Jiaming Luo
Dima
TranslateGemma Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We present TranslateGemma, a suite of open machine translation models based on the Gemma 3 foundation models. To enhance the inherent multilingual capabilities of Gemma 3 for the translation task, we employ a two-stage fine-tuning process. First, supervised fine-tuning is performed using a rich mixture of high-quality large-scale synthetic parallel data generated via state-of-the-art models and human-translated parallel data. This is followed by a reinforcement learning phase, where we optimize translation quality using an ensemble of reward models, including MetricX-QE and AutoMQM, targeting translation quality. We demonstrate the effectiveness of TranslateGemma with human evaluation on the WMT25 test set across 10 language pairs and with automatic evaluation on the WMT24++ benchmark across 55 language pairs. Automatic metrics show consistent and substantial gains over the baseline Gemma 3 models across all sizes. Notably, smaller TranslateGemma models often achieve performance comparable to larger baseline models, offering improved efficiency. We also show that TranslateGemma models retain strong multimodal capabilities, with enhanced performance on the Vistra image translation benchmark. The release of the open TranslateGemma models aims to provide the research community with powerful and adaptable tools for machine translation.
Gemma 3 Technical Report
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:We introduce Gemma 3, a multimodal addition to the Gemma family of lightweight open models, ranging in scale from 1 to 27 billion parameters. This version introduces vision understanding abilities, a wider coverage of languages and longer context - at least 128K tokens. We also change the architecture of the model to reduce the KV-cache memory that tends to explode with long context. This is achieved by increasing the ratio of local to global attention layers, and keeping the span on local attention short. The Gemma 3 models are trained with distillation and achieve superior performance to Gemma 2 for both pre-trained and instruction finetuned versions. In particular, our novel post-training recipe significantly improves the math, chat, instruction-following and multilingual abilities, making Gemma3-4B-IT competitive with Gemma2-27B-IT and Gemma3-27B-IT comparable to Gemini-1.5-Pro across benchmarks. We release all our models to the community.
Leveraging Domain Knowledge at Inference Time for LLM Translation: Retrieval versus Generation
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have been increasingly adopted for machine translation (MT), their performance for specialist domains such as medicine and law remains an open challenge. Prior work has shown that LLMs can be domain-adapted at test-time by retrieving targeted few-shot demonstrations or terminologies for inclusion in the prompt. Meanwhile, for general-purpose LLM MT, recent studies have found some success in generating similarly useful domain knowledge from an LLM itself, prior to translation. Our work studies domain-adapted MT with LLMs through a careful prompting setup, finding that demonstrations consistently outperform terminology, and retrieval consistently outperforms generation. We find that generating demonstrations with weaker models can close the gap with larger model's zero-shot performance. Given the effectiveness of demonstrations, we perform detailed analyses to understand their value. We find that domain-specificity is particularly important, and that the popular multi-domain benchmark is testing adaptation to a particular writing style more so than to a specific domain.
SMOL: Professionally translated parallel data for 115 under-represented languages
Feb 17, 2025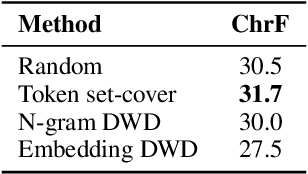
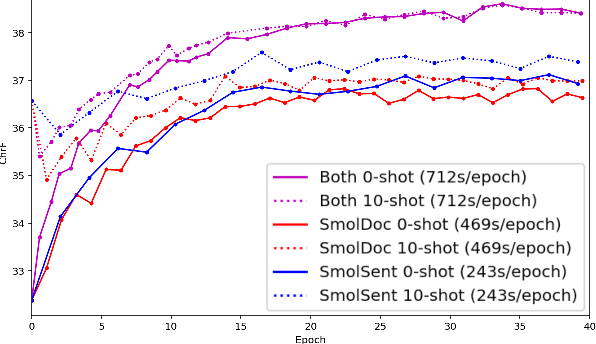
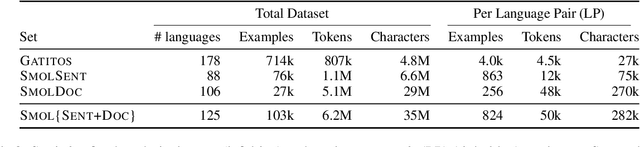
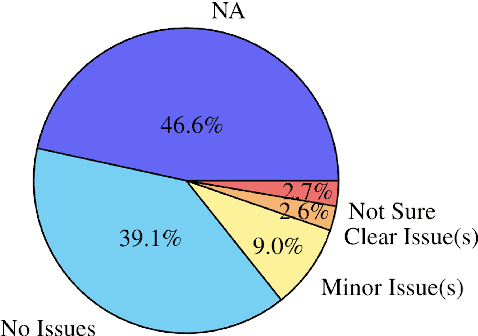
Abstract:We open-source SMOL (Set of Maximal Overall Leverage), a suite of training data to unlock translation for low-resource languages (LRLs). SMOL has been translated into 115 under-resourced languages, including many for which there exist no previous public resources, for a total of 6.1M translated tokens. SMOL comprises two sub-datasets, each carefully chosen for maximum impact given its size: SMOL-Sent, a set of sentences chosen for broad unique token coverage, and SMOL-Doc, a document-level source focusing on a broad topic coverage. They join the already released GATITOS for a trifecta of paragraph, sentence, and token-level content. We demonstrate that using SMOL to prompt or fine-tune Large Language Models yields robust ChrF improvements. In addition to translation, we provide factuality ratings and rationales for all documents in SMOL-Doc, yielding the first factuality datasets for most of these languages.
Overestimation in LLM Evaluation: A Controlled Large-Scale Study on Data Contamination's Impact on Machine Translation
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Data contamination -- the accidental consumption of evaluation examples within the pre-training data -- can undermine the validity of evaluation benchmarks. In this paper, we present a rigorous analysis of the effects of contamination on language models at 1B and 8B scales on the machine translation task. Starting from a carefully decontaminated train-test split, we systematically introduce contamination at various stages, scales, and data formats to isolate its effect and measure its impact on performance metrics. Our experiments reveal that contamination with both source and target substantially inflates BLEU scores, and this inflation is 2.5 times larger (up to 30 BLEU points) for 8B compared to 1B models. In contrast, source-only and target-only contamination generally produce smaller, less consistent over-estimations. Finally, we study how the temporal distribution and frequency of contaminated samples influence performance over-estimation across languages with varying degrees of data resources.
How Good is Your Wikipedia?
Nov 08, 2024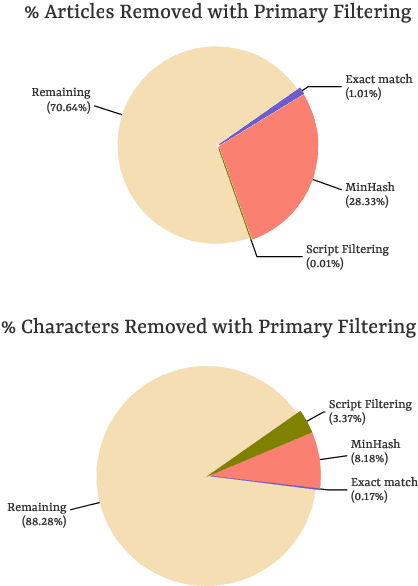
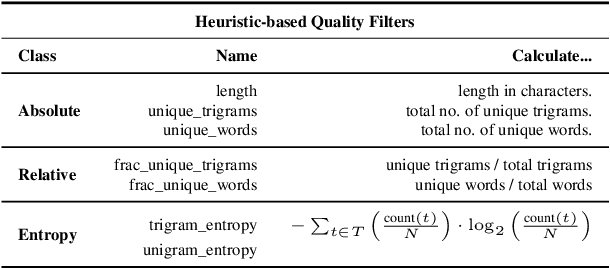
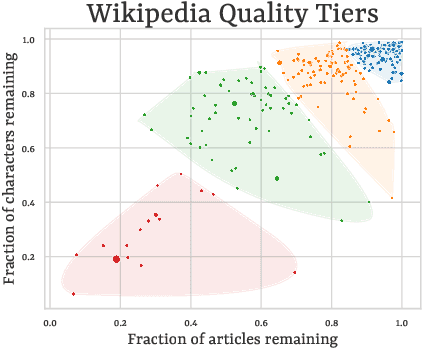
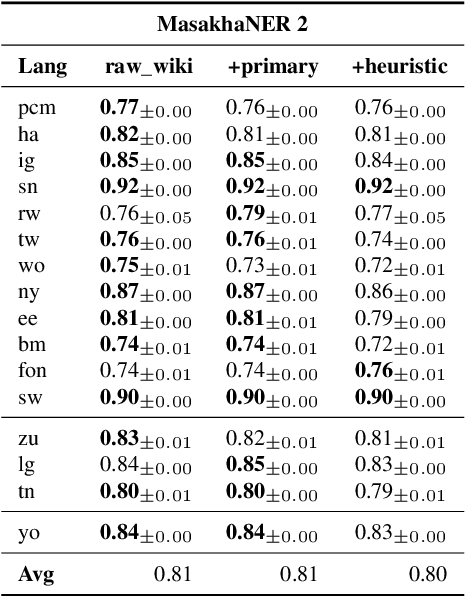
Abstract:Wikipedia's perceived high quality and broad language coverage have established it as a fundamental resource in multilingual NLP. In the context of low-resource languages, however, these quality assumptions are increasingly being scrutinised. This paper critically examines the data quality of Wikipedia in a non-English setting by subjecting it to various quality filtering techniques, revealing widespread issues such as a high percentage of one-line articles and duplicate articles. We evaluate the downstream impact of quality filtering on Wikipedia and find that data quality pruning is an effective means for resource-efficient training without hurting performance, especially for low-resource languages. Moreover, we advocate for a shift in perspective from seeking a general definition of data quality towards a more language- and task-specific one. Ultimately, we aim for this study to serve as a guide to using Wikipedia for pretraining in a multilingual setting.
Learning from others' mistakes: Finetuning machine translation models with span-level error annotations
Oct 21, 2024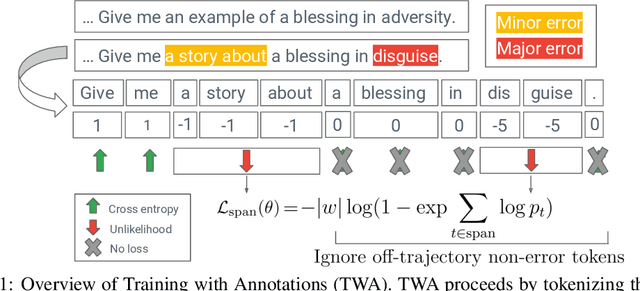


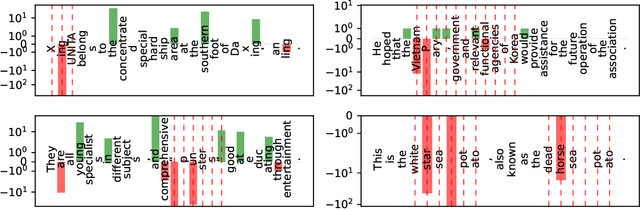
Abstract:Despite growing interest in incorporating feedback to improve language models, most efforts focus only on sequence-level annotations. In this work, we explore the potential of utilizing fine-grained span-level annotations from offline datasets to improve model quality. We develop a simple finetuning algorithm, called Training with Annotations (TWA), to directly train machine translation models on such annotated data. TWA utilizes targeted span-level error information while also flexibly learning what to penalize within a span. Moreover, TWA considers the overall trajectory of a sequence when deciding which non-error spans to utilize as positive signals. Experiments on English-German and Chinese-English machine translation show that TWA outperforms baselines such as Supervised FineTuning on sequences filtered for quality and Direct Preference Optimization on pairs constructed from the same data.
Translating Step-by-Step: Decomposing the Translation Process for Improved Translation Quality of Long-Form Texts
Sep 10, 2024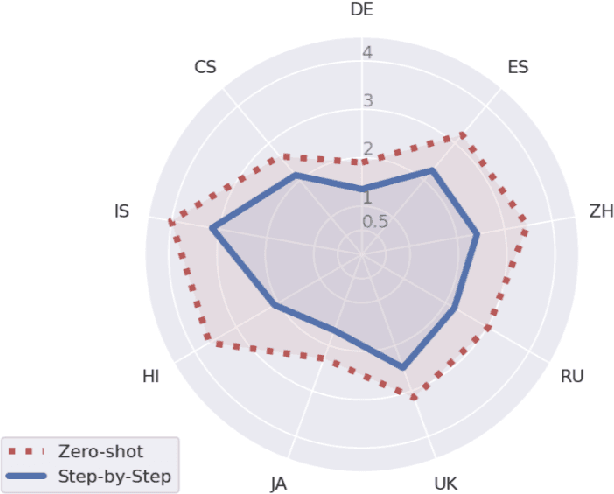
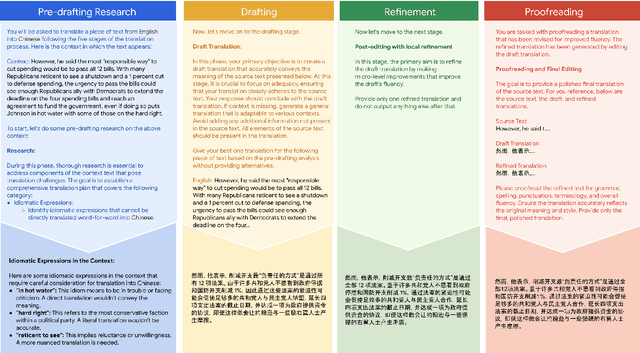

Abstract:In this paper we present a step-by-step approach to long-form text translation, drawing on established processes in translation studies. Instead of viewing machine translation as a single, monolithic task, we propose a framework that engages language models in a multi-turn interaction, encompassing pre-translation research, drafting, refining, and proofreading, resulting in progressively improved translations. Extensive automatic evaluations using Gemini 1.5 Pro across ten language pairs show that translating step-by-step yields large translation quality improvements over conventional zero-shot prompting approaches and earlier human-like baseline strategies, resulting in state-of-the-art results on WMT2024.
To Diverge or Not to Diverge: A Morphosyntactic Perspective on Machine Translation vs Human Translation
Jan 02, 2024Abstract:We conduct a large-scale fine-grained comparative analysis of machine translations (MT) against human translations (HT) through the lens of morphosyntactic divergence. Across three language pairs and two types of divergence defined as the structural difference between the source and the target, MT is consistently more conservative than HT, with less morphosyntactic diversity, more convergent patterns, and more one-to-one alignments. Through analysis on different decoding algorithms, we attribute this discrepancy to the use of beam search that biases MT towards more convergent patterns. This bias is most amplified when the convergent pattern appears around 50% of the time in training data. Lastly, we show that for a majority of morphosyntactic divergences, their presence in HT is correlated with decreased MT performance, presenting a greater challenge for MT systems.
Improving the Robustness of Summarization Models by Detecting and Removing Input Noise
Dec 20, 2022



Abstract:The evaluation of abstractive summarization models typically uses test data that is identically distributed as training data. In real-world practice, documents to be summarized may contain input noise caused by text extraction artifacts or data pipeline bugs. The robustness of model performance under distribution shift caused by such noise is relatively under-studied. We present a large empirical study quantifying the sometimes severe loss in performance (up to 12 ROUGE-1 points) from different types of input noise for a range of datasets and model sizes. We then propose a light-weight method for detecting and removing such noise in the input during model inference without requiring any extra training, auxiliary models, or even prior knowledge of the type of noise. Our proposed approach effectively mitigates the loss in performance, recovering a large fraction of the performance drop, sometimes as large as 11 ROUGE-1 points.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge