António Farinhas
MindGuard: Guardrail Classifiers for Multi-Turn Mental Health Support
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Large language models are increasingly used for mental health support, yet their conversational coherence alone does not ensure clinical appropriateness. Existing general-purpose safeguards often fail to distinguish between therapeutic disclosures and genuine clinical crises, leading to safety failures. To address this gap, we introduce a clinically grounded risk taxonomy, developed in collaboration with PhD-level psychologists, that identifies actionable harm (e.g., self-harm and harm to others) while preserving space for safe, non-crisis therapeutic content. We release MindGuard-testset, a dataset of real-world multi-turn conversations annotated at the turn level by clinical experts. Using synthetic dialogues generated via a controlled two-agent setup, we train MindGuard, a family of lightweight safety classifiers (with 4B and 8B parameters). Our classifiers reduce false positives at high-recall operating points and, when paired with clinician language models, help achieve lower attack success and harmful engagement rates in adversarial multi-turn interactions compared to general-purpose safeguards. We release all models and human evaluation data.
Movie Facts and Fibs (MF$^2$): A Benchmark for Long Movie Understanding
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Despite recent progress in vision-language models (VLMs), holistic understanding of long-form video content remains a significant challenge, partly due to limitations in current benchmarks. Many focus on peripheral, ``needle-in-a-haystack'' details, encouraging context-insensitive retrieval over deep comprehension. Others rely on large-scale, semi-automatically generated questions (often produced by language models themselves) that are easier for models to answer but fail to reflect genuine understanding. In this paper, we introduce MF$^2$, a new benchmark for evaluating whether models can comprehend, consolidate, and recall key narrative information from full-length movies (50-170 minutes long). MF$^2$ includes over 50 full-length, open-licensed movies, each paired with manually constructed sets of claim pairs -- one true (fact) and one plausible but false (fib), totalling over 850 pairs. These claims target core narrative elements such as character motivations and emotions, causal chains, and event order, and refer to memorable moments that humans can recall without rewatching the movie. Instead of multiple-choice formats, we adopt a binary claim evaluation protocol: for each pair, models must correctly identify both the true and false claims. This reduces biases like answer ordering and enables a more precise assessment of reasoning. Our experiments demonstrate that both open-weight and closed state-of-the-art models fall well short of human performance, underscoring the relative ease of the task for humans and their superior ability to retain and reason over critical narrative information -- an ability current VLMs lack.
Translate Smart, not Hard: Cascaded Translation Systems with Quality-Aware Deferral
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Larger models often outperform smaller ones but come with high computational costs. Cascading offers a potential solution. By default, it uses smaller models and defers only some instances to larger, more powerful models. However, designing effective deferral rules remains a challenge. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective approach for machine translation, using existing quality estimation (QE) metrics as deferral rules. We show that QE-based deferral allows a cascaded system to match the performance of a larger model while invoking it for a small fraction (30% to 50%) of the examples, significantly reducing computational costs. We validate this approach through both automatic and human evaluation.
$\infty$-Video: A Training-Free Approach to Long Video Understanding via Continuous-Time Memory Consolidation
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:Current video-language models struggle with long-video understanding due to limited context lengths and reliance on sparse frame subsampling, often leading to information loss. This paper introduces $\infty$-Video, which can process arbitrarily long videos through a continuous-time long-term memory (LTM) consolidation mechanism. Our framework augments video Q-formers by allowing them to process unbounded video contexts efficiently and without requiring additional training. Through continuous attention, our approach dynamically allocates higher granularity to the most relevant video segments, forming "sticky" memories that evolve over time. Experiments with Video-LLaMA and VideoChat2 demonstrate improved performance in video question-answering tasks, showcasing the potential of continuous-time LTM mechanisms to enable scalable and training-free comprehension of long videos.
Modeling User Preferences with Automatic Metrics: Creating a High-Quality Preference Dataset for Machine Translation
Oct 10, 2024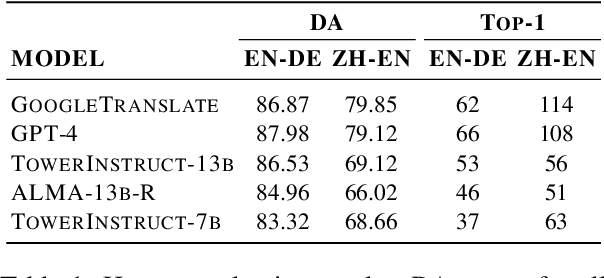

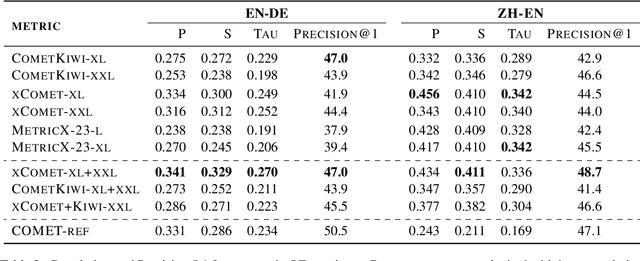
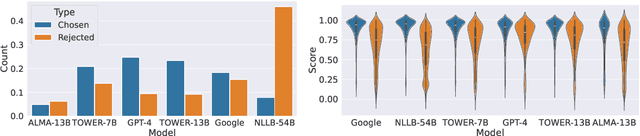
Abstract:Alignment with human preferences is an important step in developing accurate and safe large language models. This is no exception in machine translation (MT), where better handling of language nuances and context-specific variations leads to improved quality. However, preference data based on human feedback can be very expensive to obtain and curate at a large scale. Automatic metrics, on the other hand, can induce preferences, but they might not match human expectations perfectly. In this paper, we propose an approach that leverages the best of both worlds. We first collect sentence-level quality assessments from professional linguists on translations generated by multiple high-quality MT systems and evaluate the ability of current automatic metrics to recover these preferences. We then use this analysis to curate a new dataset, MT-Pref (metric induced translation preference) dataset, which comprises 18k instances covering 18 language directions, using texts sourced from multiple domains post-2022. We show that aligning TOWER models on MT-Pref significantly improves translation quality on WMT23 and FLORES benchmarks.
Reranking Laws for Language Generation: A Communication-Theoretic Perspective
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:To ensure large language models (LLMs) are used safely, one must reduce their propensity to hallucinate or to generate unacceptable answers. A simple and often used strategy is to first let the LLM generate multiple hypotheses and then employ a reranker to choose the best one. In this paper, we draw a parallel between this strategy and the use of redundancy to decrease the error rate in noisy communication channels. We conceptualize the generator as a sender transmitting multiple descriptions of a message through parallel noisy channels. The receiver decodes the message by ranking the (potentially corrupted) descriptions and selecting the one found to be most reliable. We provide conditions under which this protocol is asymptotically error-free (i.e., yields an acceptable answer almost surely) even in scenarios where the reranker is imperfect (governed by Mallows or Zipf-Mandelbrot models) and the channel distributions are statistically dependent. We use our framework to obtain reranking laws which we validate empirically on two real-world tasks using LLMs: text-to-code generation with DeepSeek-Coder 7B and machine translation of medical data with TowerInstruct 13B.
QUEST: Quality-Aware Metropolis-Hastings Sampling for Machine Translation
May 28, 2024Abstract:An important challenge in machine translation (MT) is to generate high-quality and diverse translations. Prior work has shown that the estimated likelihood from the MT model correlates poorly with translation quality. In contrast, quality evaluation metrics (such as COMET or BLEURT) exhibit high correlations with human judgments, which has motivated their use as rerankers (such as quality-aware and minimum Bayes risk decoding). However, relying on a single translation with high estimated quality increases the chances of "gaming the metric''. In this paper, we address the problem of sampling a set of high-quality and diverse translations. We provide a simple and effective way to avoid over-reliance on noisy quality estimates by using them as the energy function of a Gibbs distribution. Instead of looking for a mode in the distribution, we generate multiple samples from high-density areas through the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm, a simple Markov chain Monte Carlo approach. The results show that our proposed method leads to high-quality and diverse outputs across multiple language pairs (English$\leftrightarrow${German, Russian}) with two strong decoder-only LLMs (Alma-7b, Tower-7b).
Can Automatic Metrics Assess High-Quality Translations?
May 28, 2024Abstract:Automatic metrics for evaluating translation quality are typically validated by measuring how well they correlate with human assessments. However, correlation methods tend to capture only the ability of metrics to differentiate between good and bad source-translation pairs, overlooking their reliability in distinguishing alternative translations for the same source. In this paper, we confirm that this is indeed the case by showing that current metrics are insensitive to nuanced differences in translation quality. This effect is most pronounced when the quality is high and the variance among alternatives is low. Given this finding, we shift towards detecting high-quality correct translations, an important problem in practical decision-making scenarios where a binary check of correctness is prioritized over a nuanced evaluation of quality. Using the MQM framework as the gold standard, we systematically stress-test the ability of current metrics to identify translations with no errors as marked by humans. Our findings reveal that current metrics often over or underestimate translation quality, indicating significant room for improvement in automatic evaluation methods.
Conformal Prediction for Natural Language Processing: A Survey
May 03, 2024Abstract:The rapid proliferation of large language models and natural language processing (NLP) applications creates a crucial need for uncertainty quantification to mitigate risks such as hallucinations and to enhance decision-making reliability in critical applications. Conformal prediction is emerging as a theoretically sound and practically useful framework, combining flexibility with strong statistical guarantees. Its model-agnostic and distribution-free nature makes it particularly promising to address the current shortcomings of NLP systems that stem from the absence of uncertainty quantification. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of conformal prediction techniques, their guarantees, and existing applications in NLP, pointing to directions for future research and open challenges.
Aligning Neural Machine Translation Models: Human Feedback in Training and Inference
Nov 15, 2023



Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) is a recent technique to improve the quality of the text generated by a language model, making it closer to what humans would generate. A core ingredient in RLHF's success in aligning and improving large language models (LLMs) is its reward model, trained using human feedback on model outputs. In machine translation (MT), where metrics trained from human annotations can readily be used as reward models, recent methods using minimum Bayes risk decoding and reranking have succeeded in improving the final quality of translation. In this study, we comprehensively explore and compare techniques for integrating quality metrics as reward models into the MT pipeline. This includes using the reward model for data filtering, during the training phase through RL, and at inference time by employing reranking techniques, and we assess the effects of combining these in a unified approach. Our experimental results, conducted across multiple translation tasks, underscore the crucial role of effective data filtering, based on estimated quality, in harnessing the full potential of RL in enhancing MT quality. Furthermore, our findings demonstrate the effectiveness of combining RL training with reranking techniques, showcasing substantial improvements in translation quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge