Atharva Mehta
Who Gets Heard? Rethinking Fairness in AI for Music Systems
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:In recent years, the music research community has examined risks of AI models for music, with generative AI models in particular, raised concerns about copyright, deepfakes, and transparency. In our work, we raise concerns about cultural and genre biases in AI for music systems (music-AI systems) which affect stakeholders including creators, distributors, and listeners shaping representation in AI for music. These biases can misrepresent marginalized traditions, especially from the Global South, producing inauthentic outputs (e.g., distorted ragas) that reduces creators' trust on these systems. Such harms risk reinforcing biases, limiting creativity, and contributing to cultural erasure. To address this, we offer recommendations at dataset, model and interface level in music-AI systems.
Music for All: Exploring Multicultural Representations in Music Generation Models
Feb 12, 2025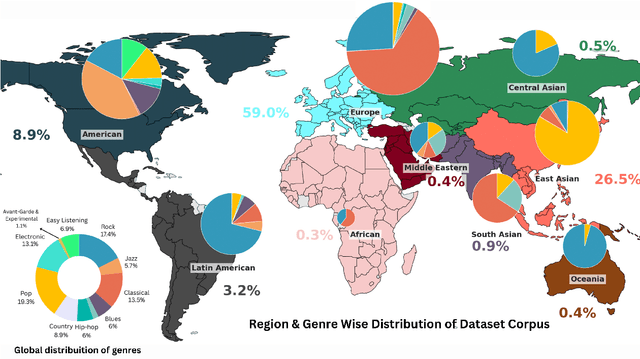
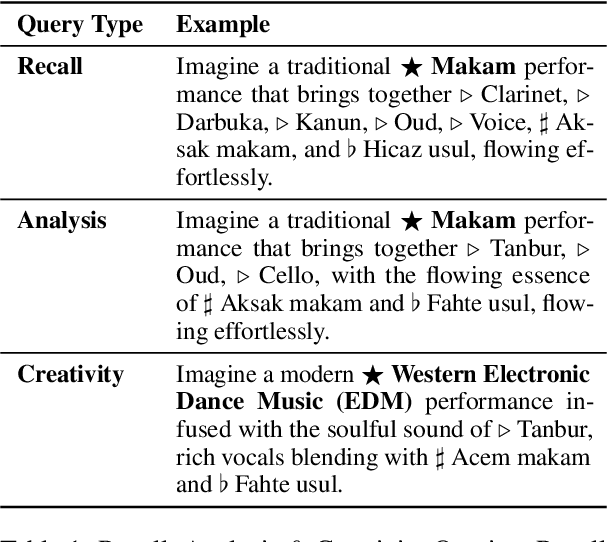
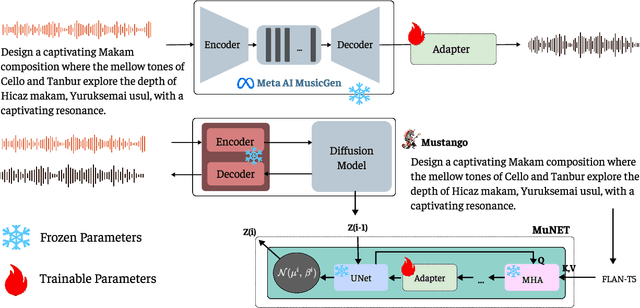
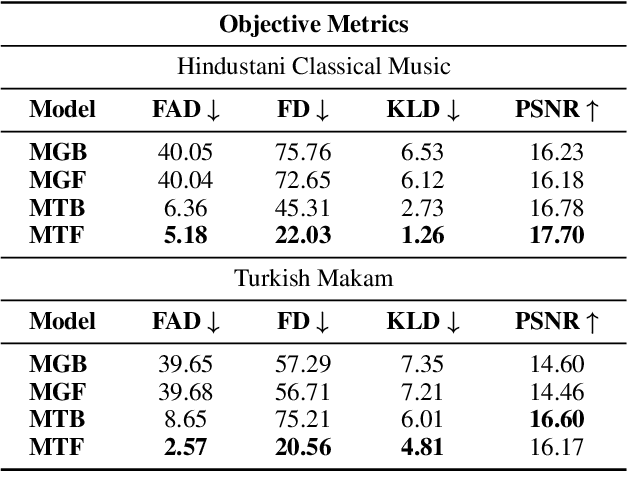
Abstract:The advent of Music-Language Models has greatly enhanced the automatic music generation capability of AI systems, but they are also limited in their coverage of the musical genres and cultures of the world. We present a study of the datasets and research papers for music generation and quantify the bias and under-representation of genres. We find that only 5.7% of the total hours of existing music datasets come from non-Western genres, which naturally leads to disparate performance of the models across genres. We then investigate the efficacy of Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) techniques in mitigating this bias. Our experiments with two popular models -- MusicGen and Mustango, for two underrepresented non-Western music traditions -- Hindustani Classical and Turkish Makam music, highlight the promises as well as the non-triviality of cross-genre adaptation of music through small datasets, implying the need for more equitable baseline music-language models that are designed for cross-cultural transfer learning.
Missing Melodies: AI Music Generation and its "Nearly" Complete Omission of the Global South
Dec 05, 2024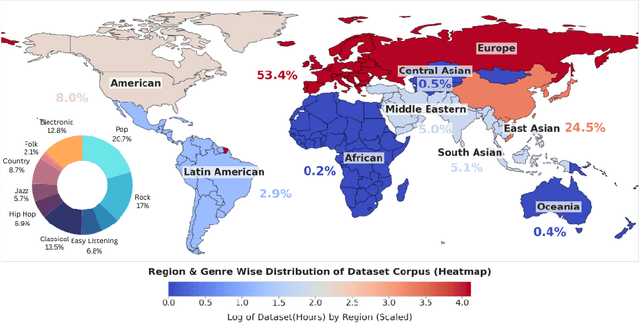
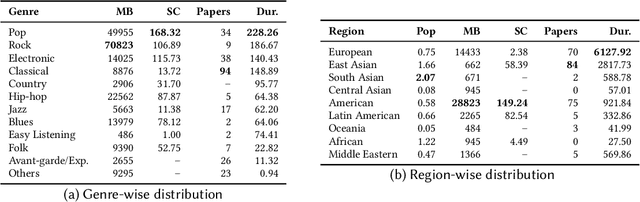
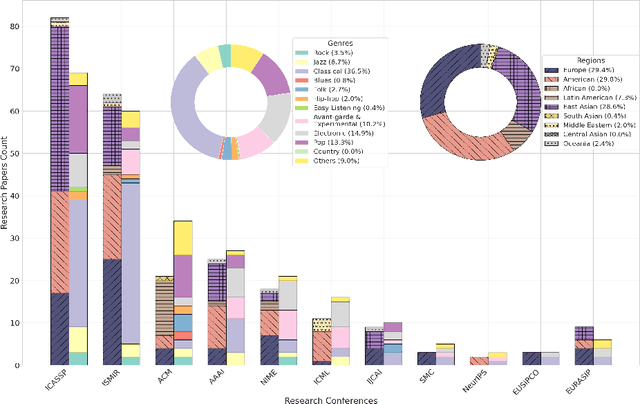

Abstract:Recent advances in generative AI have sparked renewed interest and expanded possibilities for music generation. However, the performance and versatility of these systems across musical genres are heavily influenced by the availability of training data. We conducted an extensive analysis of over one million hours of audio datasets used in AI music generation research and manually reviewed more than 200 papers from eleven prominent AI and music conferences and organizations (AAAI, ACM, EUSIPCO, EURASIP, ICASSP, ICML, IJCAI, ISMIR, NeurIPS, NIME, SMC) to identify a critical gap in the fair representation and inclusion of the musical genres of the Global South in AI research. Our findings reveal a stark imbalance: approximately 86% of the total dataset hours and over 93% of researchers focus primarily on music from the Global North. However, around 40% of these datasets include some form of non-Western music, genres from the Global South account for only 14.6% of the data. Furthermore, approximately 51% of the papers surveyed concentrate on symbolic music generation, a method that often fails to capture the cultural nuances inherent in music from regions such as South Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. As AI increasingly shapes the creation and dissemination of music, the significant underrepresentation of music genres in datasets and research presents a serious threat to global musical diversity. We also propose some important steps to mitigate these risks and foster a more inclusive future for AI-driven music generation.
Keystroke Dynamics Against Academic Dishonesty in the Age of LLMs
Jun 21, 2024



Abstract:The transition to online examinations and assignments raises significant concerns about academic integrity. Traditional plagiarism detection systems often struggle to identify instances of intelligent cheating, particularly when students utilize advanced generative AI tools to craft their responses. This study proposes a keystroke dynamics-based method to differentiate between bona fide and assisted writing within academic contexts. To facilitate this, a dataset was developed to capture the keystroke patterns of individuals engaged in writing tasks, both with and without the assistance of generative AI. The detector, trained using a modified TypeNet architecture, achieved accuracies ranging from 74.98% to 85.72% in condition-specific scenarios and from 52.24% to 80.54% in condition-agnostic scenarios. The findings highlight significant differences in keystroke dynamics between genuine and assisted writing. The outcomes of this study enhance our understanding of how users interact with generative AI and have implications for improving the reliability of digital educational platforms.
Can ChatGPT Play the Role of a Teaching Assistant in an Introductory Programming Course?
Dec 12, 2023Abstract:The emergence of Large language models (LLMs) is expected to have a major impact on education. This paper explores the potential of using ChatGPT, an LLM, as a virtual Teaching Assistant (TA) in an Introductory Programming Course. We evaluate ChatGPT's capabilities by comparing its performance with that of human TAs in some TA functions. The TA functions which we focus on include (1) solving programming assignments, (2) grading student code submissions, and (3) providing feedback to undergraduate students in an introductory programming course. Firstly, we investigate how closely ChatGPT's solutions align with those submitted by students. This analysis goes beyond code correctness and also considers code quality. Secondly, we assess ChatGPT's proficiency in grading student code submissions using a given grading rubric and compare its performance with the grades assigned by human TAs. Thirdly, we analyze the quality and relevance of the feedback provided by ChatGPT. This evaluation considers how well ChatGPT addresses mistakes and offers suggestions for improvement in student solutions from both code correctness and code quality perspectives. We conclude with a discussion on the implications of integrating ChatGPT into computing education for automated grading, personalized learning experiences, and instructional support.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge