Zhongying Liu
Optimizing Singular Spectrum for Large Language Model Compression
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, yet prohibitive parameter complexity often hinders their deployment. Existing singular value decomposition (SVD) based compression methods simply deem singular values as importance scores of decomposed components. However, this importance ordered by singular values does not necessarily correlate with the performance of a downstream task. In this work, we introduce SoCo (Singular spectrum optimization for large language model Compression), a novel compression framework that learns to rescale the decomposed components of SVD in a data-driven manner. Concretely, we employ a learnable diagonal matrix to assign importance scores for singular spectrum and develop a three-stage training process that progressively refines these scores from initial coarse compression to fine-grained sparsification-thereby striking an effective balance between aggressive model compression and performance preservation. Thanks to the learnable singular spectrum, SoCo adaptively prunes components according to the sparsified importance scores, rather than relying on the fixed order of singular values. More importantly, the remaining components with amplified importance scores can compensate for the loss of the pruned ones. Experimental evaluations across multiple LLMs and benchmarks demonstrate that SoCo surpasses the state-of-the-art methods in model compression.
HiMix: Reducing Computational Complexity in Large Vision-Language Models
Jan 17, 2025Abstract:Benefiting from recent advancements in large language models and modality alignment techniques, existing Large Vision-Language Models(LVLMs) have achieved prominent performance across a wide range of scenarios. However, the excessive computational complexity limits the widespread use of these models in practical applications. We argue that one main bottleneck in computational complexity is caused by the involvement of redundant vision sequences in model computation. This is inspired by a reassessment of the efficiency of vision and language information transmission in the language decoder of LVLMs. Then, we propose a novel hierarchical vision-language interaction mechanism called Hierarchical Vision injection for Mixture Attention (HiMix). In HiMix, only the language sequence undergoes full forward propagation, while the vision sequence interacts with the language at specific stages within each language decoder layer. It is striking that our approach significantly reduces computational complexity with minimal performance loss. Specifically, HiMix achieves a 10x reduction in the computational cost of the language decoder across multiple LVLM models while maintaining comparable performance. This highlights the advantages of our method, and we hope our research brings new perspectives to the field of vision-language understanding. Project Page: https://xuange923.github.io/HiMix
LVOS: A Benchmark for Large-scale Long-term Video Object Segmentation
May 01, 2024
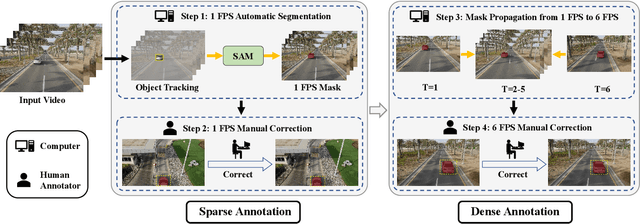

Abstract:Video object segmentation (VOS) aims to distinguish and track target objects in a video. Despite the excellent performance achieved by off-the-shell VOS models, existing VOS benchmarks mainly focus on short-term videos lasting about 5 seconds, where objects remain visible most of the time. However, these benchmarks poorly represent practical applications, and the absence of long-term datasets restricts further investigation of VOS in realistic scenarios. Thus, we propose a novel benchmark named LVOS, comprising 720 videos with 296,401 frames and 407,945 high-quality annotations. Videos in LVOS last 1.14 minutes on average, approximately 5 times longer than videos in existing datasets. Each video includes various attributes, especially challenges deriving from the wild, such as long-term reappearing and cross-temporal similar objects. Compared to previous benchmarks, our LVOS better reflects VOS models' performance in real scenarios. Based on LVOS, we evaluate 20 existing VOS models under 4 different settings and conduct a comprehensive analysis. On LVOS, these models suffer a large performance drop, highlighting the challenge of achieving precise tracking and segmentation in real-world scenarios. Attribute-based analysis indicates that key factor to accuracy decline is the increased video length, emphasizing LVOS's crucial role. We hope our LVOS can advance development of VOS in real scenes. Data and code are available at https://lingyihongfd.github.io/lvos.github.io/.
LVOS: A Benchmark for Long-term Video Object Segmentation
Nov 18, 2022Abstract:Existing video object segmentation (VOS) benchmarks focus on short-term videos which just last about 3-5 seconds and where objects are visible most of the time. These videos are poorly representative of practical applications, and the absence of long-term datasets restricts further investigation of VOS on the application in realistic scenarios. So, in this paper, we present a new benchmark dataset and evaluation methodology named LVOS, which consists of 220 videos with a total duration of 421 minutes. To the best of our knowledge, LVOS is the first densely annotated long-term VOS dataset. The videos in our LVOS last 1.59 minutes on average, which is 20 times longer than videos in existing VOS datasets. Each video includes various attributes, especially challenges deriving from the wild, such as long-term reappearing and cross-temporal similar objeccts. Moreover, we provide additional language descriptions to encourage the exploration of integrating linguistic and visual features for video object segmentation. Based on LVOS, we assess existing video object segmentation algorithms and propose a Diverse Dynamic Memory network (DDMemory) that consists of three complementary memory banks to exploit temporal information adequately. The experiment results demonstrate the strength and weaknesses of prior methods, pointing promising directions for further study. Our objective is to provide the community with a large and varied benchmark to boost the advancement of long-term VOS. Data and code are available at \url{https://lingyihongfd.github.io/lvos.github.io/}.
FERV39k: A Large-Scale Multi-Scene Dataset for Facial Expression Recognition in Videos
Mar 20, 2022
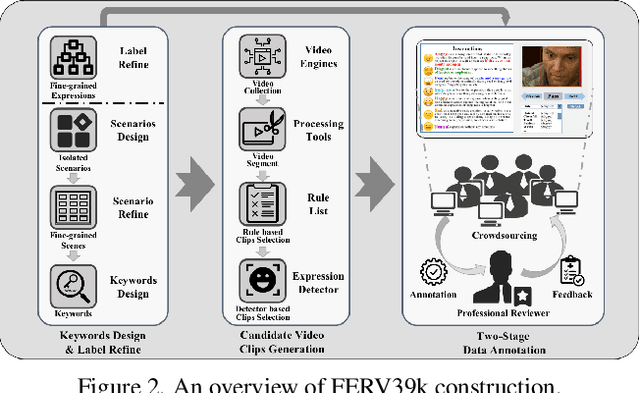
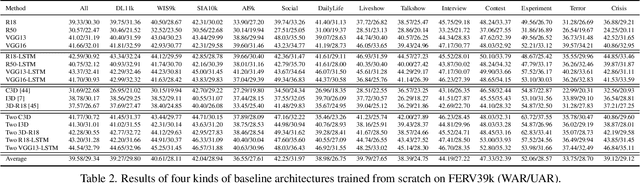
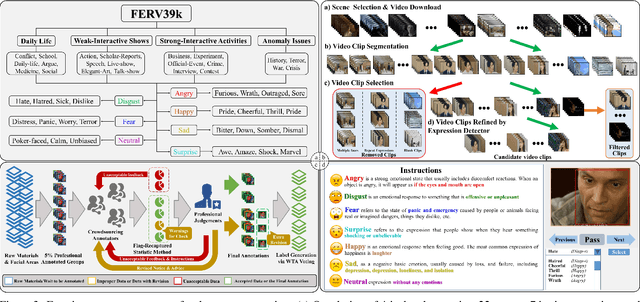
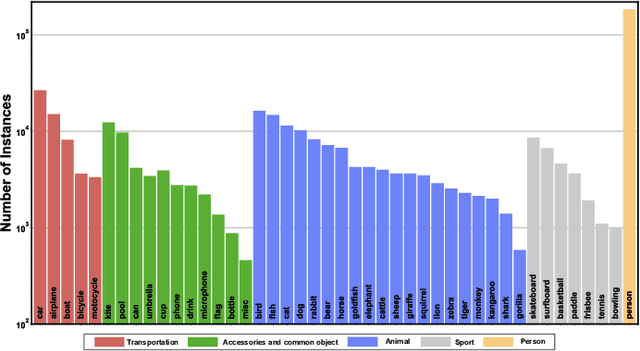
Abstract:Current benchmarks for facial expression recognition (FER) mainly focus on static images, while there are limited datasets for FER in videos. It is still ambiguous to evaluate whether performances of existing methods remain satisfactory in real-world application-oriented scenes. For example, the "Happy" expression with high intensity in Talk-Show is more discriminating than the same expression with low intensity in Official-Event. To fill this gap, we build a large-scale multi-scene dataset, coined as FERV39k. We analyze the important ingredients of constructing such a novel dataset in three aspects: (1) multi-scene hierarchy and expression class, (2) generation of candidate video clips, (3) trusted manual labelling process. Based on these guidelines, we select 4 scenarios subdivided into 22 scenes, annotate 86k samples automatically obtained from 4k videos based on the well-designed workflow, and finally build 38,935 video clips labeled with 7 classic expressions. Experiment benchmarks on four kinds of baseline frameworks were also provided and further analysis on their performance across different scenes and some challenges for future research were given. Besides, we systematically investigate key components of DFER by ablation studies. The baseline framework and our project will be available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge