Frédéric Blain
An Interdisciplinary Approach to Human-Centered Machine Translation
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Machine Translation (MT) tools are widely used today, often in contexts where professional translators are not present. Despite progress in MT technology, a gap persists between system development and real-world usage, particularly for non-expert users who may struggle to assess translation reliability. This paper advocates for a human-centered approach to MT, emphasizing the alignment of system design with diverse communicative goals and contexts of use. We survey the literature in Translation Studies and Human-Computer Interaction to recontextualize MT evaluation and design to address the diverse real-world scenarios in which MT is used today.
Are We Paying Attention to Her? Investigating Gender Disambiguation and Attention in Machine Translation
May 13, 2025Abstract:While gender bias in modern Neural Machine Translation (NMT) systems has received much attention, traditional evaluation metrics do not to fully capture the extent to which these systems integrate contextual gender cues. We propose a novel evaluation metric called Minimal Pair Accuracy (MPA), which measures the reliance of models on gender cues for gender disambiguation. MPA is designed to go beyond surface-level gender accuracy metrics by focusing on whether models adapt to gender cues in minimal pairs -- sentence pairs that differ solely in the gendered pronoun, namely the explicit indicator of the target's entity gender in the source language (EN). We evaluate a number of NMT models on the English-Italian (EN--IT) language pair using this metric, we show that they ignore available gender cues in most cases in favor of (statistical) stereotypical gender interpretation. We further show that in anti-stereotypical cases, these models tend to more consistently take masculine gender cues into account while ignoring the feminine cues. Furthermore, we analyze the attention head weights in the encoder component and show that while all models encode gender information to some extent, masculine cues elicit a more diffused response compared to the more concentrated and specialized responses to feminine gender cues.
What do Large Language Models Need for Machine Translation Evaluation?
Oct 04, 2024
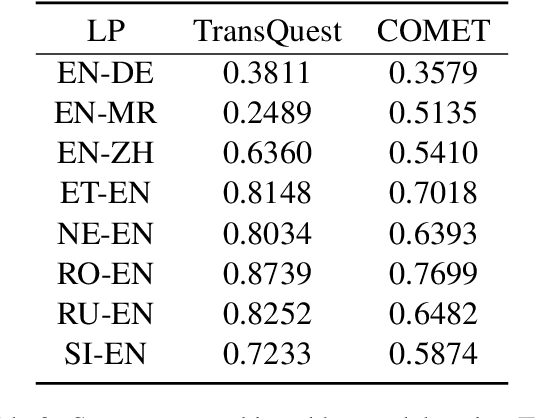
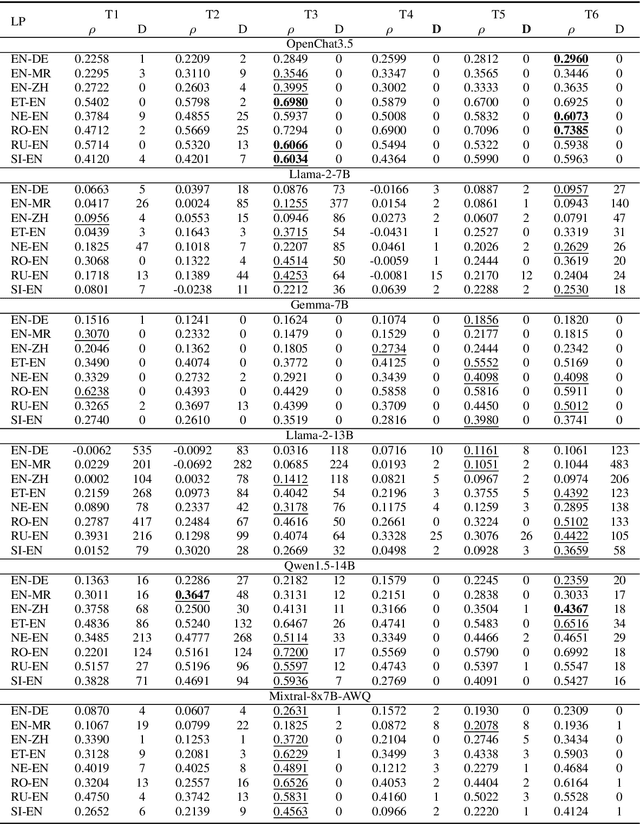
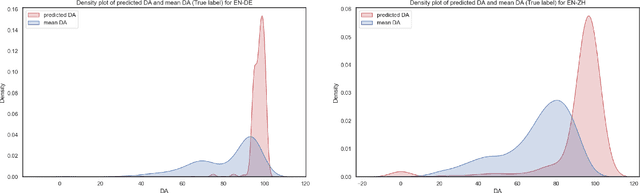
Abstract:Leveraging large language models (LLMs) for various natural language processing tasks has led to superlative claims about their performance. For the evaluation of machine translation (MT), existing research shows that LLMs are able to achieve results comparable to fine-tuned multilingual pre-trained language models. In this paper, we explore what translation information, such as the source, reference, translation errors and annotation guidelines, is needed for LLMs to evaluate MT quality. In addition, we investigate prompting techniques such as zero-shot, Chain of Thought (CoT) and few-shot prompting for eight language pairs covering high-, medium- and low-resource languages, leveraging varying LLM variants. Our findings indicate the importance of reference translations for an LLM-based evaluation. While larger models do not necessarily fare better, they tend to benefit more from CoT prompting, than smaller models. We also observe that LLMs do not always provide a numerical score when generating evaluations, which poses a question on their reliability for the task. Our work presents a comprehensive analysis for resource-constrained and training-less LLM-based evaluation of machine translation. We release the accrued prompt templates, code and data publicly for reproducibility.
DORE: A Dataset For Portuguese Definition Generation
Mar 28, 2024



Abstract:Definition modelling (DM) is the task of automatically generating a dictionary definition for a specific word. Computational systems that are capable of DM can have numerous applications benefiting a wide range of audiences. As DM is considered a supervised natural language generation problem, these systems require large annotated datasets to train the machine learning (ML) models. Several DM datasets have been released for English and other high-resource languages. While Portuguese is considered a mid/high-resource language in most natural language processing tasks and is spoken by more than 200 million native speakers, there is no DM dataset available for Portuguese. In this research, we fill this gap by introducing DORE; the first dataset for Definition MOdelling for PoRtuguEse containing more than 100,000 definitions. We also evaluate several deep learning based DM models on DORE and report the results. The dataset and the findings of this paper will facilitate research and study of Portuguese in wider contexts.
Tailoring Domain Adaptation for Machine Translation Quality Estimation
Apr 18, 2023Abstract:While quality estimation (QE) can play an important role in the translation process, its effectiveness relies on the availability and quality of training data. For QE in particular, high-quality labeled data is often lacking due to the high-cost and effort associated with labeling such data. Aside from the data scarcity challenge, QE models should also be generalizable, i.e., they should be able to handle data from different domains, both generic and specific. To alleviate these two main issues -- data scarcity and domain mismatch -- this paper combines domain adaptation and data augmentation within a robust QE system. Our method is to first train a generic QE model and then fine-tune it on a specific domain while retaining generic knowledge. Our results show a significant improvement for all the language pairs investigated, better cross-lingual inference, and a superior performance in zero-shot learning scenarios as compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
Pushing the Right Buttons: Adversarial Evaluation of Quality Estimation
Sep 22, 2021
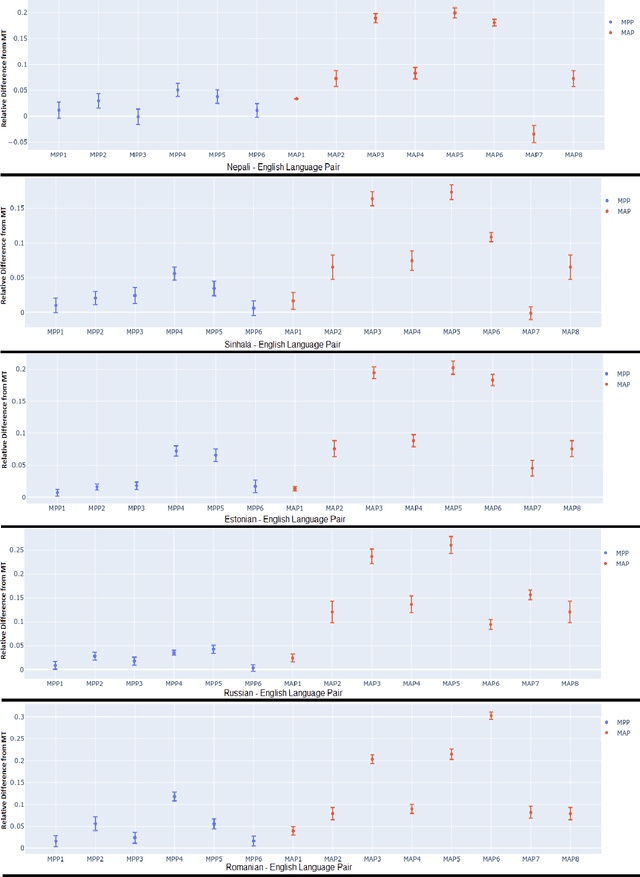

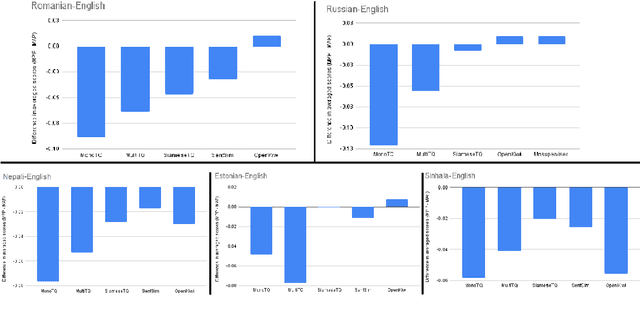
Abstract:Current Machine Translation (MT) systems achieve very good results on a growing variety of language pairs and datasets. However, they are known to produce fluent translation outputs that can contain important meaning errors, thus undermining their reliability in practice. Quality Estimation (QE) is the task of automatically assessing the performance of MT systems at test time. Thus, in order to be useful, QE systems should be able to detect such errors. However, this ability is yet to be tested in the current evaluation practices, where QE systems are assessed only in terms of their correlation with human judgements. In this work, we bridge this gap by proposing a general methodology for adversarial testing of QE for MT. First, we show that despite a high correlation with human judgements achieved by the recent SOTA, certain types of meaning errors are still problematic for QE to detect. Second, we show that on average, the ability of a given model to discriminate between meaning-preserving and meaning-altering perturbations is predictive of its overall performance, thus potentially allowing for comparing QE systems without relying on manual quality annotation.
Knowledge Distillation for Quality Estimation
Jul 01, 2021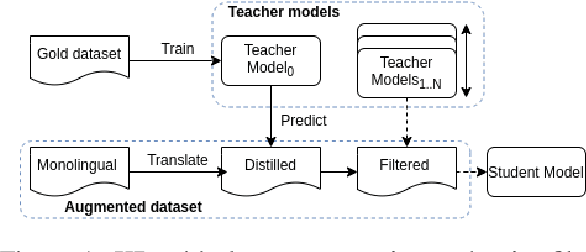
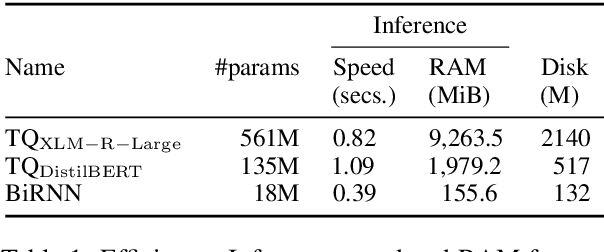
Abstract:Quality Estimation (QE) is the task of automatically predicting Machine Translation quality in the absence of reference translations, making it applicable in real-time settings, such as translating online social media conversations. Recent success in QE stems from the use of multilingual pre-trained representations, where very large models lead to impressive results. However, the inference time, disk and memory requirements of such models do not allow for wide usage in the real world. Models trained on distilled pre-trained representations remain prohibitively large for many usage scenarios. We instead propose to directly transfer knowledge from a strong QE teacher model to a much smaller model with a different, shallower architecture. We show that this approach, in combination with data augmentation, leads to light-weight QE models that perform competitively with distilled pre-trained representations with 8x fewer parameters.
Backtranslation Feedback Improves User Confidence in MT, Not Quality
Apr 12, 2021



Abstract:Translating text into a language unknown to the text's author, dubbed outbound translation, is a modern need for which the user experience has significant room for improvement, beyond the basic machine translation facility. We demonstrate this by showing three ways in which user confidence in the outbound translation, as well as its overall final quality, can be affected: backward translation, quality estimation (with alignment) and source paraphrasing. In this paper, we describe an experiment on outbound translation from English to Czech and Estonian. We examine the effects of each proposed feedback module and further focus on how the quality of machine translation systems influence these findings and the user perception of success. We show that backward translation feedback has a mixed effect on the whole process: it increases user confidence in the produced translation, but not the objective quality.
MLQE-PE: A Multilingual Quality Estimation and Post-Editing Dataset
Oct 09, 2020



Abstract:We present MLQE-PE, a new dataset for Machine Translation (MT) Quality Estimation (QE) and Automatic Post-Editing (APE). The dataset contains seven language pairs, with human labels for 9,000 translations per language pair in the following formats: sentence-level direct assessments and post-editing effort, and word-level good/bad labels. It also contains the post-edited sentences, as well as titles of the articles where the sentences were extracted from, and the neural MT models used to translate the text.
Unsupervised Quality Estimation for Neural Machine Translation
May 21, 2020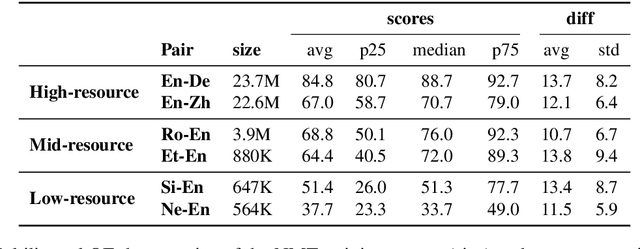



Abstract:Quality Estimation (QE) is an important component in making Machine Translation (MT) useful in real-world applications, as it is aimed to inform the user on the quality of the MT output at test time. Existing approaches require large amounts of expert annotated data, computation and time for training. As an alternative, we devise an unsupervised approach to QE where no training or access to additional resources besides the MT system itself is required. Different from most of the current work that treats the MT system as a black box, we explore useful information that can be extracted from the MT system as a by-product of translation. By employing methods for uncertainty quantification, we achieve very good correlation with human judgments of quality, rivalling state-of-the-art supervised QE models. To evaluate our approach we collect the first dataset that enables work on both black-box and glass-box approaches to QE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge