Aditya K Surikuchi
Where is the multimodal goal post? On the Ability of Foundation Models to Recognize Contextually Important Moments
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Foundation models are used for many real-world applications involving language generation from temporally-ordered multimodal events. In this work, we study the ability of models to identify the most important sub-events in a video, which is a fundamental prerequisite for narrating or summarizing multimodal events. Specifically, we focus on football games and evaluate models on their ability to distinguish between important and non-important sub-events in a game. To this end, we construct a new dataset by leveraging human preferences for importance implicit in football game highlight reels, without any additional annotation costs. Using our dataset, which we will publicly release to the community, we compare several state-of-the-art multimodal models and show that they are not far from chance level performance. Analyses of models beyond standard evaluation metrics reveal their tendency to rely on a single dominant modality and their ineffectiveness in synthesizing necessary information from multiple sources. Our findings underline the importance of modular architectures that can handle sample-level heterogeneity in multimodal data and the need for complementary training procedures that can maximize cross-modal synergy.
Movie Facts and Fibs (MF$^2$): A Benchmark for Long Movie Understanding
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Despite recent progress in vision-language models (VLMs), holistic understanding of long-form video content remains a significant challenge, partly due to limitations in current benchmarks. Many focus on peripheral, ``needle-in-a-haystack'' details, encouraging context-insensitive retrieval over deep comprehension. Others rely on large-scale, semi-automatically generated questions (often produced by language models themselves) that are easier for models to answer but fail to reflect genuine understanding. In this paper, we introduce MF$^2$, a new benchmark for evaluating whether models can comprehend, consolidate, and recall key narrative information from full-length movies (50-170 minutes long). MF$^2$ includes over 50 full-length, open-licensed movies, each paired with manually constructed sets of claim pairs -- one true (fact) and one plausible but false (fib), totalling over 850 pairs. These claims target core narrative elements such as character motivations and emotions, causal chains, and event order, and refer to memorable moments that humans can recall without rewatching the movie. Instead of multiple-choice formats, we adopt a binary claim evaluation protocol: for each pair, models must correctly identify both the true and false claims. This reduces biases like answer ordering and enables a more precise assessment of reasoning. Our experiments demonstrate that both open-weight and closed state-of-the-art models fall well short of human performance, underscoring the relative ease of the task for humans and their superior ability to retain and reason over critical narrative information -- an ability current VLMs lack.
Natural Language Generation from Visual Sequences: Challenges and Future Directions
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:The ability to use natural language to talk about visual content is at the core of human intelligence and a crucial feature of any artificial intelligence system. Various studies have focused on generating text for single images. In contrast, comparatively little attention has been paid to exhaustively analyzing and advancing work on multiple-image vision-to-text settings. In this position paper, we claim that any task dealing with temporally ordered sequences of multiple images or frames is an instance of a broader, more general problem involving the understanding of intricate relationships between the visual content and the corresponding text. We comprehensively analyze five tasks that are instances of this problem and argue that they pose a common set of challenges and share similarities in terms of modeling and evaluation approaches. Based on the insights from these various aspects and stages of multi-image-to-text generation, we highlight several open questions and suggest future research directions. We believe that these directions can advance the understanding of complex phenomena in this domain and the development of better models.
Not (yet) the whole story: Evaluating Visual Storytelling Requires More than Measuring Coherence, Grounding, and Repetition
Jul 05, 2024Abstract:Visual storytelling consists in generating a natural language story given a temporally ordered sequence of images. This task is not only challenging for models, but also very difficult to evaluate with automatic metrics since there is no consensus about what makes a story 'good'. In this paper, we introduce a novel method that measures story quality in terms of human likeness regarding three key aspects highlighted in previous work: visual grounding, coherence, and repetitiveness. We then use this method to evaluate the stories generated by several models, showing that the foundation model LLaVA obtains the best result, but only slightly so compared to TAPM, a 50-times smaller visual storytelling model. Upgrading the visual and language components of TAPM results in a model that yields competitive performance with a relatively low number of parameters. Finally, we carry out a human evaluation study, whose results suggest that a 'good' story may require more than a human-like level of visual grounding, coherence, and repetition.
LLMs instead of Human Judges? A Large Scale Empirical Study across 20 NLP Evaluation Tasks
Jun 26, 2024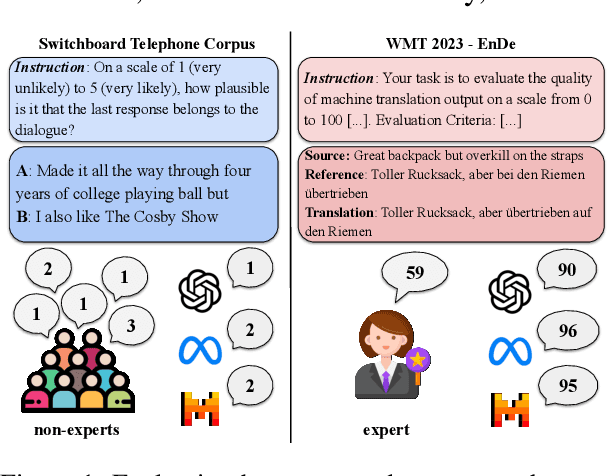
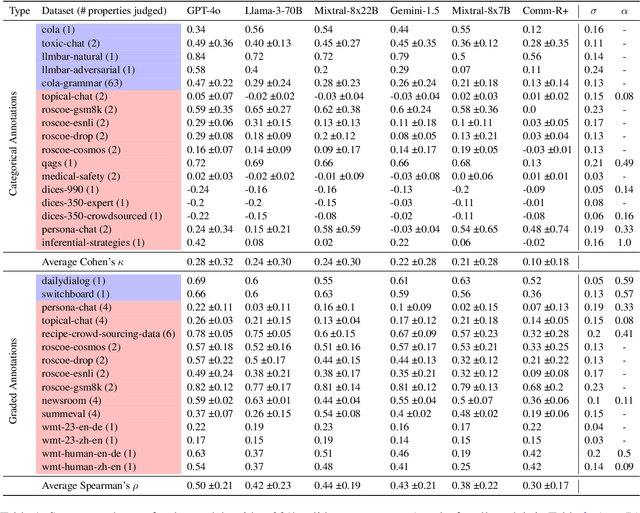
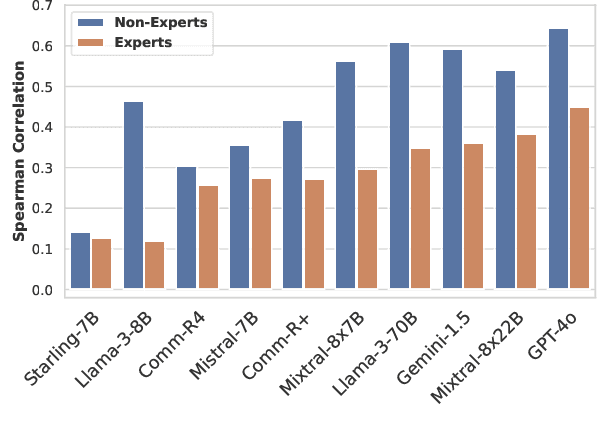
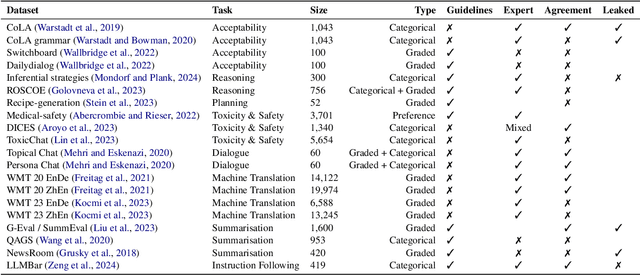
Abstract:There is an increasing trend towards evaluating NLP models with LLM-generated judgments instead of human judgments. In the absence of a comparison against human data, this raises concerns about the validity of these evaluations; in case they are conducted with proprietary models, this also raises concerns over reproducibility. We provide JUDGE-BENCH, a collection of 20 NLP datasets with human annotations, and comprehensively evaluate 11 current LLMs, covering both open-weight and proprietary models, for their ability to replicate the annotations. Our evaluations show that each LLM exhibits a large variance across datasets in its correlation to human judgments. We conclude that LLMs are not yet ready to systematically replace human judges in NLP.
GROOViST: A Metric for Grounding Objects in Visual Storytelling
Oct 26, 2023Abstract:A proper evaluation of stories generated for a sequence of images -- the task commonly referred to as visual storytelling -- must consider multiple aspects, such as coherence, grammatical correctness, and visual grounding. In this work, we focus on evaluating the degree of grounding, that is, the extent to which a story is about the entities shown in the images. We analyze current metrics, both designed for this purpose and for general vision-text alignment. Given their observed shortcomings, we propose a novel evaluation tool, GROOViST, that accounts for cross-modal dependencies, temporal misalignments (the fact that the order in which entities appear in the story and the image sequence may not match), and human intuitions on visual grounding. An additional advantage of GROOViST is its modular design, where the contribution of each component can be assessed and interpreted individually.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge