Markus Freitag
TranslateGemma Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We present TranslateGemma, a suite of open machine translation models based on the Gemma 3 foundation models. To enhance the inherent multilingual capabilities of Gemma 3 for the translation task, we employ a two-stage fine-tuning process. First, supervised fine-tuning is performed using a rich mixture of high-quality large-scale synthetic parallel data generated via state-of-the-art models and human-translated parallel data. This is followed by a reinforcement learning phase, where we optimize translation quality using an ensemble of reward models, including MetricX-QE and AutoMQM, targeting translation quality. We demonstrate the effectiveness of TranslateGemma with human evaluation on the WMT25 test set across 10 language pairs and with automatic evaluation on the WMT24++ benchmark across 55 language pairs. Automatic metrics show consistent and substantial gains over the baseline Gemma 3 models across all sizes. Notably, smaller TranslateGemma models often achieve performance comparable to larger baseline models, offering improved efficiency. We also show that TranslateGemma models retain strong multimodal capabilities, with enhanced performance on the Vistra image translation benchmark. The release of the open TranslateGemma models aims to provide the research community with powerful and adaptable tools for machine translation.
Mind the Gap... or Not? How Translation Errors and Evaluation Details Skew Multilingual Results
Nov 07, 2025
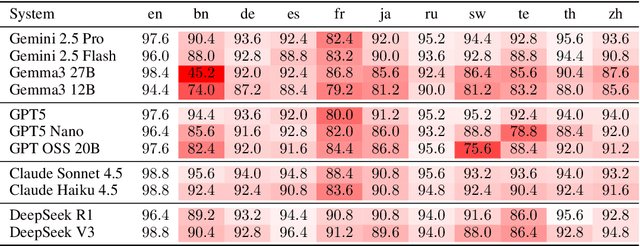

Abstract:Most current large language models (LLMs) support a wide variety of languages in addition to English, including high-resource languages (e.g. German, Chinese, French), as well as low-resource ones (e.g. Swahili, Telugu). In addition they have also shown impressive capabilities in different domains, like coding, science and math. In this short paper, taking math as an example domain, we study the performance of different LLMs across languages. Experimental results show that there exists a non-negligible and consistent gap in the performance of the models across languages. Interestingly, and somewhat against expectations, the gap exists for both high- and low-resource languages. We hope that these results influence further research into cross-lingual capability generalization for next generation LLMs. If it weren't for the fact that they are false! By analyzing one of the standard multilingual math benchmarks (MGSM), we determine that several translation errors are present in the data. Furthermore, the lack of standardized answer extraction from LLM outputs further influences the final results. We propose a method for automatic quality assurance to address the first issue at scale, and give recommendations to address the second one. Combining these two approaches we show that the aforementioned language gap mostly disappears, leading to completely different conclusions from our research. We additionally release the corrected dataset to the community.
Searching for Difficult-to-Translate Test Examples at Scale
Sep 30, 2025Abstract:NLP models require test data that are sufficiently challenging. The difficulty of an example is linked to the topic it originates from (''seed topic''). The relationship between the topic and the difficulty of its instances is stochastic in nature: an example about a difficult topic can happen to be easy, and vice versa. At the scale of the Internet, there are tens of thousands of potential topics, and finding the most difficult one by drawing and evaluating a large number of examples across all topics is computationally infeasible. We formalize this task and treat it as a multi-armed bandit problem. In this framework, each topic is an ''arm,'' and pulling an arm (at a cost) involves drawing a single example, evaluating it, and measuring its difficulty. The goal is to efficiently identify the most difficult topics within a fixed computational budget. We illustrate the bandit problem setup of finding difficult examples for the task of machine translation. We find that various bandit strategies vastly outperform baseline methods like brute-force searching the most challenging topics.
Generating Difficult-to-Translate Texts
Sep 30, 2025Abstract:Machine translation benchmarks sourced from the real world are quickly obsoleted, due to most examples being easy for state-of-the-art translation models. This limits the benchmark's ability to distinguish which model is better or to reveal models' weaknesses. Current methods for creating difficult test cases, such as subsampling or from-scratch synthesis, either fall short of identifying difficult examples or suffer from a lack of diversity and naturalness. Inspired by the iterative process of human experts probing for model failures, we propose MT-breaker, a method where a large language model iteratively refines a source text to increase its translation difficulty. The LLM iteratively queries a target machine translation model to guide its generation of difficult examples. Our approach generates examples that are more challenging for the target MT model while preserving the diversity of natural texts. While the examples are tailored to a particular machine translation model during the generation, the difficulty also transfers to other models and languages.
Deconstructing Self-Bias in LLM-generated Translation Benchmarks
Sep 30, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) begin to saturate existing benchmarks, automated benchmark creation using LLMs (LLM as a benchmark) has emerged as a scalable alternative to slow and costly human curation. While these generated test sets have to potential to cheaply rank models, we demonstrate a critical flaw. LLM generated benchmarks systematically favor the model that created the benchmark, they exhibit self bias on low resource languages to English translation tasks. We show three key findings on automatic benchmarking of LLMs for translation: First, this bias originates from two sources: the generated test data (LLM as a testset) and the evaluation method (LLM as an evaluator), with their combination amplifying the effect. Second, self bias in LLM as a benchmark is heavily influenced by the model's generation capabilities in the source language. For instance, we observe more pronounced bias in into English translation, where the model's generation system is developed, than in out of English translation tasks. Third, we observe that low diversity in source text is one attribution to self bias. Our results suggest that improving the diversity of these generated source texts can mitigate some of the observed self bias.
You Cannot Feed Two Birds with One Score: the Accuracy-Naturalness Tradeoff in Translation
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:The goal of translation, be it by human or by machine, is, given some text in a source language, to produce text in a target language that simultaneously 1) preserves the meaning of the source text and 2) achieves natural expression in the target language. However, researchers in the machine translation community usually assess translations using a single score intended to capture semantic accuracy and the naturalness of the output simultaneously. In this paper, we build on recent advances in information theory to mathematically prove and empirically demonstrate that such single-score summaries do not and cannot give the complete picture of a system's true performance. Concretely, we prove that a tradeoff exists between accuracy and naturalness and demonstrate it by evaluating the submissions to the WMT24 shared task. Our findings help explain well-known empirical phenomena, such as the observation that optimizing translation systems for a specific accuracy metric (like BLEU) initially improves the system's naturalness, while ``overfitting'' the system to the metric can significantly degrade its naturalness. Thus, we advocate for a change in how translations are evaluated: rather than comparing systems using a single number, they should be compared on an accuracy-naturalness plane.
Enhancing Human Evaluation in Machine Translation with Comparative Judgment
Feb 25, 2025

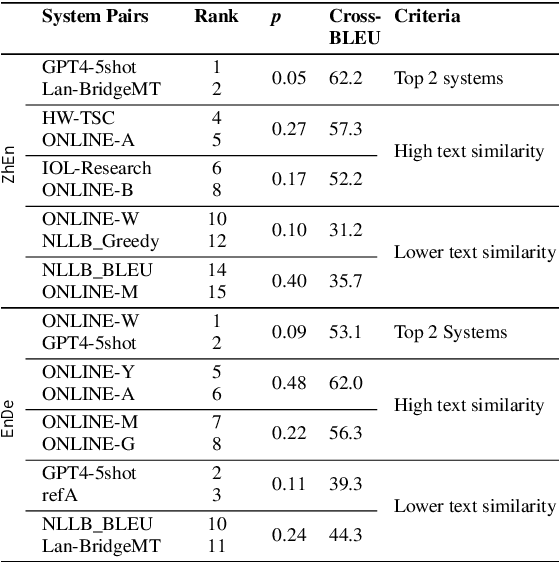
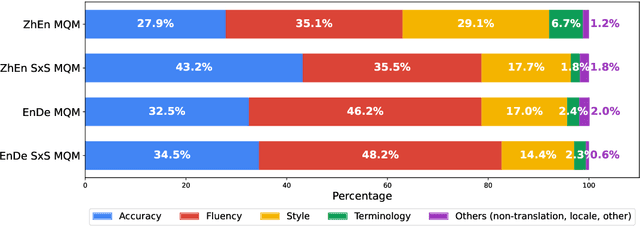
Abstract:Human evaluation is crucial for assessing rapidly evolving language models but is influenced by annotator proficiency and task design. This study explores the integration of comparative judgment into human annotation for machine translation (MT) and evaluates three annotation setups-point-wise Multidimensional Quality Metrics (MQM), side-by-side (SxS) MQM, and its simplified version SxS relative ranking (RR). In MQM, annotators mark error spans with categories and severity levels. SxS MQM extends MQM to pairwise error annotation for two translations of the same input, while SxS RR focuses on selecting the better output without labeling errors. Key findings are: (1) the SxS settings achieve higher inter-annotator agreement than MQM; (2) SxS MQM enhances inter-translation error marking consistency compared to MQM by, on average, 38.5% for explicitly compared MT systems and 19.5% for others; (3) all annotation settings return stable system rankings, with SxS RR offering a more efficient alternative to (SxS) MQM; (4) the SxS settings highlight subtle errors overlooked in MQM without altering absolute system evaluations. To spur further research, we will release the triply annotated datasets comprising 377 ZhEn and 104 EnDe annotation examples.
WMT24++: Expanding the Language Coverage of WMT24 to 55 Languages & Dialects
Feb 18, 2025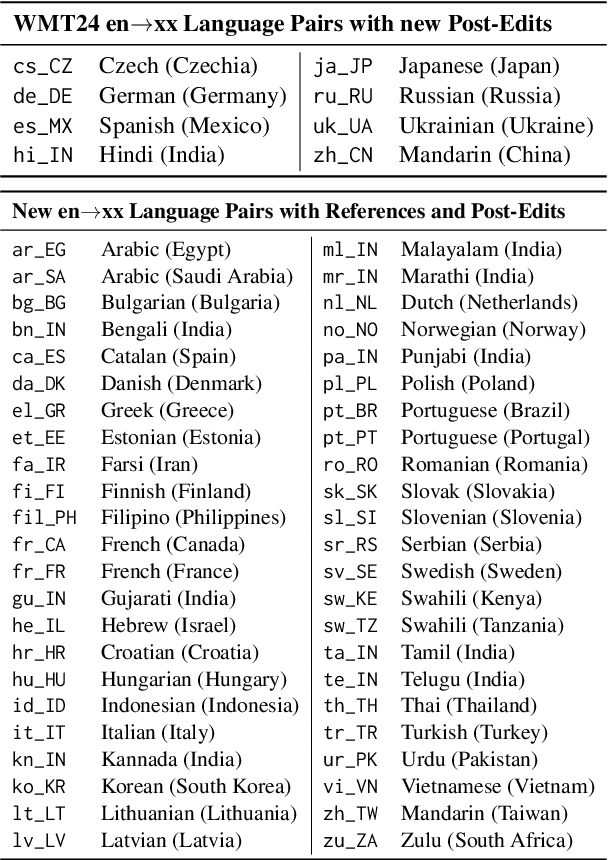
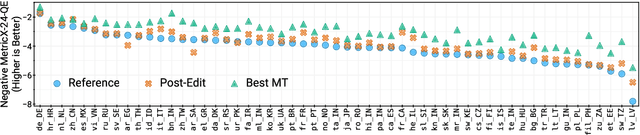

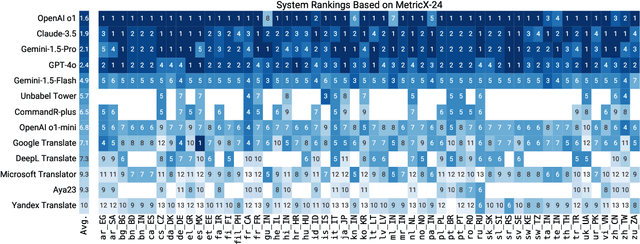
Abstract:As large language models (LLM) become more and more capable in languages other than English, it is important to collect benchmark datasets in order to evaluate their multilingual performance, including on tasks like machine translation (MT). In this work, we extend the WMT24 dataset to cover 55 languages by collecting new human-written references and post-edits for 46 new languages and dialects in addition to post-edits of the references in 8 out of 9 languages in the original WMT24 dataset. The dataset covers four domains: literary, news, social, and speech. We benchmark a variety of MT providers and LLMs on the collected dataset using automatic metrics and find that LLMs are the best-performing MT systems in all 55 languages. These results should be confirmed using a human-based evaluation, which we leave for future work.
Overestimation in LLM Evaluation: A Controlled Large-Scale Study on Data Contamination's Impact on Machine Translation
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Data contamination -- the accidental consumption of evaluation examples within the pre-training data -- can undermine the validity of evaluation benchmarks. In this paper, we present a rigorous analysis of the effects of contamination on language models at 1B and 8B scales on the machine translation task. Starting from a carefully decontaminated train-test split, we systematically introduce contamination at various stages, scales, and data formats to isolate its effect and measure its impact on performance metrics. Our experiments reveal that contamination with both source and target substantially inflates BLEU scores, and this inflation is 2.5 times larger (up to 30 BLEU points) for 8B compared to 1B models. In contrast, source-only and target-only contamination generally produce smaller, less consistent over-estimations. Finally, we study how the temporal distribution and frequency of contaminated samples influence performance over-estimation across languages with varying degrees of data resources.
From Jack of All Trades to Master of One: Specializing LLM-based Autoraters to a Test Set
Nov 23, 2024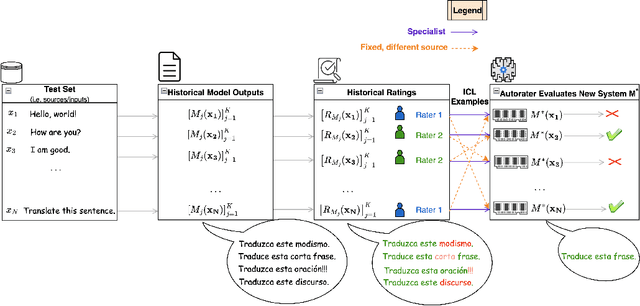

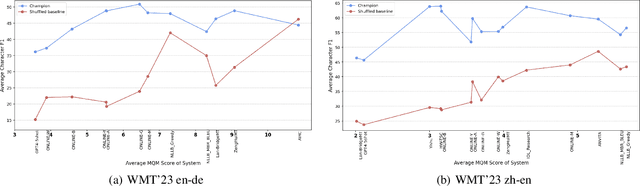

Abstract:As LLMs continue to become more powerful and versatile, human evaluation has quickly become intractable at scale and reliance on automatic metrics has become the norm. Recently, it has been shown that LLMs are themselves state-of-the-art evaluators for many tasks. These Autoraters are typically designed so that they generalize to new systems and test sets. In practice, however, evaluation is performed on a small set of fixed, canonical test sets, which are carefully curated to measure certain capabilities of interest and are not changed frequently. In this work, we design a method which specializes a prompted Autorater to a given test set, by leveraging historical ratings on the test set to construct in-context learning (ICL) examples. We evaluate our Specialist method on the task of fine-grained machine translation evaluation, and show that it dramatically outperforms the state-of-the-art XCOMET metric by 54% and 119% on the WMT'23 and WMT'24 test sets, respectively. We perform extensive analyses to understand the representations learned by our Specialist metrics, and how variability in rater behavior affects their performance. We also verify the generalizability and robustness of our Specialist method for designing automatic metrics across different numbers of ICL examples, LLM backbones, systems to evaluate, and evaluation tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge