Monojit Choudhury
To Generate or Discriminate? Methodological Considerations for Measuring Cultural Alignment in LLMs
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Socio-demographic prompting (SDP) - prompting Large Language Models (LLMs) using demographic proxies to generate culturally aligned outputs - often shows LLM responses as stereotypical and biased. While effective in assessing LLMs' cultural competency, SDP is prone to confounding factors such as prompt sensitivity, decoding parameters, and the inherent difficulty of generation over discrimination tasks due to larger output spaces. These factors complicate interpretation, making it difficult to determine if the poor performance is due to bias or the task design. To address this, we use inverse socio-demographic prompting (ISDP), where we prompt LLMs to discriminate and predict the demographic proxy from actual and simulated user behavior from different users. We use the Goodreads-CSI dataset (Saha et al., 2025), which captures difficulty in understanding English book reviews for users from India, Mexico, and the USA, and test four LLMs: Aya-23, Gemma-2, GPT-4o, and LLaMA-3.1 with ISDP. Results show that models perform better with actual behaviors than simulated ones, contrary to what SDP suggests. However, performance with both behavior types diminishes and becomes nearly equal at the individual level, indicating limits to personalization.
Fusionista2.0: Efficiency Retrieval System for Large-Scale Datasets
Nov 15, 2025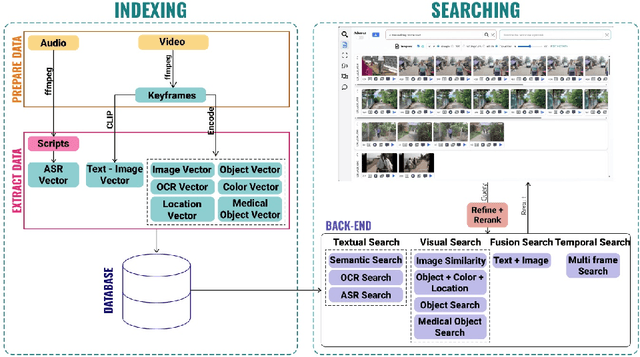

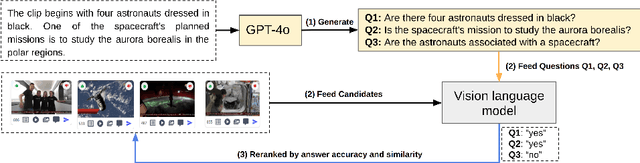
Abstract:The Video Browser Showdown (VBS) challenges systems to deliver accurate results under strict time constraints. To meet this demand, we present Fusionista2.0, a streamlined video retrieval system optimized for speed and usability. All core modules were re-engineered for efficiency: preprocessing now relies on ffmpeg for fast keyframe extraction, optical character recognition uses Vintern-1B-v3.5 for robust multilingual text recognition, and automatic speech recognition employs faster-whisper for real-time transcription. For question answering, lightweight vision-language models provide quick responses without the heavy cost of large models. Beyond these technical upgrades, Fusionista2.0 introduces a redesigned user interface with improved responsiveness, accessibility, and workflow efficiency, enabling even non-expert users to retrieve relevant content rapidly. Evaluations demonstrate that retrieval time was reduced by up to 75% while accuracy and user satisfaction both increased, confirming Fusionista2.0 as a competitive and user-friendly system for large-scale video search.
Who Gets Heard? Rethinking Fairness in AI for Music Systems
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:In recent years, the music research community has examined risks of AI models for music, with generative AI models in particular, raised concerns about copyright, deepfakes, and transparency. In our work, we raise concerns about cultural and genre biases in AI for music systems (music-AI systems) which affect stakeholders including creators, distributors, and listeners shaping representation in AI for music. These biases can misrepresent marginalized traditions, especially from the Global South, producing inauthentic outputs (e.g., distorted ragas) that reduces creators' trust on these systems. Such harms risk reinforcing biases, limiting creativity, and contributing to cultural erasure. To address this, we offer recommendations at dataset, model and interface level in music-AI systems.
An Interdisciplinary Approach to Human-Centered Machine Translation
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Machine Translation (MT) tools are widely used today, often in contexts where professional translators are not present. Despite progress in MT technology, a gap persists between system development and real-world usage, particularly for non-expert users who may struggle to assess translation reliability. This paper advocates for a human-centered approach to MT, emphasizing the alignment of system design with diverse communicative goals and contexts of use. We survey the literature in Translation Studies and Human-Computer Interaction to recontextualize MT evaluation and design to address the diverse real-world scenarios in which MT is used today.
Llama-3-Nanda-10B-Chat: An Open Generative Large Language Model for Hindi
Apr 08, 2025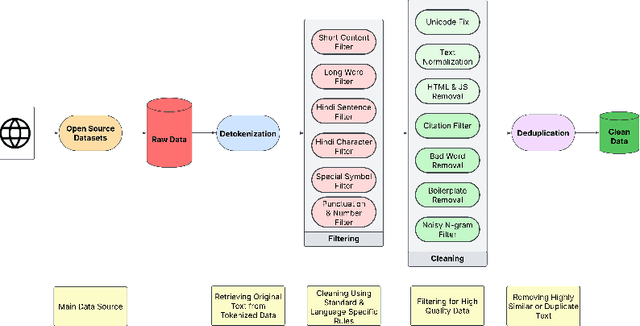
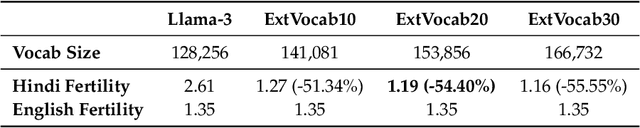
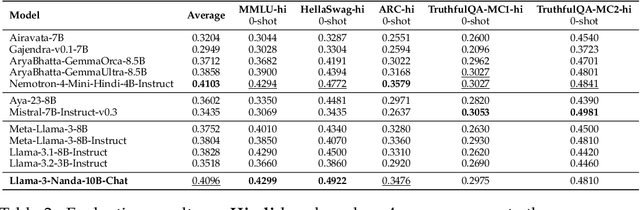

Abstract:Developing high-quality large language models (LLMs) for moderately resourced languages presents unique challenges in data availability, model adaptation, and evaluation. We introduce Llama-3-Nanda-10B-Chat, or Nanda for short, a state-of-the-art Hindi-centric instruction-tuned generative LLM, designed to push the boundaries of open-source Hindi language models. Built upon Llama-3-8B, Nanda incorporates continuous pre-training with expanded transformer blocks, leveraging the Llama Pro methodology. A key challenge was the limited availability of high-quality Hindi text data; we addressed this through rigorous data curation, augmentation, and strategic bilingual training, balancing Hindi and English corpora to optimize cross-linguistic knowledge transfer. With 10 billion parameters, Nanda stands among the top-performing open-source Hindi and multilingual models of similar scale, demonstrating significant advantages over many existing models. We provide an in-depth discussion of training strategies, fine-tuning techniques, safety alignment, and evaluation metrics, demonstrating how these approaches enabled Nanda to achieve state-of-the-art results. By open-sourcing Nanda, we aim to advance research in Hindi LLMs and support a wide range of real-world applications across academia, industry, and public services.
Llama-3.1-Sherkala-8B-Chat: An Open Large Language Model for Kazakh
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Llama-3.1-Sherkala-8B-Chat, or Sherkala-Chat (8B) for short, is a state-of-the-art instruction-tuned open generative large language model (LLM) designed for Kazakh. Sherkala-Chat (8B) aims to enhance the inclusivity of LLM advancements for Kazakh speakers. Adapted from the LLaMA-3.1-8B model, Sherkala-Chat (8B) is trained on 45.3B tokens across Kazakh, English, Russian, and Turkish. With 8 billion parameters, it demonstrates strong knowledge and reasoning abilities in Kazakh, significantly outperforming existing open Kazakh and multilingual models of similar scale while achieving competitive performance in English. We release Sherkala-Chat (8B) as an open-weight instruction-tuned model and provide a detailed overview of its training, fine-tuning, safety alignment, and evaluation, aiming to advance research and support diverse real-world applications.
Lost in Transcription, Found in Distribution Shift: Demystifying Hallucination in Speech Foundation Models
Feb 18, 2025
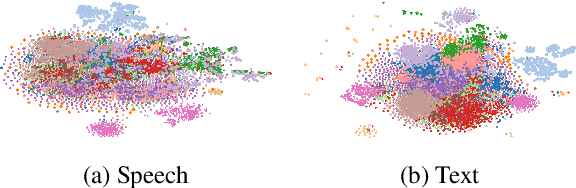
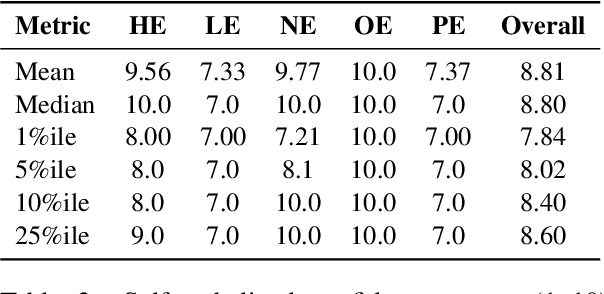
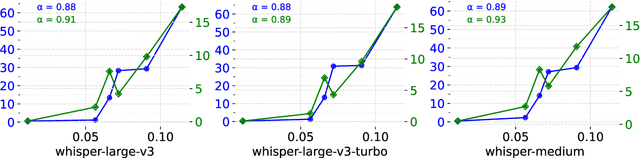
Abstract:Speech foundation models trained at a massive scale, both in terms of model and data size, result in robust systems capable of performing multiple speech tasks, including automatic speech recognition (ASR). These models transcend language and domain barriers, yet effectively measuring their performance remains a challenge. Traditional metrics like word error rate (WER) and character error rate (CER) are commonly used to evaluate ASR performance but often fail to reflect transcription quality in critical contexts, particularly when detecting fabricated outputs. This phenomenon, known as hallucination, is especially concerning in high-stakes domains such as healthcare, legal, and aviation, where errors can have severe consequences. In our work, we address this gap by investigating hallucination in ASR models. We examine how factors such as distribution shifts, model size, and model architecture influence the hallucination error rate (HER), a metric we introduce to quantify hallucinations. Our analysis of 20 ASR models reveals \numinsights~key insights: (1) High WERs can mask low hallucination rates, while low WERs may conceal dangerous hallucinations. (2) Synthetic noise, both adversarial and common perturbations like white noise, pitch shift, and time stretching, increase HER. (3) Distribution shift correlates strongly with HER ($\alpha = 0.91$). Our findings highlight the importance of incorporating HER alongside traditional metrics like WER to better assess ASR model performance, particularly in high-stakes domains.
Music for All: Exploring Multicultural Representations in Music Generation Models
Feb 12, 2025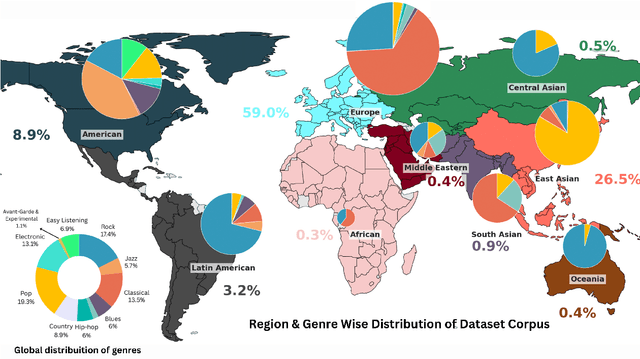
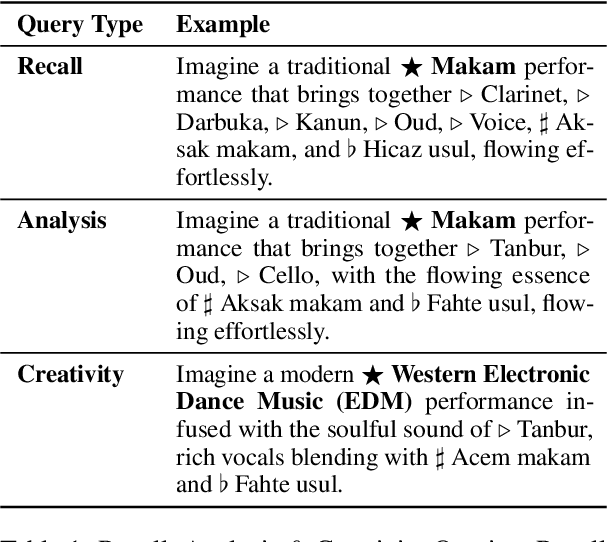
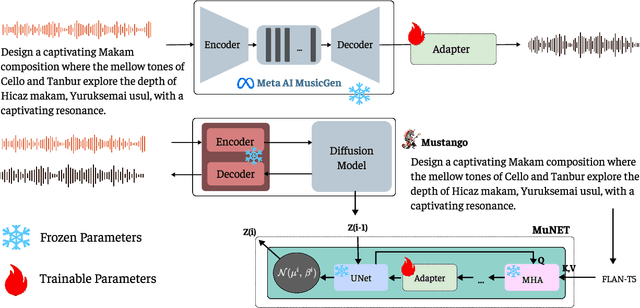
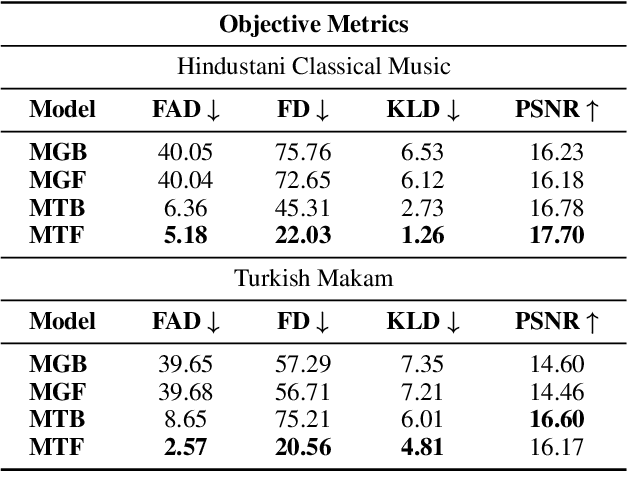
Abstract:The advent of Music-Language Models has greatly enhanced the automatic music generation capability of AI systems, but they are also limited in their coverage of the musical genres and cultures of the world. We present a study of the datasets and research papers for music generation and quantify the bias and under-representation of genres. We find that only 5.7% of the total hours of existing music datasets come from non-Western genres, which naturally leads to disparate performance of the models across genres. We then investigate the efficacy of Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) techniques in mitigating this bias. Our experiments with two popular models -- MusicGen and Mustango, for two underrepresented non-Western music traditions -- Hindustani Classical and Turkish Makam music, highlight the promises as well as the non-triviality of cross-genre adaptation of music through small datasets, implying the need for more equitable baseline music-language models that are designed for cross-cultural transfer learning.
SMAB: MAB based word Sensitivity Estimation Framework and its Applications in Adversarial Text Generation
Feb 10, 2025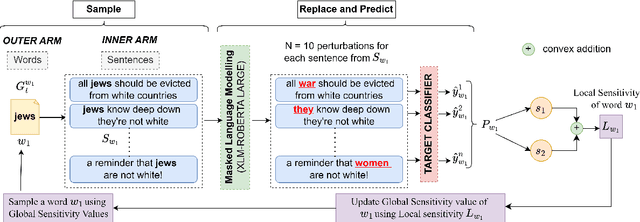

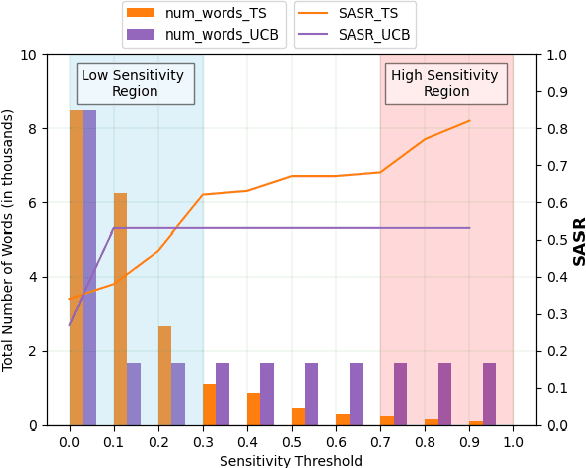

Abstract:To understand the complexity of sequence classification tasks, Hahn et al. (2021) proposed sensitivity as the number of disjoint subsets of the input sequence that can each be individually changed to change the output. Though effective, calculating sensitivity at scale using this framework is costly because of exponential time complexity. Therefore, we introduce a Sensitivity-based Multi-Armed Bandit framework (SMAB), which provides a scalable approach for calculating word-level local (sentence-level) and global (aggregated) sensitivities concerning an underlying text classifier for any dataset. We establish the effectiveness of our approach through various applications. We perform a case study on CHECKLIST generated sentiment analysis dataset where we show that our algorithm indeed captures intuitively high and low-sensitive words. Through experiments on multiple tasks and languages, we show that sensitivity can serve as a proxy for accuracy in the absence of gold data. Lastly, we show that guiding perturbation prompts using sensitivity values in adversarial example generation improves attack success rate by 15.58%, whereas using sensitivity as an additional reward in adversarial paraphrase generation gives a 12.00% improvement over SOTA approaches. Warning: Contains potentially offensive content.
Women, Infamous, and Exotic Beings: What Honorific Usages in Wikipedia Reveal about the Socio-Cultural Norms
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:Honorifics serve as powerful linguistic markers that reflect social hierarchies and cultural values. This paper presents a large-scale, cross-linguistic exploration of usage of honorific pronouns in Bengali and Hindi Wikipedia articles, shedding light on how socio-cultural factors shape language. Using LLM (GPT-4o), we annotated 10, 000 articles of real and fictional beings in each language for several sociodemographic features such as gender, age, fame, and exoticness, and the use of honorifics. We find that across all feature combinations, use of honorifics is consistently more common in Bengali than Hindi. For both languages, the use non-honorific pronouns is more commonly observed for infamous, juvenile, and exotic beings. Notably, we observe a gender bias in use of honorifics in Hindi, with men being more commonly referred to with honorifics than women.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge