. At the same time, the HR domain can also present unique challenges that drive state-of-the-art in NLP research. To support this, we provide NLP researchers and practitioners with an overview of key HR tasks from an NLP perspective, illustrating how specific sub-tasks (e.g., skill extraction) contribute to broader objectives (e.g., job matching). Through this survey, we identify opportunities in NLP for HR and suggest directions for future exploration.
From Single to Multi: How LLMs Hallucinate in Multi-Document Summarization
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:Although many studies have investigated and reduced hallucinations in large language models (LLMs) for single-document tasks, research on hallucination in multi-document summarization (MDS) tasks remains largely unexplored. Specifically, it is unclear how the challenges arising from handling multiple documents (e.g., repetition and diversity of information) affect models outputs. In this work, we investigate how hallucinations manifest in LLMs when summarizing topic-specific information from multiple documents. Since no benchmarks exist for investigating hallucinations in MDS, we use existing news and conversation datasets, annotated with topic-specific insights, to create two novel multi-document benchmarks. When evaluating 5 LLMs on our benchmarks, we observe that on average, up to 75% of the content in LLM-generated summary is hallucinated, with hallucinations more likely to occur towards the end of the summaries. Moreover, when summarizing non-existent topic-related information, gpt-3.5-turbo and GPT-4o still generate summaries about 79.35% and 44% of the time, raising concerns about their tendency to fabricate content. To understand the characteristics of these hallucinations, we manually evaluate 700+ insights and find that most errors stem from either failing to follow instructions or producing overly generic insights. Motivated by these observations, we investigate the efficacy of simple post-hoc baselines in mitigating hallucinations but find them only moderately effective. Our results underscore the need for more effective approaches to systematically mitigate hallucinations in MDS. We release our dataset and code at github.com/megagonlabs/Hallucination_MDS.
Holistic Reasoning with Long-Context LMs: A Benchmark for Database Operations on Massive Textual Data
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:The rapid increase in textual information means we need more efficient methods to sift through, organize, and understand it all. While retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) models excel in accessing information from large document collections, they struggle with complex tasks that require aggregation and reasoning over information spanning across multiple documents--what we call holistic reasoning. Long-context language models (LCLMs) have great potential for managing large-scale documents, but their holistic reasoning capabilities remain unclear. In this work, we introduce HoloBench, a novel framework that brings database reasoning operations into text-based contexts, making it easier to systematically evaluate how LCLMs handle holistic reasoning across large documents. Our approach adjusts key factors such as context length, information density, distribution of information, and query complexity to evaluate LCLMs comprehensively. Our experiments show that the amount of information in the context has a bigger influence on LCLM performance than the actual context length. Furthermore, the complexity of queries affects performance more than the amount of information, particularly for different types of queries. Interestingly, queries that involve finding maximum or minimum values are easier for LCLMs and are less affected by context length, even though they pose challenges for RAG systems. However, tasks requiring the aggregation of multiple pieces of information show a noticeable drop in accuracy as context length increases. Additionally, we find that while grouping relevant information generally improves performance, the optimal positioning varies across models. Our findings surface both the advancements and the ongoing challenges in achieving a holistic understanding of long contexts.
A Blueprint Architecture of Compound AI Systems for Enterprise
Jun 02, 2024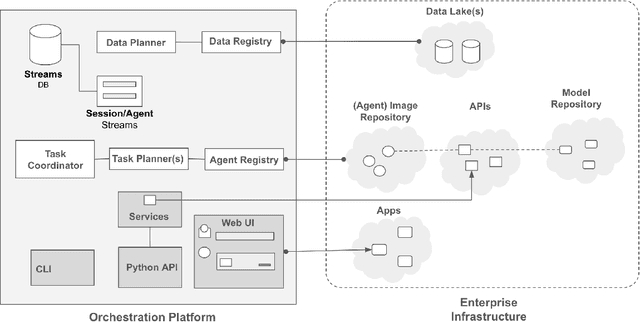
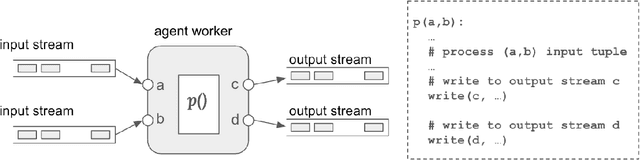
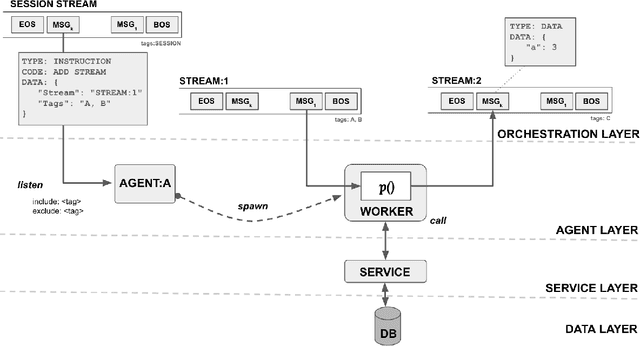
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have showcased remarkable capabilities surpassing conventional NLP challenges, creating opportunities for use in production use cases. Towards this goal, there is a notable shift to building compound AI systems, wherein LLMs are integrated into an expansive software infrastructure with many components like models, retrievers, databases and tools. In this paper, we introduce a blueprint architecture for compound AI systems to operate in enterprise settings cost-effectively and feasibly. Our proposed architecture aims for seamless integration with existing compute and data infrastructure, with ``stream'' serving as the key orchestration concept to coordinate data and instructions among agents and other components. Task and data planners, respectively, break down, map, and optimize tasks and data to available agents and data sources defined in respective registries, given production constraints such as accuracy and latency.
Retrieval Helps or Hurts? A Deeper Dive into the Efficacy of Retrieval Augmentation to Language Models
Feb 21, 2024Abstract:While large language models (LMs) demonstrate remarkable performance, they encounter challenges in providing accurate responses when queried for information beyond their pre-trained memorization. Although augmenting them with relevant external information can mitigate these issues, failure to consider the necessity of retrieval may adversely affect overall performance. Previous research has primarily focused on examining how entities influence retrieval models and knowledge recall in LMs, leaving other aspects relatively unexplored. In this work, our goal is to offer a more detailed, fact-centric analysis by exploring the effects of combinations of entities and relations. To facilitate this, we construct a new question answering (QA) dataset called WiTQA (Wikipedia Triple Question Answers). This dataset includes questions about entities and relations of various popularity levels, each accompanied by a supporting passage. Our extensive experiments with diverse LMs and retrievers reveal when retrieval does not consistently enhance LMs from the viewpoints of fact-centric popularity.Confirming earlier findings, we observe that larger LMs excel in recalling popular facts. However, they notably encounter difficulty with infrequent entity-relation pairs compared to retrievers. Interestingly, they can effectively retain popular relations of less common entities. We demonstrate the efficacy of our finer-grained metric and insights through an adaptive retrieval system that selectively employs retrieval and recall based on the frequencies of entities and relations in the question.
Reasoning Capacity in Multi-Agent Systems: Limitations, Challenges and Human-Centered Solutions
Feb 02, 2024Abstract:Remarkable performance of large language models (LLMs) in a variety of tasks brings forth many opportunities as well as challenges of utilizing them in production settings. Towards practical adoption of LLMs, multi-agent systems hold great promise to augment, integrate, and orchestrate LLMs in the larger context of enterprise platforms that use existing proprietary data and models to tackle complex real-world tasks. Despite the tremendous success of these systems, current approaches rely on narrow, single-focus objectives for optimization and evaluation, often overlooking potential constraints in real-world scenarios, including restricted budgets, resources and time. Furthermore, interpreting, analyzing, and debugging these systems requires different components to be evaluated in relation to one another. This demand is currently not feasible with existing methodologies. In this postion paper, we introduce the concept of reasoning capacity as a unifying criterion to enable integration of constraints during optimization and establish connections among different components within the system, which also enable a more holistic and comprehensive approach to evaluation. We present a formal definition of reasoning capacity and illustrate its utility in identifying limitations within each component of the system. We then argue how these limitations can be addressed with a self-reflective process wherein human-feedback is used to alleviate shortcomings in reasoning and enhance overall consistency of the system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge