André F. T. Martins
Learning with the $p$-adics
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Existing machine learning frameworks operate over the field of real numbers ($\mathbb{R}$) and learn representations in real (Euclidean or Hilbert) vector spaces (e.g., $\mathbb{R}^d$). Their underlying geometric properties align well with intuitive concepts such as linear separability, minimum enclosing balls, and subspace projection; and basic calculus provides a toolbox for learning through gradient-based optimization. But is this the only possible choice? In this paper, we study the suitability of a radically different field as an alternative to $\mathbb{R}$ -- the ultrametric and non-archimedean space of $p$-adic numbers, $\mathbb{Q}_p$. The hierarchical structure of the $p$-adics and their interpretation as infinite strings make them an appealing tool for code theory and hierarchical representation learning. Our exploratory theoretical work establishes the building blocks for classification, regression, and representation learning with the $p$-adics, providing learning models and algorithms. We illustrate how simple Quillian semantic networks can be represented as a compact $p$-adic linear network, a construction which is not possible with the field of reals. We finish by discussing open problems and opportunities for future research enabled by this new framework.
Sample-efficient Integration of New Modalities into Large Language Models
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Multimodal foundation models can process several modalities. However, since the space of possible modalities is large and evolving over time, training a model from scratch to encompass all modalities is unfeasible. Moreover, integrating a modality into a pre-existing foundation model currently requires a significant amount of paired data, which is often not available for low-resource modalities. In this paper, we introduce a method for sample-efficient modality integration (SEMI) into Large Language Models (LLMs). To this end, we devise a hypernetwork that can adapt a shared projector -- placed between modality-specific encoders and an LLM -- to any modality. The hypernetwork, trained on high-resource modalities (i.e., text, speech, audio, video), is conditioned on a few samples from any arbitrary modality at inference time to generate a suitable adapter. To increase the diversity of training modalities, we artificially multiply the number of encoders through isometric transformations. We find that SEMI achieves a significant boost in sample efficiency during few-shot integration of new modalities (i.e., satellite images, astronomical images, inertial measurements, and molecules) with encoders of arbitrary embedding dimensionality. For instance, to reach the same accuracy as 32-shot SEMI, training the projector from scratch needs 64$\times$ more data. As a result, SEMI holds promise to extend the modality coverage of foundation models.
Should We Still Pretrain Encoders with Masked Language Modeling?
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:Learning high-quality text representations is fundamental to a wide range of NLP tasks. While encoder pretraining has traditionally relied on Masked Language Modeling (MLM), recent evidence suggests that decoder models pretrained with Causal Language Modeling (CLM) can be effectively repurposed as encoders, often surpassing traditional encoders on text representation benchmarks. However, it remains unclear whether these gains reflect an inherent advantage of the CLM objective or arise from confounding factors such as model and data scale. In this paper, we address this question through a series of large-scale, carefully controlled pretraining ablations, training a total of 30 models ranging from 210 million to 1 billion parameters, and conducting over 15,000 fine-tuning and evaluation runs. We find that while training with MLM generally yields better performance across text representation tasks, CLM-trained models are more data-efficient and demonstrate improved fine-tuning stability. Building on these findings, we experimentally show that a biphasic training strategy that sequentially applies CLM and then MLM, achieves optimal performance under a fixed computational training budget. Moreover, we demonstrate that this strategy becomes more appealing when initializing from readily available pretrained CLM models (from the existing LLM ecosystem), reducing the computational burden needed to train best-in-class encoder models. We release all project artifacts at https://hf.co/MLMvsCLM to foster further research.
An Interdisciplinary Approach to Human-Centered Machine Translation
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Machine Translation (MT) tools are widely used today, often in contexts where professional translators are not present. Despite progress in MT technology, a gap persists between system development and real-world usage, particularly for non-expert users who may struggle to assess translation reliability. This paper advocates for a human-centered approach to MT, emphasizing the alignment of system design with diverse communicative goals and contexts of use. We survey the literature in Translation Studies and Human-Computer Interaction to recontextualize MT evaluation and design to address the diverse real-world scenarios in which MT is used today.
Movie Facts and Fibs (MF$^2$): A Benchmark for Long Movie Understanding
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Despite recent progress in vision-language models (VLMs), holistic understanding of long-form video content remains a significant challenge, partly due to limitations in current benchmarks. Many focus on peripheral, ``needle-in-a-haystack'' details, encouraging context-insensitive retrieval over deep comprehension. Others rely on large-scale, semi-automatically generated questions (often produced by language models themselves) that are easier for models to answer but fail to reflect genuine understanding. In this paper, we introduce MF$^2$, a new benchmark for evaluating whether models can comprehend, consolidate, and recall key narrative information from full-length movies (50-170 minutes long). MF$^2$ includes over 50 full-length, open-licensed movies, each paired with manually constructed sets of claim pairs -- one true (fact) and one plausible but false (fib), totalling over 850 pairs. These claims target core narrative elements such as character motivations and emotions, causal chains, and event order, and refer to memorable moments that humans can recall without rewatching the movie. Instead of multiple-choice formats, we adopt a binary claim evaluation protocol: for each pair, models must correctly identify both the true and false claims. This reduces biases like answer ordering and enables a more precise assessment of reasoning. Our experiments demonstrate that both open-weight and closed state-of-the-art models fall well short of human performance, underscoring the relative ease of the task for humans and their superior ability to retain and reason over critical narrative information -- an ability current VLMs lack.
EuroLLM-9B: Technical Report
Jun 04, 2025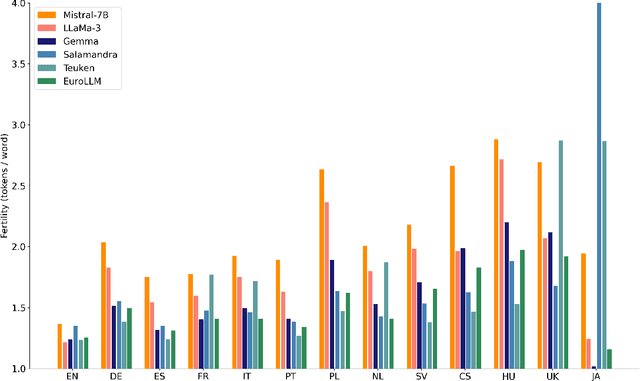
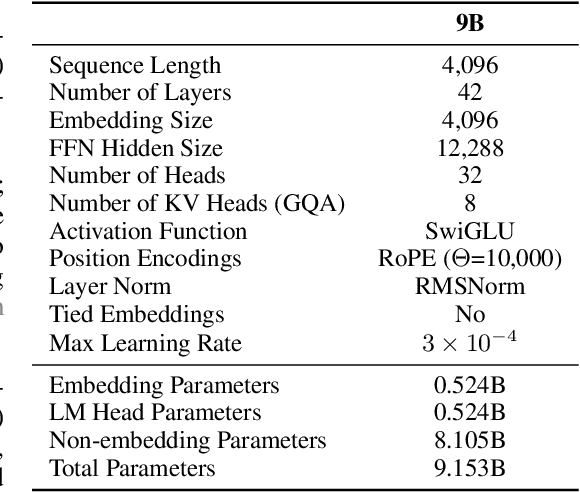
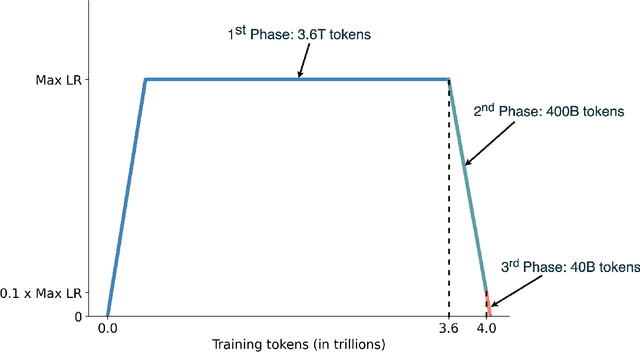
Abstract:This report presents EuroLLM-9B, a large language model trained from scratch to support the needs of European citizens by covering all 24 official European Union languages and 11 additional languages. EuroLLM addresses the issue of European languages being underrepresented and underserved in existing open large language models. We provide a comprehensive overview of EuroLLM-9B's development, including tokenizer design, architectural specifications, data filtering, and training procedures. We describe the pre-training data collection and filtering pipeline, including the creation of EuroFilter, an AI-based multilingual filter, as well as the design of EuroBlocks-Synthetic, a novel synthetic dataset for post-training that enhances language coverage for European languages. Evaluation results demonstrate EuroLLM-9B's competitive performance on multilingual benchmarks and machine translation tasks, establishing it as the leading open European-made LLM of its size. To support open research and adoption, we release all major components of this work, including the base and instruction-tuned models, the EuroFilter classifier, and the synthetic post-training dataset.
Multilingual Contextualization of Large Language Models for Document-Level Machine Translation
Apr 16, 2025

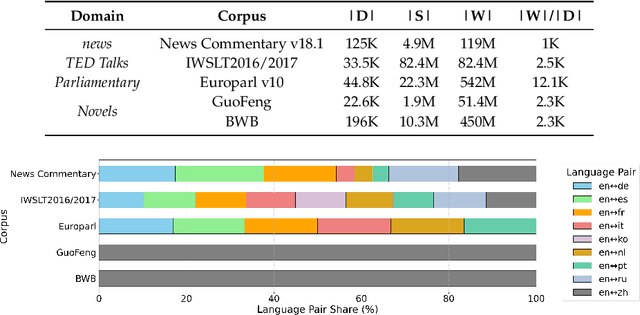
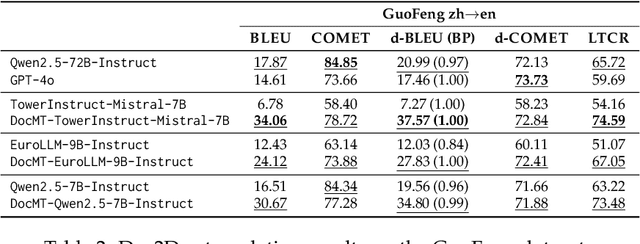
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong performance in sentence-level machine translation, but scaling to document-level translation remains challenging, particularly in modeling long-range dependencies and discourse phenomena across sentences and paragraphs. In this work, we propose a method to improve LLM-based long-document translation through targeted fine-tuning on high-quality document-level data, which we curate and introduce as DocBlocks. Our approach supports multiple translation paradigms, including direct document-to-document and chunk-level translation, by integrating instructions both with and without surrounding context. This enables models to better capture cross-sentence dependencies while maintaining strong sentence-level translation performance. Experimental results show that incorporating multiple translation paradigms improves document-level translation quality and inference speed compared to prompting and agent-based methods.
Do LLMs Understand Your Translations? Evaluating Paragraph-level MT with Question Answering
Apr 10, 2025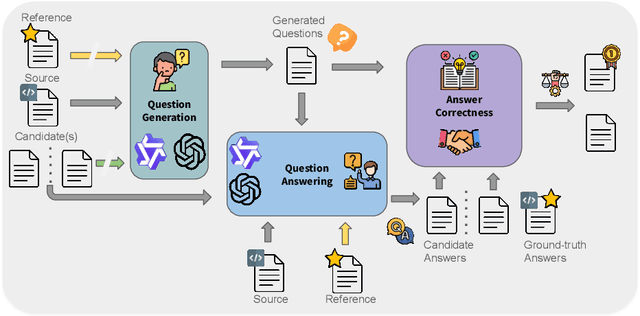
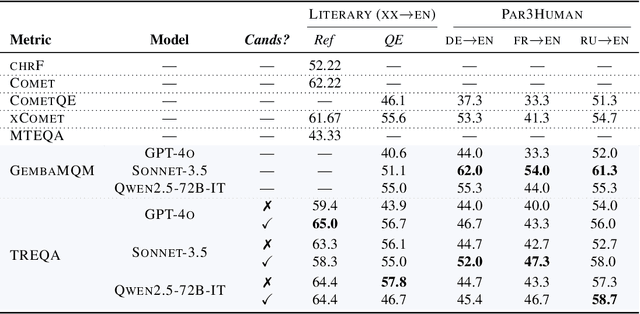

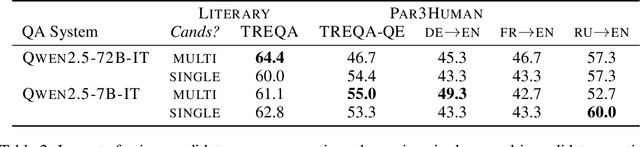
Abstract:Despite the steady progress in machine translation evaluation, existing automatic metrics struggle to capture how well meaning is preserved beyond sentence boundaries. We posit that reliance on a single intrinsic quality score, trained to mimic human judgments, might be insufficient for evaluating translations of long, complex passages, and a more ``pragmatic'' approach that assesses how accurately key information is conveyed by a translation in context is needed. We introduce TREQA (Translation Evaluation via Question-Answering), a framework that extrinsically evaluates translation quality by assessing how accurately candidate translations answer reading comprehension questions that target key information in the original source or reference texts. In challenging domains that require long-range understanding, such as literary texts, we show that TREQA is competitive with and, in some cases, outperforms state-of-the-art neural and LLM-based metrics in ranking alternative paragraph-level translations, despite never being explicitly optimized to correlate with human judgments. Furthermore, the generated questions and answers offer interpretability: empirical analysis shows that they effectively target translation errors identified by experts in evaluated datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/deep-spin/treqa
M-Prometheus: A Suite of Open Multilingual LLM Judges
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:The use of language models for automatically evaluating long-form text (LLM-as-a-judge) is becoming increasingly common, yet most LLM judges are optimized exclusively for English, with strategies for enhancing their multilingual evaluation capabilities remaining largely unexplored in the current literature. This has created a disparity in the quality of automatic evaluation methods for non-English languages, ultimately hindering the development of models with better multilingual capabilities. To bridge this gap, we introduce M-Prometheus, a suite of open-weight LLM judges ranging from 3B to 14B parameters that can provide both direct assessment and pairwise comparison feedback on multilingual outputs. M-Prometheus models outperform state-of-the-art open LLM judges on multilingual reward benchmarks spanning more than 20 languages, as well as on literary machine translation (MT) evaluation covering 4 language pairs. Furthermore, M-Prometheus models can be leveraged at decoding time to significantly improve generated outputs across all 3 tested languages, showcasing their utility for the development of better multilingual models. Lastly, through extensive ablations, we identify the key factors for obtaining an effective multilingual judge, including backbone model selection and training on natively multilingual feedback data instead of translated data. We release our models, training dataset, and code.
Zero-shot Benchmarking: A Framework for Flexible and Scalable Automatic Evaluation of Language Models
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:As language models improve and become capable of performing more complex tasks across modalities, evaluating them automatically becomes increasingly challenging. Developing strong and robust task-specific automatic metrics gets harder, and human-annotated test sets -- which are expensive to create -- saturate more quickly. A compelling alternative is to design reliable strategies to automate the creation of test data and evaluation, but previous attempts either rely on pre-existing data, or focus solely on individual tasks. We present Zero-shot Benchmarking (ZSB), a framework for creating high-quality benchmarks for any task by leveraging language models for both synthetic test data creation and evaluation. ZSB is simple and flexible: it requires only the creation of a prompt for data generation and one for evaluation; it is scalable to tasks and languages where collecting real-world data is costly or impractical; it is model-agnostic, allowing the creation of increasingly challenging benchmarks as models improve. To assess the effectiveness of our framework, we create benchmarks for five text-only tasks and a multi-modal one: general capabilities in four languages (English, Chinese, French, and Korean), translation, and general vision-language capabilities in English. We then rank a broad range of open and closed systems on our benchmarks. ZSB rankings consistently correlate strongly with human rankings, outperforming widely-adopted standard benchmarks. Through ablations, we find that strong benchmarks can be created with open models, and that judge model size and dataset variety are crucial drivers of performance. We release all our benchmarks, and code to reproduce our experiments and to produce new benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge