Lucia Specia
Detecting Machine-Generated Music with Explainability -- A Challenge and Early Benchmarks
Dec 18, 2024
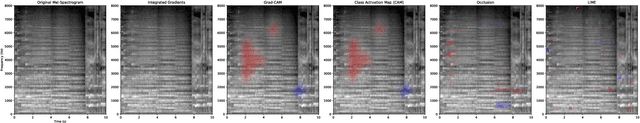
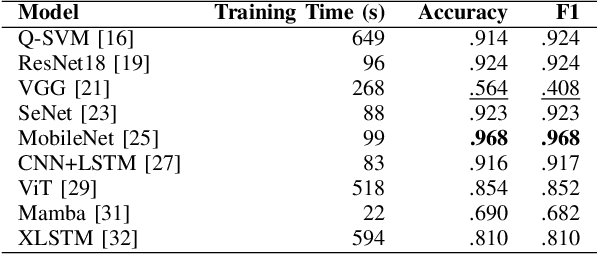
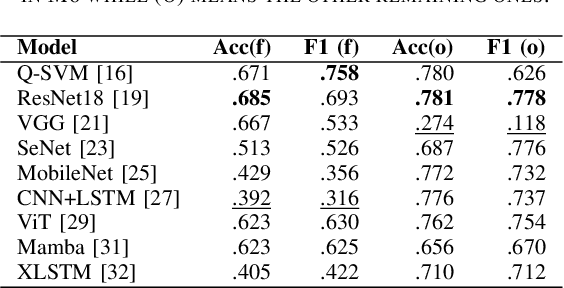
Abstract:Machine-generated music (MGM) has become a groundbreaking innovation with wide-ranging applications, such as music therapy, personalised editing, and creative inspiration within the music industry. However, the unregulated proliferation of MGM presents considerable challenges to the entertainment, education, and arts sectors by potentially undermining the value of high-quality human compositions. Consequently, MGM detection (MGMD) is crucial for preserving the integrity of these fields. Despite its significance, MGMD domain lacks comprehensive benchmark results necessary to drive meaningful progress. To address this gap, we conduct experiments on existing large-scale datasets using a range of foundational models for audio processing, establishing benchmark results tailored to the MGMD task. Our selection includes traditional machine learning models, deep neural networks, Transformer-based architectures, and State Space Models (SSM). Recognising the inherently multimodal nature of music, which integrates both melody and lyrics, we also explore fundamental multimodal models in our experiments. Beyond providing basic binary classification outcomes, we delve deeper into model behaviour using multiple explainable Aritificial Intelligence (XAI) tools, offering insights into their decision-making processes. Our analysis reveals that ResNet18 performs the best according to in-domain and out-of-domain tests. By providing a comprehensive comparison of benchmark results and their interpretability, we propose several directions to inspire future research to develop more robust and effective detection methods for MGM.
Detecting Document-level Paraphrased Machine Generated Content: Mimicking Human Writing Style and Involving Discourse Features
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:The availability of high-quality APIs for Large Language Models (LLMs) has facilitated the widespread creation of Machine-Generated Content (MGC), posing challenges such as academic plagiarism and the spread of misinformation. Existing MGC detectors often focus solely on surface-level information, overlooking implicit and structural features. This makes them susceptible to deception by surface-level sentence patterns, particularly for longer texts and in texts that have been subsequently paraphrased. To overcome these challenges, we introduce novel methodologies and datasets. Besides the publicly available dataset Plagbench, we developed the paraphrased Long-Form Question and Answer (paraLFQA) and paraphrased Writing Prompts (paraWP) datasets using GPT and DIPPER, a discourse paraphrasing tool, by extending artifacts from their original versions. To address the challenge of detecting highly similar paraphrased texts, we propose MhBART, an encoder-decoder model designed to emulate human writing style while incorporating a novel difference score mechanism. This model outperforms strong classifier baselines and identifies deceptive sentence patterns. To better capture the structure of longer texts at document level, we propose DTransformer, a model that integrates discourse analysis through PDTB preprocessing to encode structural features. It results in substantial performance gains across both datasets -- 15.5\% absolute improvement on paraLFQA, 4\% absolute improvement on paraWP, and 1.5\% absolute improvement on M4 compared to SOTA approaches.
M6: Multi-generator, Multi-domain, Multi-lingual and cultural, Multi-genres, Multi-instrument Machine-Generated Music Detection Databases
Dec 08, 2024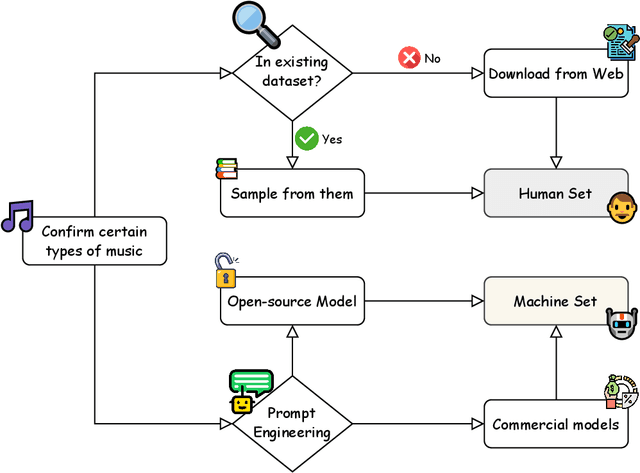
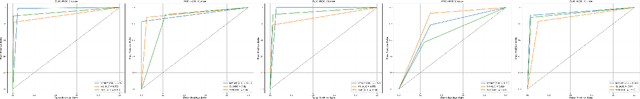
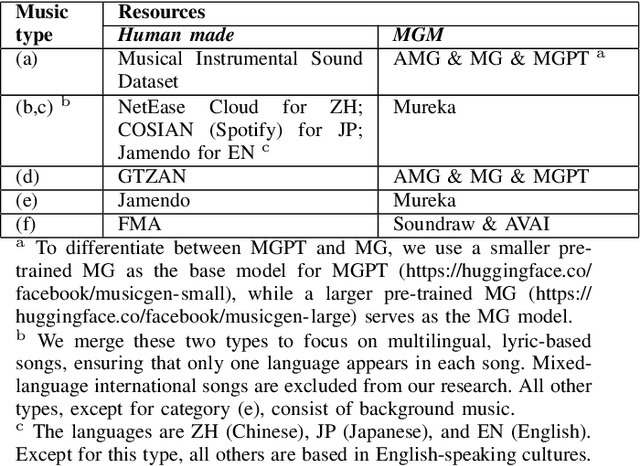
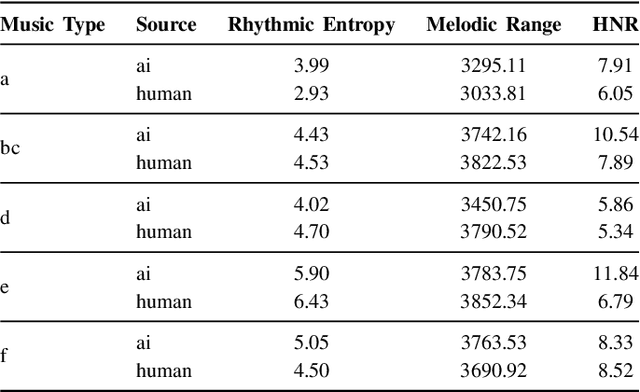
Abstract:Machine-generated music (MGM) has emerged as a powerful tool with applications in music therapy, personalised editing, and creative inspiration for the music community. However, its unregulated use threatens the entertainment, education, and arts sectors by diminishing the value of high-quality human compositions. Detecting machine-generated music (MGMD) is, therefore, critical to safeguarding these domains, yet the field lacks comprehensive datasets to support meaningful progress. To address this gap, we introduce \textbf{M6}, a large-scale benchmark dataset tailored for MGMD research. M6 is distinguished by its diversity, encompassing multiple generators, domains, languages, cultural contexts, genres, and instruments. We outline our methodology for data selection and collection, accompanied by detailed data analysis, providing all WAV form of music. Additionally, we provide baseline performance scores using foundational binary classification models, illustrating the complexity of MGMD and the significant room for improvement. By offering a robust and multifaceted resource, we aim to empower future research to develop more effective detection methods for MGM. We believe M6 will serve as a critical step toward addressing this societal challenge. The dataset and code will be freely available to support open collaboration and innovation in this field.
From Audio Deepfake Detection to AI-Generated Music Detection -- A Pathway and Overview
Nov 30, 2024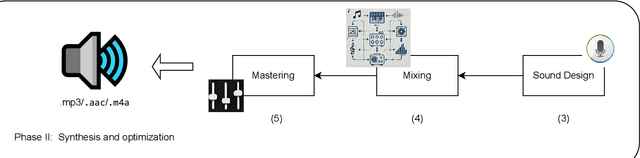
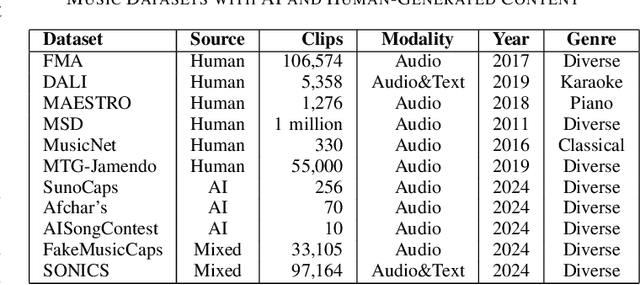
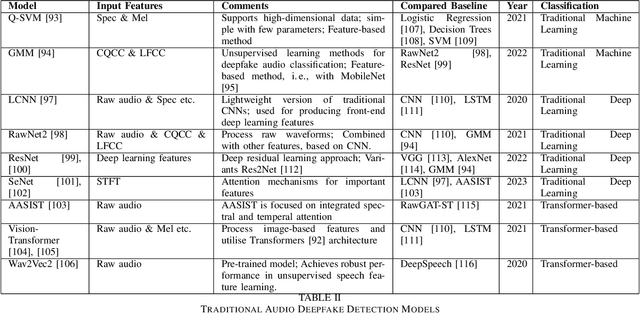
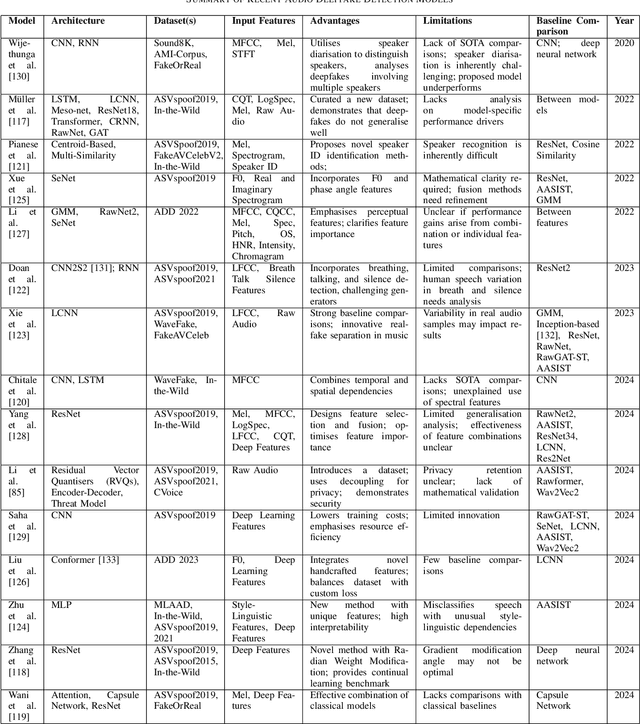
Abstract:As Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies continue to evolve, their use in generating realistic, contextually appropriate content has expanded into various domains. Music, an art form and medium for entertainment, deeply rooted into human culture, is seeing an increased involvement of AI into its production. However, the unregulated use of AI music generation (AIGM) tools raises concerns about potential negative impacts on the music industry, copyright and artistic integrity, underscoring the importance of effective AIGM detection. This paper provides an overview of existing AIGM detection methods. To lay a foundation to the general workings and challenges of AIGM detection, we first review general principles of AIGM, including recent advancements in deepfake audios, as well as multimodal detection techniques. We further propose a potential pathway for leveraging foundation models from audio deepfake detection to AIGM detection. Additionally, we discuss implications of these tools and propose directions for future research to address ongoing challenges in the field.
Tuning Language Models by Mixture-of-Depths Ensemble
Oct 16, 2024Abstract:Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) traditionally rely on final-layer loss for training and final-layer representations for predictions, potentially overlooking the predictive power embedded in intermediate layers. Surprisingly, we find that focusing training efforts on these intermediate layers can yield training losses comparable to those of final layers, with complementary test-time performance. We introduce a novel tuning framework, Mixture-of-Depths (MoD), which trains late layers as ensembles contributing to the final logits through learned routing weights. With the auxiliary distillation loss and additional normalization modules, we ensure that the outputs of the late layers adapt to language modeling. Our MoD framework, which can be integrated with any existing tuning method, shows consistent improvement on various language modelling tasks. Furthermore, by replacing traditional trainable modules with MoD, our approach achieves similar performance with significantly fewer trainable parameters, demonstrating the potential of leveraging predictive power from intermediate representations during training.
DiffuseDef: Improved Robustness to Adversarial Attacks
Jun 28, 2024Abstract:Pretrained language models have significantly advanced performance across various natural language processing tasks. However, adversarial attacks continue to pose a critical challenge to system built using these models, as they can be exploited with carefully crafted adversarial texts. Inspired by the ability of diffusion models to predict and reduce noise in computer vision, we propose a novel and flexible adversarial defense method for language classification tasks, DiffuseDef, which incorporates a diffusion layer as a denoiser between the encoder and the classifier. During inference, the adversarial hidden state is first combined with sampled noise, then denoised iteratively and finally ensembled to produce a robust text representation. By integrating adversarial training, denoising, and ensembling techniques, we show that DiffuseDef improves over different existing adversarial defense methods and achieves state-of-the-art performance against common adversarial attacks.
From Understanding to Utilization: A Survey on Explainability for Large Language Models
Jan 23, 2024Abstract:This survey paper delves into the burgeoning field of explainability for Large Language Models (LLMs), a critical yet challenging aspect of natural language processing. With LLMs playing a pivotal role in various applications, their "black-box" nature raises concerns about transparency and ethical use. This paper emphasizes the necessity for enhanced explainability in LLMs, addressing both the general public's trust and the technical community's need for a deeper understanding of these models. We concentrate on pre-trained Transformer-based LLMs, such as LLaMA, which present unique interpretability challenges due to their scale and complexity. Our review categorizes existing explainability methods and discusses their application in improving model transparency and reliability. We also discuss representative evaluation methods, highlighting their strengths and limitations. The goal of this survey is to bridge the gap between theoretical understanding and practical application, offering insights for future research and development in the field of LLM explainability.
Reducing Hallucinations in Neural Machine Translation with Feature Attribution
Nov 17, 2022



Abstract:Neural conditional language generation models achieve the state-of-the-art in Neural Machine Translation (NMT) but are highly dependent on the quality of parallel training dataset. When trained on low-quality datasets, these models are prone to various error types, including hallucinations, i.e. outputs that are fluent, but unrelated to the source sentences. These errors are particularly dangerous, because on the surface the translation can be perceived as a correct output, especially if the reader does not understand the source language. We present a case study focusing on model understanding and regularisation to reduce hallucinations in NMT. We first use feature attribution methods to study the behaviour of an NMT model that produces hallucinations. We then leverage these methods to propose a novel loss function that substantially helps reduce hallucinations and does not require retraining the model from scratch.
Scene Text Recognition with Semantics
Oct 19, 2022
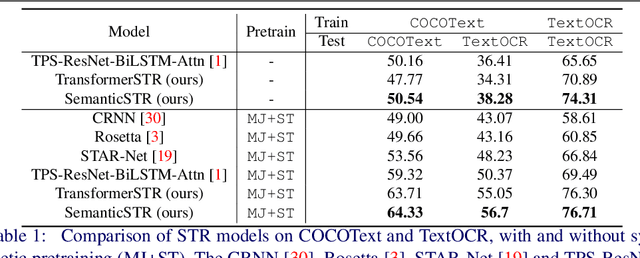
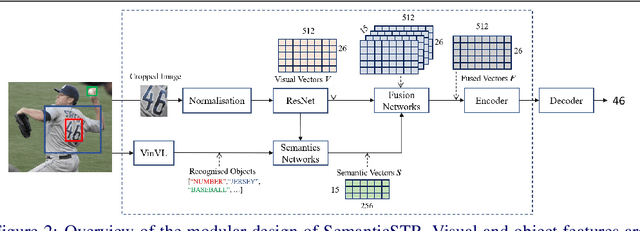
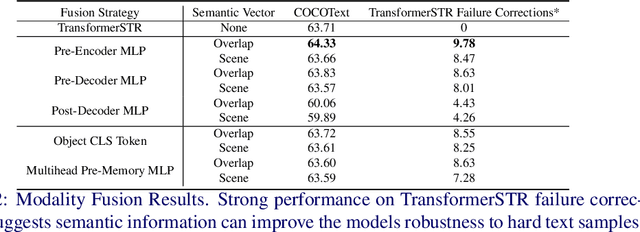
Abstract:Scene Text Recognition (STR) models have achieved high performance in recent years on benchmark datasets where text images are presented with minimal noise. Traditional STR recognition pipelines take a cropped image as sole input and attempt to identify the characters present. This infrastructure can fail in instances where the input image is noisy or the text is partially obscured. This paper proposes using semantic information from the greater scene to contextualise predictions. We generate semantic vectors using object tags and fuse this information into a transformer-based architecture. The results demonstrate that our multimodal approach yields higher performance than traditional benchmark models, particularly on noisy instances.
Contrastive Video-Language Learning with Fine-grained Frame Sampling
Oct 10, 2022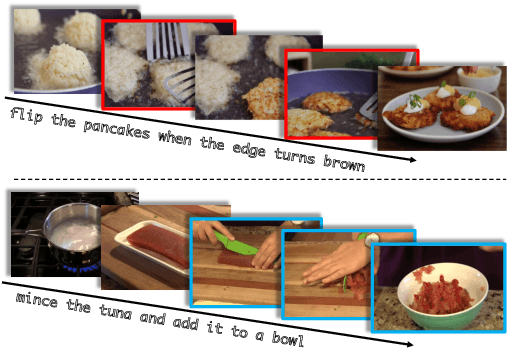
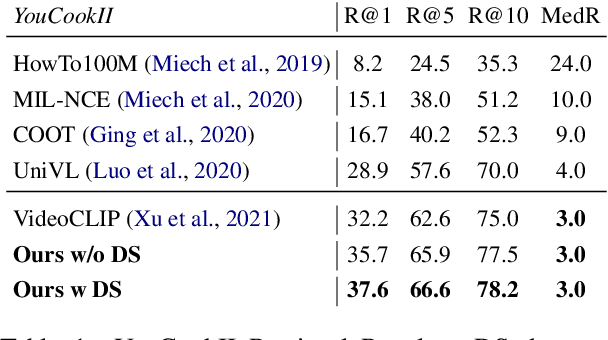
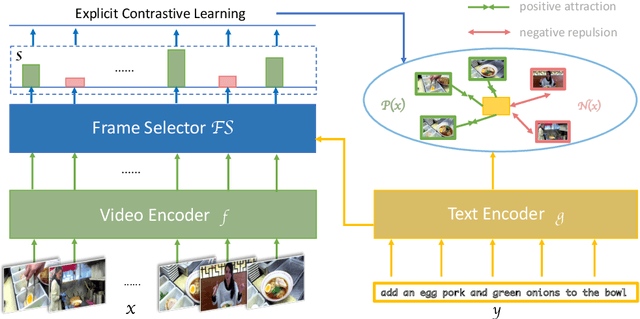
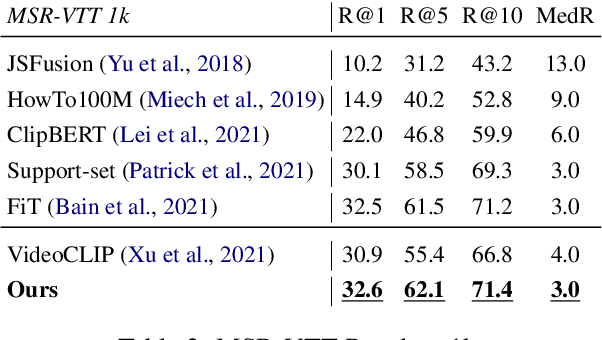
Abstract:Despite recent progress in video and language representation learning, the weak or sparse correspondence between the two modalities remains a bottleneck in the area. Most video-language models are trained via pair-level loss to predict whether a pair of video and text is aligned. However, even in paired video-text segments, only a subset of the frames are semantically relevant to the corresponding text, with the remainder representing noise; where the ratio of noisy frames is higher for longer videos. We propose FineCo (Fine-grained Contrastive Loss for Frame Sampling), an approach to better learn video and language representations with a fine-grained contrastive objective operating on video frames. It helps distil a video by selecting the frames that are semantically equivalent to the text, improving cross-modal correspondence. Building on the well established VideoCLIP model as a starting point, FineCo achieves state-of-the-art performance on YouCookII, a text-video retrieval benchmark with long videos. FineCo also achieves competitive results on text-video retrieval (MSR-VTT), and video question answering datasets (MSR-VTT QA and MSR-VTT MC) with shorter videos.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge