Yujie Zhong
ThinkGen: Generalized Thinking for Visual Generation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrates that Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning enables systematic solutions to complex understanding tasks. However, its extension to generation tasks remains nascent and limited by scenario-specific mechanisms that hinder generalization and adaptation. In this work, we present ThinkGen, the first think-driven visual generation framework that explicitly leverages MLLM's CoT reasoning in various generation scenarios. ThinkGen employs a decoupled architecture comprising a pretrained MLLM and a Diffusion Transformer (DiT), wherein the MLLM generates tailored instructions based on user intent, and DiT produces high-quality images guided by these instructions. We further propose a separable GRPO-based training paradigm (SepGRPO), alternating reinforcement learning between the MLLM and DiT modules. This flexible design enables joint training across diverse datasets, facilitating effective CoT reasoning for a wide range of generative scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ThinkGen achieves robust, state-of-the-art performance across multiple generation benchmarks. Code is available: https://github.com/jiaosiyuu/ThinkGen
RoboTron-Sim: Improving Real-World Driving via Simulated Hard-Case
Aug 06, 2025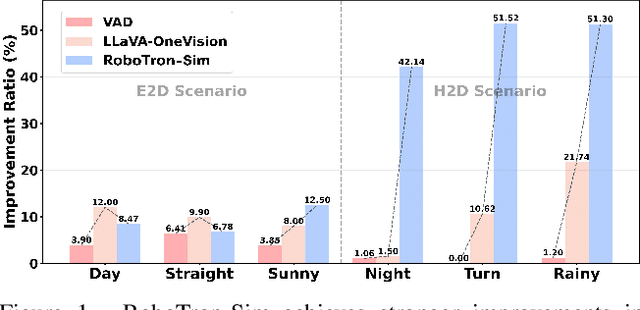



Abstract:Collecting real-world data for rare high-risk scenarios, long-tailed driving events, and complex interactions remains challenging, leading to poor performance of existing autonomous driving systems in these critical situations. In this paper, we propose RoboTron-Sim that improves real-world driving in critical situations by utilizing simulated hard cases. First, we develop a simulated dataset called Hard-case Augmented Synthetic Scenarios (HASS), which covers 13 high-risk edge-case categories, as well as balanced environmental conditions such as day/night and sunny/rainy. Second, we introduce Scenario-aware Prompt Engineering (SPE) and an Image-to-Ego Encoder (I2E Encoder) to enable multimodal large language models to effectively learn real-world challenging driving skills from HASS, via adapting to environmental deviations and hardware differences between real-world and simulated scenarios. Extensive experiments on nuScenes show that RoboTron-Sim improves driving performance in challenging scenarios by around 50%, achieving state-of-the-art results in real-world open-loop planning. Qualitative results further demonstrate the effectiveness of RoboTron-Sim in better managing rare high-risk driving scenarios. Project page: https://stars79689.github.io/RoboTron-Sim/
DisTime: Distribution-based Time Representation for Video Large Language Models
May 30, 2025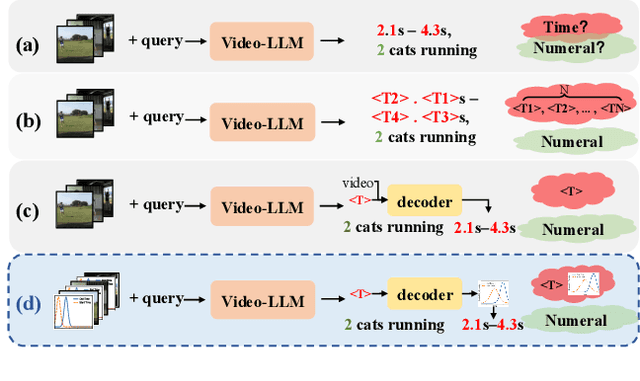
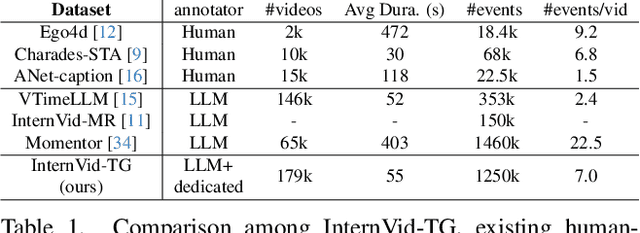
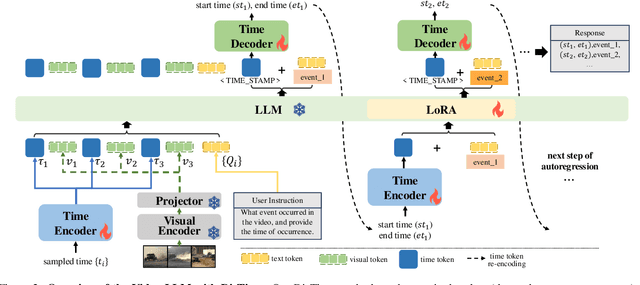
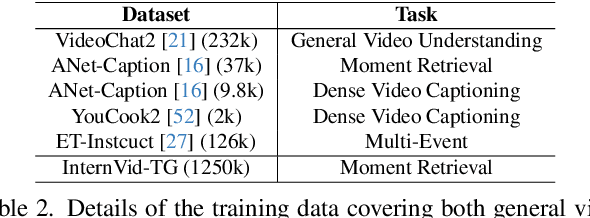
Abstract:Despite advances in general video understanding, Video Large Language Models (Video-LLMs) face challenges in precise temporal localization due to discrete time representations and limited temporally aware datasets. Existing methods for temporal expression either conflate time with text-based numerical values, add a series of dedicated temporal tokens, or regress time using specialized temporal grounding heads. To address these issues, we introduce DisTime, a lightweight framework designed to enhance temporal comprehension in Video-LLMs. DisTime employs a learnable token to create a continuous temporal embedding space and incorporates a Distribution-based Time Decoder that generates temporal probability distributions, effectively mitigating boundary ambiguities and maintaining temporal continuity. Additionally, the Distribution-based Time Encoder re-encodes timestamps to provide time markers for Video-LLMs. To overcome temporal granularity limitations in existing datasets, we propose an automated annotation paradigm that combines the captioning capabilities of Video-LLMs with the localization expertise of dedicated temporal models. This leads to the creation of InternVid-TG, a substantial dataset with 1.25M temporally grounded events across 179k videos, surpassing ActivityNet-Caption by 55 times. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DisTime achieves state-of-the-art performance across benchmarks in three time-sensitive tasks while maintaining competitive performance in Video QA tasks. Code and data are released at https://github.com/josephzpng/DisTime.
v-CLR: View-Consistent Learning for Open-World Instance Segmentation
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we address the challenging problem of open-world instance segmentation. Existing works have shown that vanilla visual networks are biased toward learning appearance information, \eg texture, to recognize objects. This implicit bias causes the model to fail in detecting novel objects with unseen textures in the open-world setting. To address this challenge, we propose a learning framework, called view-Consistent LeaRning (v-CLR), which aims to enforce the model to learn appearance-invariant representations for robust instance segmentation. In v-CLR, we first introduce additional views for each image, where the texture undergoes significant alterations while preserving the image's underlying structure. We then encourage the model to learn the appearance-invariant representation by enforcing the consistency between object features across different views, for which we obtain class-agnostic object proposals using off-the-shelf unsupervised models that possess strong object-awareness. These proposals enable cross-view object feature matching, greatly reducing the appearance dependency while enhancing the object-awareness. We thoroughly evaluate our method on public benchmarks under both cross-class and cross-dataset settings, achieving state-of-the-art performance. Project page: https://visual-ai.github.io/vclr
AP-CAP: Advancing High-Quality Data Synthesis for Animal Pose Estimation via a Controllable Image Generation Pipeline
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:The task of 2D animal pose estimation plays a crucial role in advancing deep learning applications in animal behavior analysis and ecological research. Despite notable progress in some existing approaches, our study reveals that the scarcity of high-quality datasets remains a significant bottleneck, limiting the full potential of current methods. To address this challenge, we propose a novel Controllable Image Generation Pipeline for synthesizing animal pose estimation data, termed AP-CAP. Within this pipeline, we introduce a Multi-Modal Animal Image Generation Model capable of producing images with expected poses. To enhance the quality and diversity of the generated data, we further propose three innovative strategies: (1) Modality-Fusion-Based Animal Image Synthesis Strategy to integrate multi-source appearance representations, (2) Pose-Adjustment-Based Animal Image Synthesis Strategy to dynamically capture diverse pose variations, and (3) Caption-Enhancement-Based Animal Image Synthesis Strategy to enrich visual semantic understanding. Leveraging the proposed model and strategies, we create the MPCH Dataset (Modality-Pose-Caption Hybrid), the first hybrid dataset that innovatively combines synthetic and real data, establishing the largest-scale multi-source heterogeneous benchmark repository for animal pose estimation to date. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method in improving both the performance and generalization capability of animal pose estimators.
Optimizing Singular Spectrum for Large Language Model Compression
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, yet prohibitive parameter complexity often hinders their deployment. Existing singular value decomposition (SVD) based compression methods simply deem singular values as importance scores of decomposed components. However, this importance ordered by singular values does not necessarily correlate with the performance of a downstream task. In this work, we introduce SoCo (Singular spectrum optimization for large language model Compression), a novel compression framework that learns to rescale the decomposed components of SVD in a data-driven manner. Concretely, we employ a learnable diagonal matrix to assign importance scores for singular spectrum and develop a three-stage training process that progressively refines these scores from initial coarse compression to fine-grained sparsification-thereby striking an effective balance between aggressive model compression and performance preservation. Thanks to the learnable singular spectrum, SoCo adaptively prunes components according to the sparsified importance scores, rather than relying on the fixed order of singular values. More importantly, the remaining components with amplified importance scores can compensate for the loss of the pruned ones. Experimental evaluations across multiple LLMs and benchmarks demonstrate that SoCo surpasses the state-of-the-art methods in model compression.
HiMix: Reducing Computational Complexity in Large Vision-Language Models
Jan 17, 2025Abstract:Benefiting from recent advancements in large language models and modality alignment techniques, existing Large Vision-Language Models(LVLMs) have achieved prominent performance across a wide range of scenarios. However, the excessive computational complexity limits the widespread use of these models in practical applications. We argue that one main bottleneck in computational complexity is caused by the involvement of redundant vision sequences in model computation. This is inspired by a reassessment of the efficiency of vision and language information transmission in the language decoder of LVLMs. Then, we propose a novel hierarchical vision-language interaction mechanism called Hierarchical Vision injection for Mixture Attention (HiMix). In HiMix, only the language sequence undergoes full forward propagation, while the vision sequence interacts with the language at specific stages within each language decoder layer. It is striking that our approach significantly reduces computational complexity with minimal performance loss. Specifically, HiMix achieves a 10x reduction in the computational cost of the language decoder across multiple LVLM models while maintaining comparable performance. This highlights the advantages of our method, and we hope our research brings new perspectives to the field of vision-language understanding. Project Page: https://xuange923.github.io/HiMix
Manga Generation via Layout-controllable Diffusion
Dec 26, 2024



Abstract:Generating comics through text is widely studied. However, there are few studies on generating multi-panel Manga (Japanese comics) solely based on plain text. Japanese manga contains multiple panels on a single page, with characteristics such as coherence in storytelling, reasonable and diverse page layouts, consistency in characters, and semantic correspondence between panel drawings and panel scripts. Therefore, generating manga poses a significant challenge. This paper presents the manga generation task and constructs the Manga109Story dataset for studying manga generation solely from plain text. Additionally, we propose MangaDiffusion to facilitate the intra-panel and inter-panel information interaction during the manga generation process. The results show that our method particularly ensures the number of panels, reasonable and diverse page layouts. Based on our approach, there is potential to converting a large amount of textual stories into more engaging manga readings, leading to significant application prospects.
CharGen: High Accurate Character-Level Visual Text Generation Model with MultiModal Encoder
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:Recently, significant advancements have been made in diffusion-based visual text generation models. Although the effectiveness of these methods in visual text rendering is rapidly improving, they still encounter challenges such as inaccurate characters and strokes when rendering complex visual text. In this paper, we propose CharGen, a highly accurate character-level visual text generation and editing model. Specifically, CharGen employs a character-level multimodal encoder that not only extracts character-level text embeddings but also encodes glyph images character by character. This enables it to capture fine-grained cross-modality features more effectively. Additionally, we introduce a new perceptual loss in CharGen to enhance character shape supervision and address the issue of inaccurate strokes in generated text. It is worth mentioning that CharGen can be integrated into existing diffusion models to generate visual text with high accuracy. CharGen significantly improves text rendering accuracy, outperforming recent methods in public benchmarks such as AnyText-benchmark and MARIO-Eval, with improvements of more than 8% and 6%, respectively. Notably, CharGen achieved a 5.5% increase in accuracy on Chinese test sets.
InstructSeg: Unifying Instructed Visual Segmentation with Multi-modal Large Language Models
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Boosted by Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs), text-guided universal segmentation models for the image and video domains have made rapid progress recently. However, these methods are often developed separately for specific domains, overlooking the similarities in task settings and solutions across these two areas. In this paper, we define the union of referring segmentation and reasoning segmentation at both the image and video levels as Instructed Visual Segmentation (IVS). Correspondingly, we propose InstructSeg, an end-to-end segmentation pipeline equipped with MLLMs for IVS. Specifically, we employ an object-aware video perceiver to extract temporal and object information from reference frames, facilitating comprehensive video understanding. Additionally, we introduce vision-guided multi-granularity text fusion to better integrate global and detailed text information with fine-grained visual guidance. By leveraging multi-task and end-to-end training, InstructSeg demonstrates superior performance across diverse image and video segmentation tasks, surpassing both segmentation specialists and MLLM-based methods with a single model. Our code is available at https://github.com/congvvc/InstructSeg.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge