Ricardo Rei
INESC-ID Lisboa, Instituto Superior Técnico, Unbabel AI
EuroLLM-22B: Technical Report
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:This report presents EuroLLM-22B, a large language model trained from scratch to support the needs of European citizens by covering all 24 official European Union languages and 11 additional languages. EuroLLM addresses the issue of European languages being underrepresented and underserved in existing open large language models. We provide a comprehensive overview of EuroLLM-22B's development, including tokenizer design, architectural specifications, data filtering, and training procedures. Across a broad set of multilingual benchmarks, EuroLLM-22B demonstrates strong performance in reasoning, instruction following, and translation, achieving results competitive with models of comparable size. To support future research, we release our base and instruction-tuned models, our multilingual web pretraining data and updated EuroBlocks instruction datasets, as well as our pre-training and evaluation codebases.
MindGuard: Guardrail Classifiers for Multi-Turn Mental Health Support
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Large language models are increasingly used for mental health support, yet their conversational coherence alone does not ensure clinical appropriateness. Existing general-purpose safeguards often fail to distinguish between therapeutic disclosures and genuine clinical crises, leading to safety failures. To address this gap, we introduce a clinically grounded risk taxonomy, developed in collaboration with PhD-level psychologists, that identifies actionable harm (e.g., self-harm and harm to others) while preserving space for safe, non-crisis therapeutic content. We release MindGuard-testset, a dataset of real-world multi-turn conversations annotated at the turn level by clinical experts. Using synthetic dialogues generated via a controlled two-agent setup, we train MindGuard, a family of lightweight safety classifiers (with 4B and 8B parameters). Our classifiers reduce false positives at high-recall operating points and, when paired with clinician language models, help achieve lower attack success and harmful engagement rates in adversarial multi-turn interactions compared to general-purpose safeguards. We release all models and human evaluation data.
EuroLLM-9B: Technical Report
Jun 04, 2025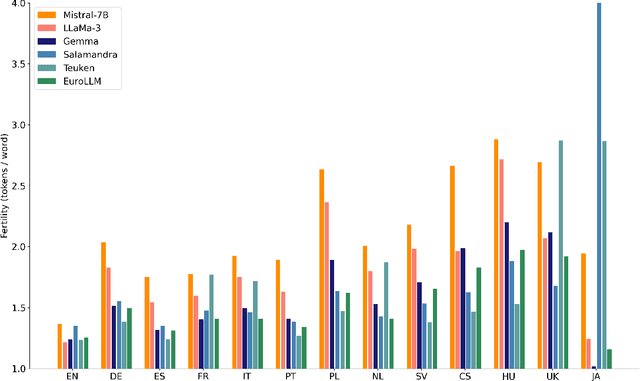
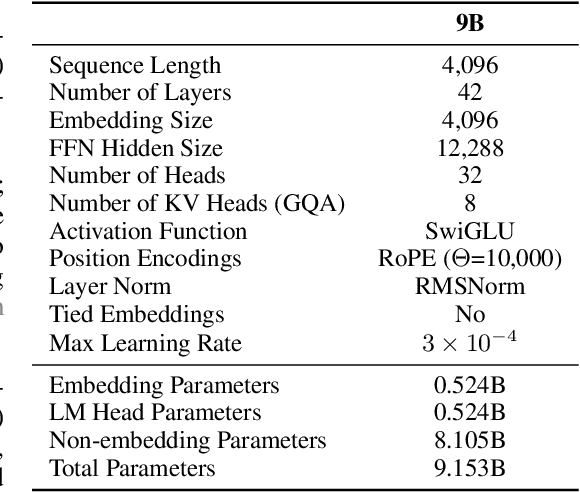
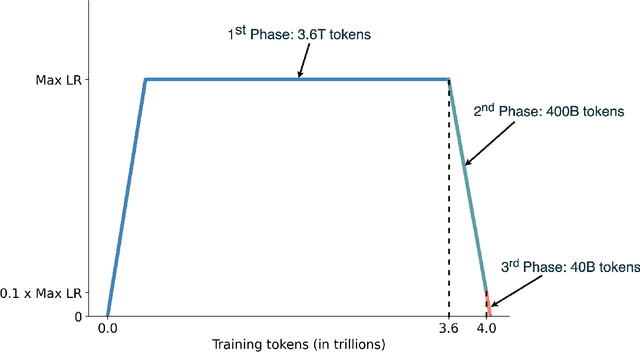
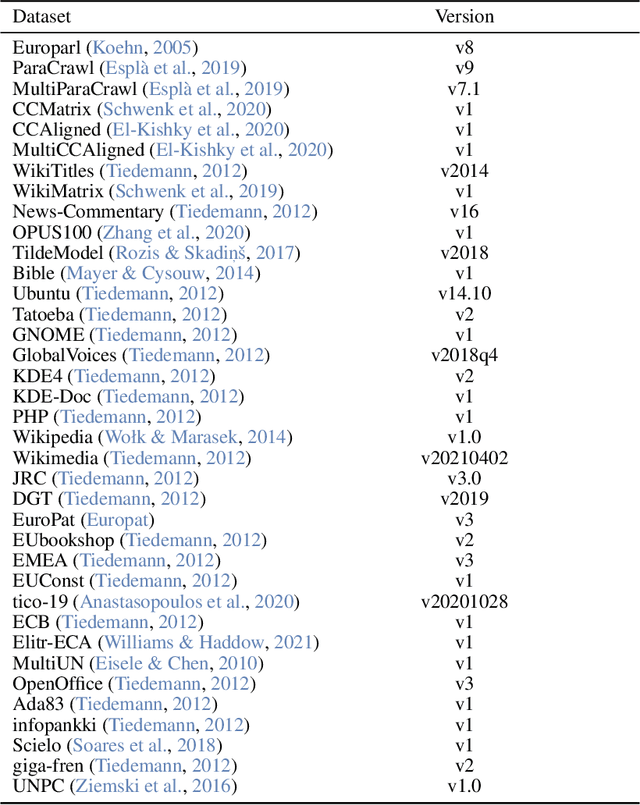
Abstract:This report presents EuroLLM-9B, a large language model trained from scratch to support the needs of European citizens by covering all 24 official European Union languages and 11 additional languages. EuroLLM addresses the issue of European languages being underrepresented and underserved in existing open large language models. We provide a comprehensive overview of EuroLLM-9B's development, including tokenizer design, architectural specifications, data filtering, and training procedures. We describe the pre-training data collection and filtering pipeline, including the creation of EuroFilter, an AI-based multilingual filter, as well as the design of EuroBlocks-Synthetic, a novel synthetic dataset for post-training that enhances language coverage for European languages. Evaluation results demonstrate EuroLLM-9B's competitive performance on multilingual benchmarks and machine translation tasks, establishing it as the leading open European-made LLM of its size. To support open research and adoption, we release all major components of this work, including the base and instruction-tuned models, the EuroFilter classifier, and the synthetic post-training dataset.
M-Prometheus: A Suite of Open Multilingual LLM Judges
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:The use of language models for automatically evaluating long-form text (LLM-as-a-judge) is becoming increasingly common, yet most LLM judges are optimized exclusively for English, with strategies for enhancing their multilingual evaluation capabilities remaining largely unexplored in the current literature. This has created a disparity in the quality of automatic evaluation methods for non-English languages, ultimately hindering the development of models with better multilingual capabilities. To bridge this gap, we introduce M-Prometheus, a suite of open-weight LLM judges ranging from 3B to 14B parameters that can provide both direct assessment and pairwise comparison feedback on multilingual outputs. M-Prometheus models outperform state-of-the-art open LLM judges on multilingual reward benchmarks spanning more than 20 languages, as well as on literary machine translation (MT) evaluation covering 4 language pairs. Furthermore, M-Prometheus models can be leveraged at decoding time to significantly improve generated outputs across all 3 tested languages, showcasing their utility for the development of better multilingual models. Lastly, through extensive ablations, we identify the key factors for obtaining an effective multilingual judge, including backbone model selection and training on natively multilingual feedback data instead of translated data. We release our models, training dataset, and code.
Zero-shot Benchmarking: A Framework for Flexible and Scalable Automatic Evaluation of Language Models
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:As language models improve and become capable of performing more complex tasks across modalities, evaluating them automatically becomes increasingly challenging. Developing strong and robust task-specific automatic metrics gets harder, and human-annotated test sets -- which are expensive to create -- saturate more quickly. A compelling alternative is to design reliable strategies to automate the creation of test data and evaluation, but previous attempts either rely on pre-existing data, or focus solely on individual tasks. We present Zero-shot Benchmarking (ZSB), a framework for creating high-quality benchmarks for any task by leveraging language models for both synthetic test data creation and evaluation. ZSB is simple and flexible: it requires only the creation of a prompt for data generation and one for evaluation; it is scalable to tasks and languages where collecting real-world data is costly or impractical; it is model-agnostic, allowing the creation of increasingly challenging benchmarks as models improve. To assess the effectiveness of our framework, we create benchmarks for five text-only tasks and a multi-modal one: general capabilities in four languages (English, Chinese, French, and Korean), translation, and general vision-language capabilities in English. We then rank a broad range of open and closed systems on our benchmarks. ZSB rankings consistently correlate strongly with human rankings, outperforming widely-adopted standard benchmarks. Through ablations, we find that strong benchmarks can be created with open models, and that judge model size and dataset variety are crucial drivers of performance. We release all our benchmarks, and code to reproduce our experiments and to produce new benchmarks.
XL-Instruct: Synthetic Data for Cross-Lingual Open-Ended Generation
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Cross-lingual open-ended generation -- i.e. generating responses in a desired language different from that of the user's query -- is an important yet understudied problem. We introduce XL-AlpacaEval, a new benchmark for evaluating cross-lingual generation capabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs), and propose XL-Instruct, a high-quality synthetic data generation method. Fine-tuning with just 8K XL-Instruct-generated instructions significantly improves model performance, increasing the win rate against GPT-4o-Mini from 7.4% to 21.5%, and improving on several fine-grained quality metrics. Additionally, models fine-tuned on XL-Instruct exhibit strong zero-shot transfer to both English-only and multilingual generation tasks. Given its consistent gains across the board, we strongly recommend incorporating XL-Instruct in the post-training pipeline of future multilingual LLMs. To facilitate further research, we will publicly and freely release the XL-Instruct and XL-AlpacaEval datasets, which constitute two of the few cross-lingual resources currently available in the literature.
Adding Chocolate to Mint: Mitigating Metric Interference in Machine Translation
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:As automatic metrics become increasingly stronger and widely adopted, the risk of unintentionally "gaming the metric" during model development rises. This issue is caused by metric interference (Mint), i.e., the use of the same or related metrics for both model tuning and evaluation. Mint can misguide practitioners into being overoptimistic about the performance of their systems: as system outputs become a function of the interfering metric, their estimated quality loses correlation with human judgments. In this work, we analyze two common cases of Mint in machine translation-related tasks: filtering of training data, and decoding with quality signals. Importantly, we find that Mint strongly distorts instance-level metric scores, even when metrics are not directly optimized for -- questioning the common strategy of leveraging a different, yet related metric for evaluation that is not used for tuning. To address this problem, we propose MintAdjust, a method for more reliable evaluation under Mint. On the WMT24 MT shared task test set, MintAdjust ranks translations and systems more accurately than state-of-the-art-metrics across a majority of language pairs, especially for high-quality systems. Furthermore, MintAdjust outperforms AutoRank, the ensembling method used by the organizers.
EuroBERT: Scaling Multilingual Encoders for European Languages
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:General-purpose multilingual vector representations, used in retrieval, regression and classification, are traditionally obtained from bidirectional encoder models. Despite their wide applicability, encoders have been recently overshadowed by advances in generative decoder-only models. However, many innovations driving this progress are not inherently tied to decoders. In this paper, we revisit the development of multilingual encoders through the lens of these advances, and introduce EuroBERT, a family of multilingual encoders covering European and widely spoken global languages. Our models outperform existing alternatives across a diverse range of tasks, spanning multilingual capabilities, mathematics, and coding, and natively supporting sequences of up to 8,192 tokens. We also examine the design decisions behind EuroBERT, offering insights into our dataset composition and training pipeline. We publicly release the EuroBERT models, including intermediate training checkpoints, together with our training framework.
Translate Smart, not Hard: Cascaded Translation Systems with Quality-Aware Deferral
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Larger models often outperform smaller ones but come with high computational costs. Cascading offers a potential solution. By default, it uses smaller models and defers only some instances to larger, more powerful models. However, designing effective deferral rules remains a challenge. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective approach for machine translation, using existing quality estimation (QE) metrics as deferral rules. We show that QE-based deferral allows a cascaded system to match the performance of a larger model while invoking it for a small fraction (30% to 50%) of the examples, significantly reducing computational costs. We validate this approach through both automatic and human evaluation.
WMT24++: Expanding the Language Coverage of WMT24 to 55 Languages & Dialects
Feb 18, 2025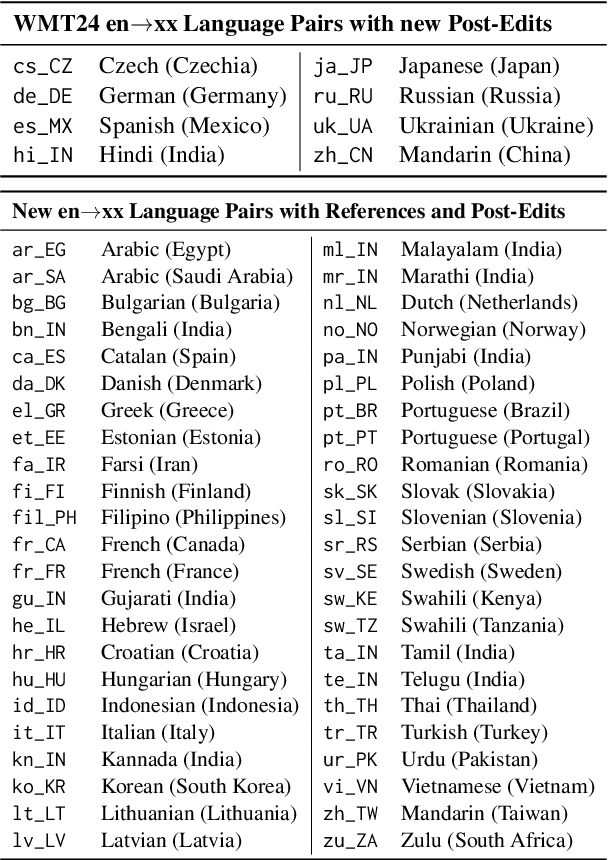
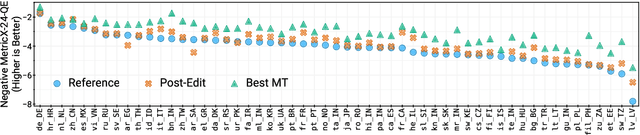

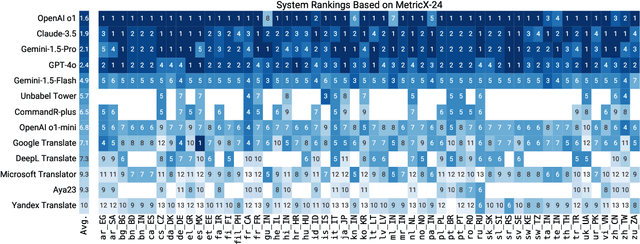
Abstract:As large language models (LLM) become more and more capable in languages other than English, it is important to collect benchmark datasets in order to evaluate their multilingual performance, including on tasks like machine translation (MT). In this work, we extend the WMT24 dataset to cover 55 languages by collecting new human-written references and post-edits for 46 new languages and dialects in addition to post-edits of the references in 8 out of 9 languages in the original WMT24 dataset. The dataset covers four domains: literary, news, social, and speech. We benchmark a variety of MT providers and LLMs on the collected dataset using automatic metrics and find that LLMs are the best-performing MT systems in all 55 languages. These results should be confirmed using a human-based evaluation, which we leave for future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge