Elizabeth Nielsen
TranslateGemma Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We present TranslateGemma, a suite of open machine translation models based on the Gemma 3 foundation models. To enhance the inherent multilingual capabilities of Gemma 3 for the translation task, we employ a two-stage fine-tuning process. First, supervised fine-tuning is performed using a rich mixture of high-quality large-scale synthetic parallel data generated via state-of-the-art models and human-translated parallel data. This is followed by a reinforcement learning phase, where we optimize translation quality using an ensemble of reward models, including MetricX-QE and AutoMQM, targeting translation quality. We demonstrate the effectiveness of TranslateGemma with human evaluation on the WMT25 test set across 10 language pairs and with automatic evaluation on the WMT24++ benchmark across 55 language pairs. Automatic metrics show consistent and substantial gains over the baseline Gemma 3 models across all sizes. Notably, smaller TranslateGemma models often achieve performance comparable to larger baseline models, offering improved efficiency. We also show that TranslateGemma models retain strong multimodal capabilities, with enhanced performance on the Vistra image translation benchmark. The release of the open TranslateGemma models aims to provide the research community with powerful and adaptable tools for machine translation.
SMOL: Professionally translated parallel data for 115 under-represented languages
Feb 17, 2025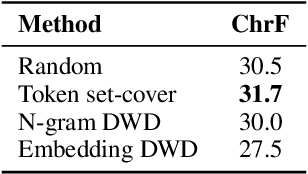
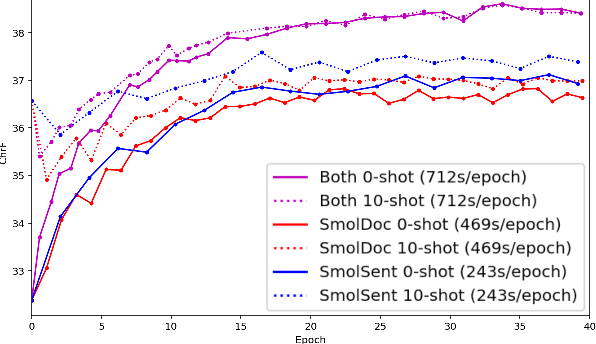
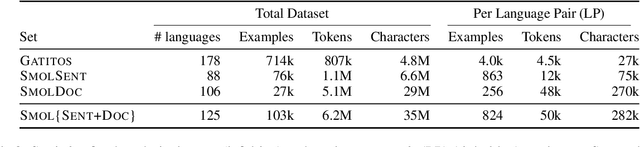
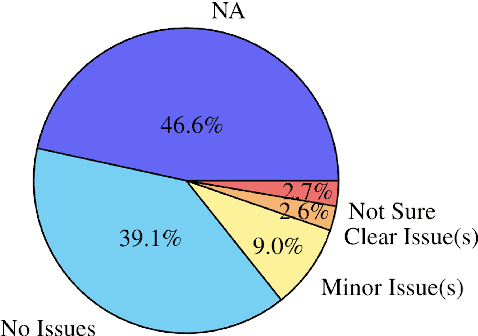
Abstract:We open-source SMOL (Set of Maximal Overall Leverage), a suite of training data to unlock translation for low-resource languages (LRLs). SMOL has been translated into 115 under-resourced languages, including many for which there exist no previous public resources, for a total of 6.1M translated tokens. SMOL comprises two sub-datasets, each carefully chosen for maximum impact given its size: SMOL-Sent, a set of sentences chosen for broad unique token coverage, and SMOL-Doc, a document-level source focusing on a broad topic coverage. They join the already released GATITOS for a trifecta of paragraph, sentence, and token-level content. We demonstrate that using SMOL to prompt or fine-tune Large Language Models yields robust ChrF improvements. In addition to translation, we provide factuality ratings and rationales for all documents in SMOL-Doc, yielding the first factuality datasets for most of these languages.
Spelling convention sensitivity in neural language models
Mar 06, 2023



Abstract:We examine whether large neural language models, trained on very large collections of varied English text, learn the potentially long-distance dependency of British versus American spelling conventions, i.e., whether spelling is consistently one or the other within model-generated strings. In contrast to long-distance dependencies in non-surface underlying structure (e.g., syntax), spelling consistency is easier to measure both in LMs and the text corpora used to train them, which can provide additional insight into certain observed model behaviors. Using a set of probe words unique to either British or American English, we first establish that training corpora exhibit substantial (though not total) consistency. A large T5 language model does appear to internalize this consistency, though only with respect to observed lexical items (not nonce words with British/American spelling patterns). We further experiment with correcting for biases in the training data by fine-tuning T5 on synthetic data that has been debiased, and find that finetuned T5 remains only somewhat sensitive to spelling consistency. Further experiments show GPT2 to be similarly limited.
Prosodic features improve sentence segmentation and parsing
Feb 23, 2023Abstract:Parsing spoken dialogue presents challenges that parsing text does not, including a lack of clear sentence boundaries. We know from previous work that prosody helps in parsing single sentences (Tran et al. 2018), but we want to show the effect of prosody on parsing speech that isn't segmented into sentences. In experiments on the English Switchboard corpus, we find prosody helps our model both with parsing and with accurately identifying sentence boundaries. However, we find that the best-performing parser is not necessarily the parser that produces the best sentence segmentation performance. We suggest that the best parses instead come from modelling sentence boundaries jointly with other constituent boundaries.
Zero-shot Cross-Linguistic Learning of Event Semantics
Jul 05, 2022
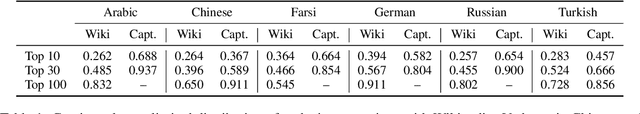
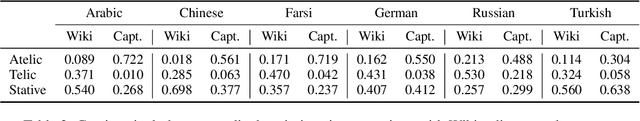
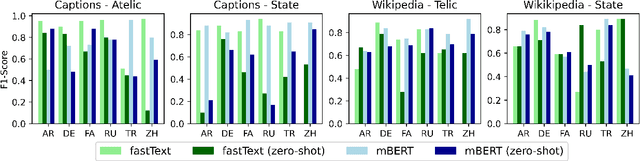
Abstract:Typologically diverse languages offer systems of lexical and grammatical aspect that allow speakers to focus on facets of event structure in ways that comport with the specific communicative setting and discourse constraints they face. In this paper, we look specifically at captions of images across Arabic, Chinese, Farsi, German, Russian, and Turkish and describe a computational model for predicting lexical aspects. Despite the heterogeneity of these languages, and the salient invocation of distinctive linguistic resources across their caption corpora, speakers of these languages show surprising similarities in the ways they frame image content. We leverage this observation for zero-shot cross-lingual learning and show that lexical aspects can be predicted for a given language despite not having observed any annotated data for this language at all.
Prosodic segmentation for parsing spoken dialogue
May 26, 2021



Abstract:Parsing spoken dialogue poses unique difficulties, including disfluencies and unmarked boundaries between sentence-like units. Previous work has shown that prosody can help with parsing disfluent speech (Tran et al. 2018), but has assumed that the input to the parser is already segmented into sentence-like units (SUs), which isn't true in existing speech applications. We investigate how prosody affects a parser that receives an entire dialogue turn as input (a turn-based model), instead of gold standard pre-segmented SUs (an SU-based model). In experiments on the English Switchboard corpus, we find that when using transcripts alone, the turn-based model has trouble segmenting SUs, leading to worse parse performance than the SU-based model. However, prosody can effectively replace gold standard SU boundaries: with prosody, the turn-based model performs as well as the SU-based model (90.79 vs. 90.65 F1 score, respectively), despite performing two tasks (SU segmentation and parsing) rather than one (parsing alone). Analysis shows that pitch and intensity features are the most important for this corpus, since they allow the model to correctly distinguish an SU boundary from a speech disfluency -- a distinction that the model otherwise struggles to make.
The role of context in neural pitch accent detection in English
Apr 30, 2020



Abstract:Prosody is a rich information source in natural language, serving as a marker for phenomena such as contrast. In order to make this information available to downstream tasks, we need a way to detect prosodic events in speech. We propose a new model for pitch accent detection, inspired by the work of Stehwien et al. (2018), who presented a CNN-based model for this task. Our model makes greater use of context by using full utterances as input and adding an LSTM layer. We find that these innovations lead to an improvement from 87.5% to 88.7% accuracy on pitch accent detection on American English speech in the Boston University Radio News Corpus, a state-of-the-art result. We also find that a simple baseline that just predicts a pitch accent on every content word yields 82.2% accuracy, and we suggest that this is the appropriate baseline for this task. Finally, we conduct ablation tests that show pitch is the most important acoustic feature for this task and this corpus.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge